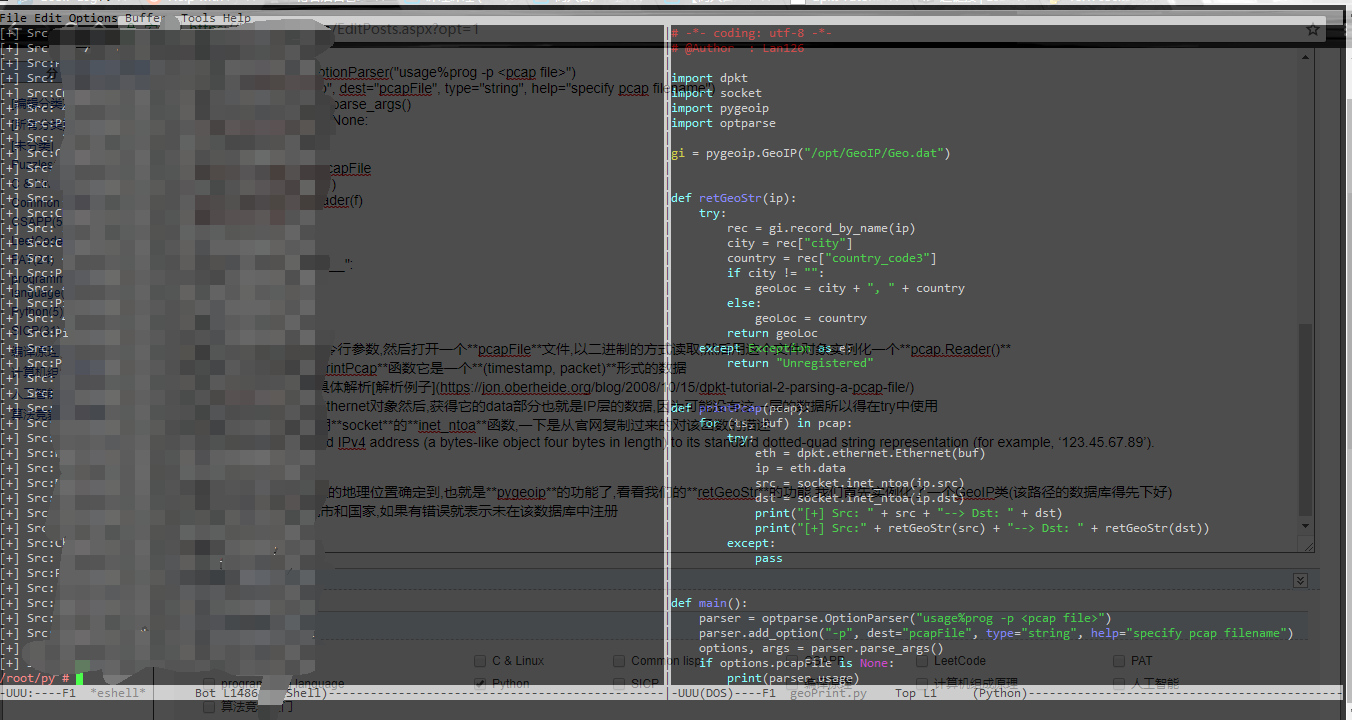
利用dpkt解析包
平台为centos,python3
代码如下
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Author : Lan126
import dpkt
import socket
import pygeoip
import optparse
gi = pygeoip.GeoIP("/opt/GeoIp/Geo.dat")
def retGeoStr(ip):
try:
rec = gi.record_by_name(ip)
city = rec["city"]
country = rec["country_code3"]
if city != "":
geoLoc = city + ", " + country
else:
geoLoc = country
return geoLoc
except Exception as e:
return "Unregistered"
def printPcap(pcap):
for (ts, buf) in pcap:
try:
eth = dpkt.ethernet.Ethernet(buf)
ip = eth.data
src = socket.inet_ntoa(ip.src)
dst = socket.inet_ntoa(ip.dst)
print("[+] Src: " + src + "--> Dst: " + dst)
print("[+] Src:" + retGeoStr(src) + "--> Dst: " + retGeoStr(dst))
except:
pass
def main():
parser = optparse.OptionParser("usage%prog -p <pcap file>")
parser.add_option("-p", dest="pcapFile", type="string", help="specify pcap filename")
options, args = parser.parse_args()
if options.pacapFile is None:
print(parser.usage)
exit(0)
pcapFile = options.pacapFile
f = open(pcapFile, "rb")
pcap = dpkt.pcap.Reader(f)
printPcap(pcap)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
思路
先看main,照例先设置命令行参数,然后打开一个pcapFile文件,以二进制的方式读取,然后用这个文件对象实例化一个pcap.Reader()
对象,这个对象被传给printPcap函数它是一个(timestamp, packet)形式的数据
关于pacapFile的更具体解析解析例子
重点就是首先实例一个Ethernet对象然后,获得它的data部分也就是IP层的数据,因为可能没有这一层的数据所以得在try中使用
然后就是为了方便显示用socket的inet_ntoa函数,一下是从官网复制过来的对该函数的描述
Convert a 32-bit packed IPv4 address (a bytes-like object four bytes in length) to its standard dotted-quad string representation (for example, ‘123.45.67.89’).
最后看一看如何将ip地址的地理位置确定到,也就是pygeoip的功能了,看看我们的retGeoStr的功能,我们首先实例化了一个GeoIP类(该路径的数据库得先下好)
然后用给定的IP查询,城市和国家,如果有错误就表示未在该数据库中注册
结果图
补充
还可以利用谷歌地球进行可视化分析大概就是这样