梯度的实现:
1 import numpy as np 2 3 def numerical_gradient(f,x): 4 #数值微分求梯度,f为函数,x为NumPy数组,该函数对数组x的各个元素求数值微分 5 6 h=1e-4#0.0001 7 grad=np.zeros_like(x)#生成和x形状相同的数组 8 9 for idx in range(x.size): 10 tmp_val=x[idx] 11 #f(x+h)的计算 12 x[idx]=tmp_val+h 13 fxh1=f(x) 14 15 #f(x-h)的计算 16 x[idx]=tmp_val-h 17 fxh2=f(x) 18 19 grad[idx]=(fxh1-fxh2)/(2*h) 20 x[idx]=tmp_val #还原值 21 22 return grad 23 24 def function_2(x): 25 return x[0]**2+x[1]**2 26 27 print(numerical_gradient(function_2,np.array([3.0,4.0])))
梯度下降法的实现:
def gradient_descent(f,init_x,lr=0.01,step_num=100): #f是函数 x=init_x #init_x是初始值 for i in range(step_num): grad=numerical_gradient(f,x) x-=lr*grad return x
神经网络的梯度
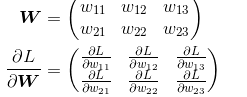
下面,我们以一个简单的神经网络为例,来实现求梯度的代码:
1 # coding: utf-8 2 import sys, os 3 sys.path.append(os.pardir) # 为了导入父目录中的文件而进行的设定 4 import numpy as np 5 from common.functions import softmax, cross_entropy_error 6 from common.gradient import numerical_gradient 7 8 9 class simpleNet: 10 def __init__(self): 11 self.W = np.random.randn(2,3) 12 13 def predict(self, x): 14 return np.dot(x, self.W) 15 16 def loss(self, x, t): 17 z = self.predict(x) #z=xW 18 y = softmax(z) 19 loss = cross_entropy_error(y, t) #交叉熵误差 20 21 return loss 22 23 x = np.array([0.6, 0.9]) 24 t = np.array([0, 0, 1]) 25 26 net = simpleNet() 27 28 f = lambda w: net.loss(x, t) #f是损失函数 29 dW = numerical_gradient(f, net.W) 30 31 print(dW)

学习算法的实现:
前提
神经网络存在合适的权重和偏置,调整权重和偏置以便拟合训练数据的过程称为“学习”。神经网络的学习分成下面 4 个步骤。
步骤 1(mini-batch)
从训练数据中随机选出一部分数据,这部分数据称为 mini-batch。我们的目标是减小 mini-batch 的损失函数的值。
步骤 2(计算梯度)
为了减小 mini-batch 的损失函数的值,需要求出各个权重参数的梯度。梯度表示损失函数的值减小最多的方向。
步骤 3(更新参数)
将权重参数沿梯度方向进行微小更新。
步骤 4(重复)
重复步骤 1、步骤 2、步骤 3。
2层神经网络的类:
1 import sys,os 2 sys.path.append(os.pardir) 3 from common.functions import * 4 from common.gradient import numerical_gradient 5 6 class TwoLayerNet: 7 def __init__(self,input_size,hidden_size,output_size,weight_init_std=0.01): 8 #初始化权重 9 self.params={} 10 self.params['W1']=weight_init_std*np.random.randn(input_size,hidden_size) 11 self.params['b1']=np.zeros(hidden_size) 12 self.params['W2']=weight_init_std*np.random.randn(hidden_size,output_size) 13 self.params['b2']=np.zeros(output_size) 14 15 def predict(self,x): 16 W1,W2=self.params['W1'],self.params['W2'] 17 b1,b2=self.params['b1'],self.params['b2'] 18 19 a1=np.dot(x,W1)+b1 20 z1=sigmoid(a1) 21 a2=np.dot(z1,W2)+b2 22 y=softmax(a2) 23 24 return y 25 26 def loss(self,x,t): 27 y=self.predict(x) 28 29 return cross_entropy_error(y,t) 30 31 def accuracy(self,x,t): 32 y=self.predict(x) 33 y=np.argmax(y,axis=1) 34 t=np.argmax(t,axis=1) 35 36 accuracy=np.sum(y==t)/float(x.shape[0]) 37 return accuracy 38 39 def numerical_gradient(self,x,t): 40 loss_W=lambda W: self.loss(x,t) 41 42 grads={} 43 grads['W1']=numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['W1']) 44 grads['b1']=numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['b1']) 45 grads['W2']=numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['W2']) 46 grads['b2']=numerical_gradient(loss_W,self.params['b2']) 47 48 return grads
mini-batch的实现:
1 import numpy as np 2 from dataset.mnist import load_mnist 3 from two_layer_net import TwoLayerNet 4 5 (x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_ 6 label = True) 7 8 train_loss_list = [] 9 10 # 超参数 11 iters_num = 10000 12 train_size = x_train.shape[0] 13 batch_size = 100 14 learning_rate = 0.1 15 16 network = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size=50, output_size=10) 17 18 for i in range(iters_num): 19 # 获取mini-batch 20 batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size) 21 x_batch = x_train[batch_mask] 22 t_batch = t_train[batch_mask] 23 24 # 计算梯度 25 grad = network.numerical_gradient(x_batch, t_batch) 26 # grad = network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch) # 高速版! 27 28 # 更新参数 29 for key in ('W1', 'b1', 'W2', 'b2'): 30 network.params[key] -= learning_rate * grad[key] 31 32 # 记录学习过程 33 loss = network.loss(x_batch, t_batch) 34 train_loss_list.append(loss)