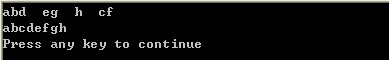
求解二叉树的高度
树是递归定义的,所以用递归算法去求一棵二叉树的高度很方便。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
char data;
Node *lchild;
Node *rchild;
};
void High(Node *T, int &h)
{
if (T == NULL)
h = 0;
else {
int left_h;
High(T->lchild, left_h);
int right_h;
High(T->rchild, right_h);
h = 1 + max(left_h, right_h);
}
}
Node *CreateBiTree(Node *&T) { // 算法6.4
// 按先序次序输入二叉树中结点的值(一个字符),空格字符表示空树,
// 构造二叉链表表示的二叉树T。
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '#')
T = NULL;
else {
if (!(T = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node))))
return 0;
T->data = ch; // 生成根结点
CreateBiTree(T->lchild); // 构造左子树
CreateBiTree(T->rchild); // 构造右子树
}
return T;
} // CreateBiTree
void Free(Node *&T)
{
if (T == NULL)
return;
Free(T->lchild);
// T->lchild = NULL;
Free(T->rchild);
// T->rchild = NULL;
free(T);
T = NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
freopen("cin.txt", "r", stdin);
Node *T = NULL;
CreateBiTree(T);
int height;
High(T, height);
cout << height << endl;
Free(T);
return 0;
}
/* cin.txt:
A
B
C
#
#
D
E
#
G
#
#
F
#
#
#
*/
构造的树:
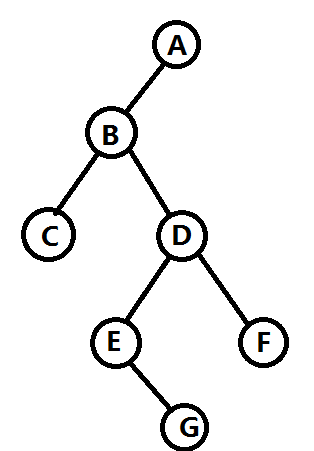
中序遍历
void inOrder(BiTree T,void(*vist)( element e)){
stack<Bitree> S;
while (true){
if (T) { s.push(T);T=T->Lchild;}
else {T=s.top(); visit(T);s.pop();T=T->Rchild;}
if(s.empty()&&T==NULL) break;
}
}先序遍历
void inOrder(BiTree T,void(*vist)( element e)){
stack<Bitree> S;
while(true){
if(T){ visit(T);
if(T->rChild) s.push(T->rChild);T=T->lChild;}
else {T=s.top();s.pop();}
if (s.empty()&&T==NULL) break; }
}后序遍历
void inOrder(BiTree T,void(*vist)( element e)){
stack<Bitree> S;
int flat[20];
while(true){
while(true){
s.push(T);T=T->lChild; flag(s.size()]=0;
if (!T){ T=->rChild; if (T) flag[s.size()]=1; else break;}
while (true){ if(flag[s.size()]){ T=s.top(); visit(T); s.pop();}
else T=T->rChild;
}
if (s.empty()&&T==NULL) break;
}
}
这三种方案都属于深度优先,还有广度优先的遍历,利用队列解决。
利用栈实现二叉树的先序,中序,后序遍历的非递归操作,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BiTNode{
char data;
BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
}BiTNode,*BiTree;
void CreateBiTree(BiTree &T)//建树,按先序顺序输入节点
{
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
if(ch==' ')
{
T=NULL;
return;
}
else
{
T=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
if(!T)
exit(1);
T->data=ch;
CreateBiTree(T->lchild);
CreateBiTree(T->rchild);
}
}
void InOrderTraverse(BiTree T)//非递归中序遍历
{
stack<BiTree> Stack;
if(!T)
{
printf("空树!
");
return;
}
while(T || !Stack.empty())
{
while(T)
{
Stack.push(T);
T=T->lchild;
}
T=Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
printf("%c",T->data);
T=T->rchild;
}
}
void PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T)//非递归先序遍历
{
stack<BiTree> Stack;
if(!T)
{
printf("空树!
");
return;
}
while(T || !Stack.empty())
{
while(T)
{
Stack.push(T);
printf("%c",T->data);
T=T->lchild;
}
T=Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
T=T->rchild;
}
}
void PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T)//非递归后序遍历,用一个标记标记右子树是否访问过
{
int flag[20];
stack<BiTree> Stack;
if(!T)
{
printf("空树!
");
return;
}
while(T)
{
Stack.push(T);
flag[Stack.size()]=0;
T=T->lchild;
}
while(!Stack.empty())
{
T=Stack.top();
while(T->rchild && flag[Stack.size()]==0)
{
flag[Stack.size()]=1;
T=T->rchild;
while(T)
{
Stack.push(T);
flag[Stack.size()]=0;
T=T->lchild;
}
}
T=Stack.top();
printf("%c",T->data);
Stack.pop();
}
}
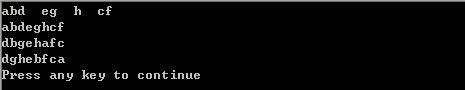
void main()
{
BiTree T;
CreateBiTree(T);
PreOrderTraverse(T);
printf("
");
InOrderTraverse(T);
printf("
");
PostOrderTraverse(T);
printf("
");
} 
利用队列实现二叉树层次遍历
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BiTNode{
char data;
BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
}BiTNode,*BiTree;
void CreateBiTree(BiTree &T)//建树
{
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
if(ch==' ')
{
T=NULL;
return;
}
else
{
T=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
if(!T)
exit(1);
T->data=ch;
CreateBiTree(T->lchild);
CreateBiTree(T->rchild);
}
}
void LevelOrderTraverse(BiTree T)//层次遍历
{
queue<BiTree> Queue;
if(!T)
{
printf("空树!
");
return;
}
Queue.push(T);
while(!Queue.empty())
{
T=Queue.front();
Queue.pop();
printf("%c",T->data);
if(T->lchild)
Queue.push(T->lchild);
if(T->rchild)
Queue.push(T->rchild);
}
}
void main()
{
BiTree T;
CreateBiTree(T);
LevelOrderTraverse(T);
printf("
");
}