一、树的概述:
线性表、栈、队列都是线型的数据结构,该种数据结构之间的元素只存在一对一的关系,而树的结构内元素是非线性的关系,存在着一对多的关系,例如一个父节点可以包含多个子节点。
树指的是N个有父子关系的节点的有限集合,满足以下关系:
1、当N=0时,该节点集合为空,这棵树被称为空树。
2、在任意的非空树中,有且仅有一个根节点。
3、当N>1时,除根节点以外的其余节点可分为M个互为相交的有限集合T1,T2...Tm,其中的每个集合本身又是一棵树并成为根的子树
二、树的递归特性:
一棵树由根和若干棵子树组成,而每个子树又由若干棵更小的子树组成。
树中任何一个节点可以有0或多个子节点,但只能有一个父节点。但是根节点没有父节点,叶子节点没有子节点。树干中每个节点既可以是上一级节点的子节点,也可以是下一级节点的父节点,因此同一个节点既可以是父节点,也可以是子节点。
三、节点的分类:
(按照节点是否包含子节点来划分)
1、普通节点:包含子节点的节点
2、叶子节点:没有子节点的节点,因此叶子节点不可以作为父节点。
(按照节点是否具有唯一的父节点来划分)
1、根节点:没有父节点的节点,根节点不可作为子节点。
2、普通节点:具有唯一的父节点。
一棵树只能有一个根节点,多棵树被称为森林。
四、树的术语:
节点:树的最基本组成单元,常包括一个数据元素以及若干指针用于指向其他节点。
节点的度(degree):节点拥有的子树的个数。
树的度:树中所有节点的度的最大值
叶子节点:度为0的节点被称为叶子节点或终端节点。
分支节点:度不为0的节点被称为分支节点或非终端节点。
节点的层次(level):节点的层次从根开始算起,根的层次值为1,其余节点的层次值为父节点层次值加一
树的深度(depth):树中节点的最大层次值称为树的深度或高度。
有序树与无序树:如果将树中节点 的各个子树看成从左到右是有序的(即不能互换),则称该树为有序树,否则是无序树。
祖先节点(ancestor):从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点。
后代节点(descendant):以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的后代节点。
森林:森林是两棵树或两棵以上互不相交的树的集合。
五、树的操作
为了实现树的这种数据结构,程序必须能记录节点与节点之间的父子关系,为此有两种选择:
1、父节点表示法:每个子节点都记录它的父节点。(为诶一个节点都增加一个parent域来记录该节点的父节点)
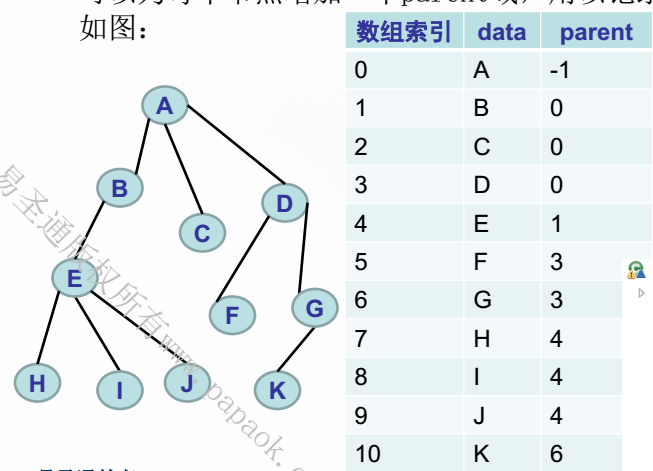
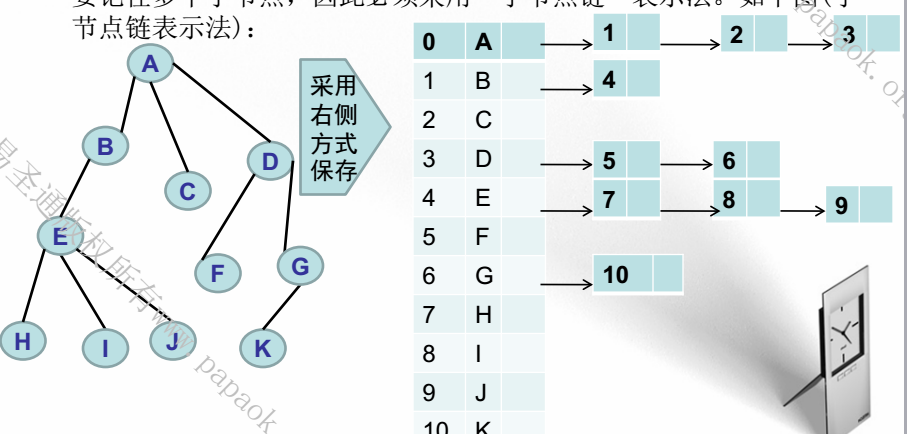
2、孩子节点表示法:每个非叶子节点通过一个链表来记录它所有的子节点。
父节点表示:
package com.zxc.TreeLearning; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * Created by Administrator on 2018/2/18 0018 * 父节点表示法表示树 */ public class CommonTree { public static class Node { String data; int parent; public Node(String data, int parent) { this.data = data; this.parent = parent; } public String toString() { return "父节点表示法|data" + data + ",parent=" + parent; } } private int treeSize = 100;//树节点的数量 private Node[] nodes=new Node[this.treeSize];//使用一个数组来记录树中所有节点 private int nodeNums;//记录节点数 public CommonTree(){ } /** * * @param node:要查找的节点 * @return */ public int pos(Node node){ for(int i=0;i<this.treeSize;i++){ if(nodes[i]==node){ return i; } } return -1; } /** * * @param data:当前节点数据 * @param parent:指定它的父节点 */ public Node add(String data,Node parent) { for (int i = 0; i < this.treeSize; i++) { if (nodes[i] == null) { nodes[i] = new Node(data, pos(parent)); this.nodeNums++; return nodes[i]; } } return null; } /** * * @return 该树的高度 */ public int deep(){ int max=0; for(int i=0;i<this.treeSize&&nodes[i]!=null;i++){ int count=1; int m=nodes[i].parent; //找到当前m所指的节点的父亲,直到没有节点位置,或者到root节点为止 while(m!=-1&&nodes[m]!=null){ m=nodes[m].parent; count++; } if(count>max){ max=count; } } return max; } /** * * @param parent:指定父节点 * @return 当前父节点下的子节点 */ public List<Node> getchild(Node parent){ List<Node> list=new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<this.treeSize;i++){ if(nodes[i]!=null&&nodes[i].parent==this.pos(parent)){ list.add(nodes[i]); } } return list; } public Node root(String data){ nodes[0]=new Node(data,-1); this.nodeNums++; return nodes[0]; } @Test public void test(){ Node root=this.root("root"); Node a=this.add("A",root); Node b=this.add("B",a); Node c=this.add("C",root); Node d=this.add("D",c); System.out.println(this.deep()); List<Node> list=this.getchild(c); for(Node node:list){ System.out.println(node.data); } } }
子节点表示法:
package com.zxc.TreeLearning; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * Created by Administrator on 2018/2/19 0019. * 子节点链表示法 */ public class CommonTreeB { private static class SonNode{//子节点链每个节点的信息 private int pos;//记录当前节点的位置 private SonNode next;//子节点记录下一个节点的对象 public SonNode(int pos,SonNode next){ this.pos=pos;//当前节点位置 this.next=next;//下一个节点位置 } } //子节点链 private static class Node{//单个节点的信息 String data; //记录第一个子节点:用于保存对该子节点链的引用,通过这种关系,可以记录树中节点之间的关系 SonNode first; public Node(String data){ this.data=data; this.first=null; } public String toString(){ if(first!=null){ return "TreeChild$Node[data="+data+",first="+first.pos+"]"; }else{ return "TreeChild$Node[data="+data+",first=-1]"; } } } private int treeSize=100; private Node[] nodes=new Node[treeSize]; private int nodeNums; public Node root(String data) { nodes[0]=new Node(data); nodeNums++; return nodes[0]; } public Node addNode(String data,Node parent){ for(int i=0;i<treeSize;i++){ if(nodes[i]==null){ nodes[i]=new Node(data); if(parent.first==null){//没有孩子链 parent.first=new SonNode(i,null);//parent的儿子节点链的第一个节点 }else{//父节点中有子节点,应该传到最后,再连接 SonNode next=parent.first; while(next.next!=null){ next=next.next; } next.next=new SonNode(i,null); } nodeNums++; return nodes[i]; } } return null; } private int deep(Node node){//从下到上的深度 if(node.first==null){ return 1; }else{ int max=0; SonNode son=node.first; while(son!=null){ int temp=deep(nodes[son.pos]); if(temp>max){ max=temp; } son=son.next; } return max+1; } } public List getChildren(Node parent){ List list=new ArrayList(); SonNode node=parent.first; while(node!=null){ list.add(nodes[node.pos]); node=node.next; } return list; } @Test public void ok(){ Node root=this.root("A"); Node B=this.addNode("B",root); Node C=this.addNode("C",root); Node D=this.addNode("D",root); Node E=this.addNode("E",B); Node F=this.addNode("F",D); Node G=this.addNode("G",D); Node H=this.addNode("H",E); Node I=this.addNode("I",E); Node J=this.addNode("J",E); Node K=this.addNode("K",G); System.out.println(this.deep(G)); List<Node> list=this.getChildren(B); for(Node b:list){ System.out.println(b.data); } } }