掌握数组的概念和内存中的存放
掌握数组的访问,修改
掌握数组的几种典型应用
数组
数组是一个变量,存储相同数据类型的一组数据。
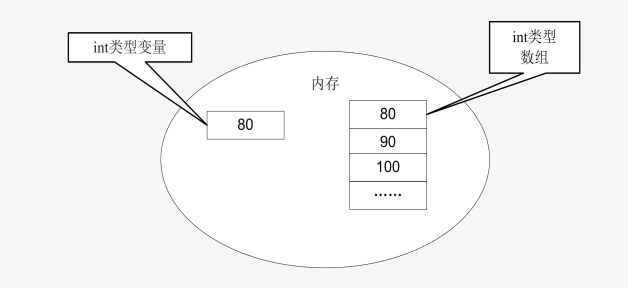 声明一个变量就是在内存空间划出一块合适的空间。
声明一个变量就是在内存空间划出一块合适的空间。
声明一个数组就是在内存空间中化出一串连续的空间。
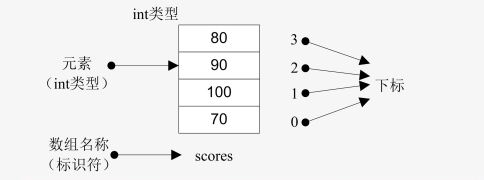
数组的基本要素:
- 标识符:数组的名称,用于区分数组。
- 数组元素:向数组中存放的数据。
- 元素下标:对数组元素进行编号,从0开始,数组中的每个元素都能通过下标来访问。
- 元素类型: 数组元素的数据类型。
Java中, 数组长度是固定不变的, 避免数组下标越界
数组的定义使用:
1 . 声明数组: int [] a ; 2 , 分配空间 a = new int [5]; 3 , 赋值 a[0] = 8; 4 , 处理数据 a[0] = a[0]*10;
数组的初始化:
// 声明数组并分配空间。 int[] a = new int [10]; //边声明, 边赋值 int [] a ={1,2,3};
易犯的几种错误:
1, public class ErrorDemo1 { public static void main(String[ ] args){ int[ ] score = new int[ ]; //编译出错, 没有写明数组的大小 score[0] = 89; score[1] = 63; System.out.println(score[0]); } } 2, public class ErrorDemo2 { public static void main(String[ ] args) { int[ ] scores = new int[2]; scores[0] = 90; scores[1] = 85; scores[2] = 65;//编译出错, 数组越界 System.out.println(scores[2]); } } 3, public class ErrorDemo3 { public static void main(String[ ] args){ int[ ] score; //编译出错, 没有进行初始化 score[0] = 89; score[1] = 63; System.out.println(score[0]); } } 4 , public static void main(String[ ] args){ int[ ] score = new int[5]; score = {60, 80, 90, 70, 85}; int[ ] score2; score2 = {60, 80, 90, 70, 85};//编译出错,创建数组并赋值的方式 必须在一条语句中完成 } 5, public static void main(String[ ] args){ String[] str = new String[3]; str[0] = "100"; str[1] = 11;//编译出错,类型不匹配,Java是强类型语言 System.out.println(str[1]); }
数组应用--- 遍历
//第一种 按长度循环 for 循环 int a[] = {0,1,2,3}; for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){ System.out.println(a[i]); } //第二种,在JDK 1.5 之后增加的foreach 循环,可以用来处理数组的每个元素,而不必指定下标值 int a[] = {0,1,2,3}; for(int i : a){ System.out.println(i); }
多维数组
因为一个数组可被声明为具有任何类型,所以你可以创建数组的数组(和数组的数组的数组,等等),即多维数组。
int twoDim [ ] [ ] = new int [4] [ ] ; twoDim [0] = new int [5]; twoDim [1] = new int [5];
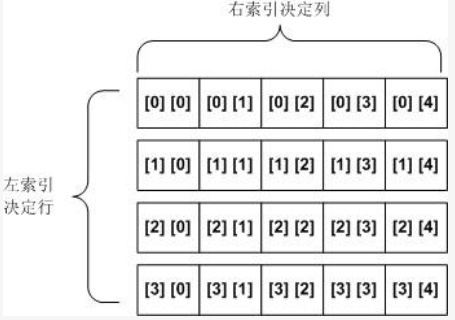
二维数组
指定一维和二维的长度,即行和列。
//保存每种车的名称与价格 String[][] cars = new String[3][2]; cars[0][0] = "Benz"; cars[0][1] = "50"; cars[1][0] = "Audi"; cars[1][1] = "30"; for (String[] u: cars){ System.out.println("汽车品牌为:" + u[0] + " 价格为(W):" + u[1]); /*当然还可以使用三维四维N维,但维数越高,程 序可读性和维护性越低,不推荐使用三维以上, 而是有其他的解决方案替代。*/
列举一些常用的代码习惯‘:
- 包名com.公司网址.项目名.模块名
- 类名大驼峰规则,每个单词的首字母大写
- 变量名和方法名小驼峰规则
- 常量全大写
- 注释先代码后方法
- 功能单一,每个方法力求只做一件事
- 前花括号在语句后,后花括号单独一行
- 规范缩进,增加可读性