vector之二维向量
一维向量:以指定类型数据为元素
二维向量:以向量为元素
vector<int> 盛放int类型的数
vector<vector<int>> 变量名; 盛放vector<int>类型的向量
一维向量for循环和二维向量for循环一样!
实例运行:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> //下面用到vector所以需要包含头文件 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //在主函数中,返回值类型为int类型 7 int main() 8 { 9 vector<vector<int>> array_td; //二维向量的格式对吗? 10 11 vector<int> array_od(3, 2); //初始化格式对吗? 12 13 for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++) 14 { 15 array_td.push_back(array_od); //push_back用法:括号中是要压缩的元素(整数或向量) 16 } 17 //出错点:数组中最大索引值总是小于数组维度-1 18 for (int i = 0; i < array_td.size(); i++) //array_td.size()中括号! 19 { 20 for (int j=0; j<array_td[0].size(); j++) 21 { 22 cout << array_td[i][j]; //二维数组的元素的引用 23 } 24 cout << endl; 25 } 26 return 0; //最后返回值为0 27 }
https://www.cnblogs.com/fuhang/p/9077624.html
https://blog.csdn.net/laobai1015/article/details/51218871
https://www.cnblogs.com/otakuhan/p/8598790.html
关于C++STL中vector容器 begin()与end()函数理解:
begin总是返回该容器的起始地址;end总是返回该容器的结尾地址。
从begin插入数据则插入数据不断往下移动;从end插入数据则数据也是不断往下移动。

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 9 vector<int> value; 10 vector<int> value1; 11 12 int i=0; 13 14 value.push_back(67); 15 value.push_back(0); 16 value.push_back(24); 17 value.push_back(68); 18 cout << value[0] << endl; 19 cout << value[1] << endl; 20 cout << value[2] << endl; 21 cout << value[3] << endl; 22 cout << endl; 23 while (i <= 3) 24 { 25 //value1.insert(value1.begin(), value[i]); 26 value1.insert(value1.end(), value[i]); 27 i++; 28 } 29 cout << value1[0] << endl; 30 cout << value1[1] << endl; 31 cout << value1[2] << endl; 32 cout << value1[3] << endl; 33 34 return 0; 35 }
value1.insert(value1.begin(), value[i]);
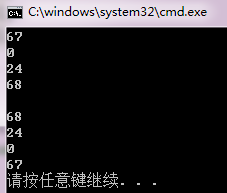
value1.insert(value1.end(), value[i]);

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 9 vector<int> value; 10 vector<int> value1; 11 12 int i=0; 13 14 value.push_back(67); 15 value.push_back(0); 16 value.push_back(24); 17 value.push_back(68); 18 cout << value[0] << endl; 19 cout << value[1] << endl; 20 cout << value[2] << endl; 21 cout << value[3] << endl; 22 cout << endl; 23 //while (i <= 3) 24 //{ 25 // //value1.insert(value1.begin(), value[i]); 26 // value1.insert(value1.end(), value[i]); 27 // i++; 28 //} 29 value1.insert(value1.begin(), value.begin(), value.end()); 30 cout << value1[0] << endl; 31 cout << value1[1] << endl; 32 cout << value1[2] << endl; 33 cout << value1[3] << endl; 34 35 return 0; 36 }
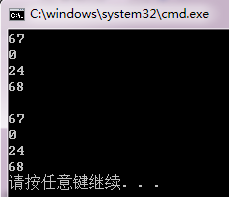
https://blog.csdn.net/duan19920101/article/details/51679517
https://blog.csdn.net/laobai1015/article/details/51567564
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40803710/article/details/80638386
C++ 中vector的使用方法
https://blog.csdn.net/duan19920101/article/details/50617190/
