一、读取默认配置文件
1、application.properties:
#端口号
server.port=9090
#自定义属性
test.msg=hello
2、用注解@Value读取属性
package com.gui.hello;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class HelloController {
@Value("${test.msg}")
private String msg;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return msg;
}
}
3、访问: http://localhost:9090/test/hello
结果:
二、读取自定义配置文件
1、步骤
1. 创建自定义配置文件
2. 将配置绑定到实体类
@Configuration //将配置文件与实体类绑定
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/config/userinfo.properties") //指明配置文件的位置
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "userinfo") //指明配置文件的名称
1
2
3
3. 在控制器中注册实体类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(UserInfo.class) //注册实体类
1
2、实例
1. 在resources/config目录下创建配置文件userinfo.properties:
userinfo.name=xiaoming
userinfo.age=25
userinfo.city=HangZhou
1
2
3
2. 将配置绑定到实体类
UserInfo.java
package com.gui.hello.domain;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
/**
* 用户信息类
*/
@Configuration //将配置文件与实体类绑定
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/config/userinfo.properties") //指明配置文件的位置
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "userinfo") //指明配置文件的名称
public class UserInfo {
private String name;
private int age;
private String city;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
3. 控制器中注册实体类
UserInfoController.java
package com.gui.hello.web;
import com.gui.hello.domain.UserInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController //结果返回json
@RequestMapping("/userinfo")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(UserInfo.class) //注册实体类
public class UserInfoController {
@Value("${userinfo.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${userinfo.age}")
private int age;
@Value("${userinfo.city}")
private String city;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "我的名字叫"+name+",我今年"+age+"岁了,我住在"+city;
}
}
4、运行结果
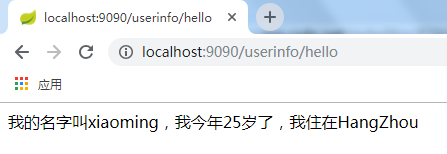
访问:http://localhost:9090/userinfo/hello
结果:
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「龟的小号」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hju22/java/article/details/87871158