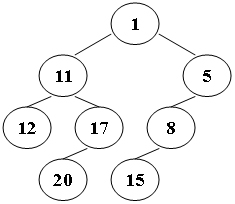
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <queue> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int maxn=31; 6 int pos[maxn],in[maxn]; 7 int n,m; 8 vector<int> res[31]; 9 struct node{ 10 int data; 11 node* left,*right; 12 int lvl; 13 }; 14 node* create(int inl,int inr,int posl,int posr){ 15 if(inl > inr) return NULL; 16 node* root = new node; 17 root->data = pos[posr]; 18 int k; 19 for(k=inl;k<=inr;k++){ 20 if(pos[posr]==in[k]) break; 21 } 22 int numleft=k-inl; 23 root->left = create(inl,k-1,posl,posl+numleft-1); 24 root->right = create(k+1,inr,posl+numleft,posr-1); 25 return root; 26 } 27 void pr(node* root){ 28 queue<node*> q; 29 root->lvl=0; 30 q.push(root); 31 while(!q.empty()){ 32 node* now=q.front(); 33 q.pop(); 34 res[now->lvl].push_back(now->data); 35 if(now->left!=NULL){ 36 now->left->lvl=now->lvl+1; 37 q.push(now->left); 38 } 39 if(now->right!=NULL){ 40 now->right->lvl=now->lvl+1; 41 q.push(now->right); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 int main(){ 46 scanf("%d",&n); 47 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 48 scanf("%d",&in[i]); 49 } 50 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 51 scanf("%d",&pos[i]); 52 } 53 node* root = create(0,n-1,0,n-1); 54 pr(root); 55 int cnt=0; 56 for(int i=0;i<32;i++){ 57 if(i%2==0){ 58 for(int j=res[i].size()-1;j>=0;j--){ 59 printf("%d",res[i][j]); 60 cnt++; 61 if(cnt<n)printf(" "); 62 } 63 } 64 else{ 65 for(int j=0;j<res[i].size();j++){ 66 printf("%d",res[i][j]); 67 cnt++; 68 if(cnt<n)printf(" "); 69 } 70 } 71 if(cnt==n)break; 72 } 73 }
注意点:最简单的一道30分题了。只要会建树,再层序遍历,把每层的数据保存起来,再根据层数正着输出或是反向输出就ac了。
ps:也可以用deque双向队列更方便的实现。每层的输出其实可以不用开vector数组,一层遍历完后输出就好了。
