(Ⅰ) 顺序表实现相加
①C方法(很简单的对应相加。。
#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; typedef struct PolyNode *Poly; struct PolyNode { int a; int n; Poly link; }; void Attach(int a,int n,Poly *pLast) { Poly p; p = (Poly)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode)); p->a = a; p->n = n; p->link = NULL; (*pLast)->link = p; *pLast = p; } Poly ReadPoly() { Poly P,Last,t; int a,n,x,num=1; P = (Poly)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode)); P->link = NULL; Last = P; while(cin >> x) { char ch = cin.get(); if(ch == ' ') { n = x; Attach(a,n,&Last); break; } else { if(num == 1) { a = x; num++; } else { n = x; Attach(a,n,&Last); num=1; } } } t = P; P = P->link; free(t); return P; } Poly Add(Poly P1,Poly P2) { Poly head,tail,t; int sum; tail = (Poly)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode)); head = tail; while(P1&&P2) { if(P1->n == P2->n) { sum = P1->a + P2->a; if(sum) Attach(sum,P1->n,&tail); P1 = P1->link; P2 = P2->link; continue; } else if((P1->n) > (P2->n)) { Attach(P1->a,P1->n,&tail); P1 = P1->link; continue; } else { Attach(P2->a,P2->n,&tail); P2 = P2->link; continue; } } for(;P1;P1=P1->link) Attach(P1->a,P1->n,&tail); for(;P2;P2=P2->link) Attach(P2->a,P2->n,&tail); tail->link = NULL; t = head; head = head->link; free(t); return head; } void PrintPoly(Poly P) { int f = 0; if(!P) { cout << "0 0" <<endl; return; } while(P) { if(!f) f = 1; else cout << " "; printf("%dx^%d",P->a,P->n); P = P->link; } } int main() { Poly P1,P2,P3; P1 = ReadPoly(); P2 = ReadPoly(); P3 = Add(P1,P2); PrintPoly(P3); return 0; }
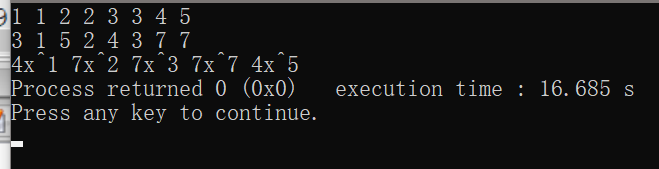
(有bug,懒得改了。。
②C++方法
(Ⅱ) 链表实现相加
①C++方法一
#include<iostream> using namespace std; ///构建多项式的结点 struct Node { double a; ///系数 int n; ///指数,ax^n Node* next; Node(double a1,int n1,Node* nextValue = NULL) { a = a1; n = n1; next = nextValue; } Node* InsertAfter(double a,int n); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Node& N); }; Node* Node::InsertAfter(double a,int n) { next = new Node(a,n,next); return next; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Node& N) { if(N.a == 0.0) return out; cout << N.a; switch(N.n) { case 0: break; case 1: cout << "X" ; break; default: cout << "X^" << N.n; break; } return out; } class Poly ///改名字辽 { private: Node* head; ///结构体是可以滴 //Node* curlenth; friend istream& operator>>(istream& in,const Poly& P); ///输入流运算符重载 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Poly& P); //Poly& operator=(Poly& P); friend Poly operator+(Poly& A,Poly& B); public: Poly() ///构造函数,建立空链表(你写的那个是顺序表~ { head = new Node(0,-1); } ~Poly() { Empty(); } void Empty(); ///将链表清空 Node* getHead() const ///得到头指针,head是私有,无法直接访问,只能通过函数 { return head; } }; void Poly::Empty() { Node *temp; while(head->next != NULL) ///链表不为空时,删去所有结点,保留头结点 { temp = head->next; head->next = temp->next; delete temp; } } istream& operator>>(istream& in,const Poly& P) ///用尾插法,建立多项式 { Node *last = P.getHead(); int a,n; ///a为系数,n为指数:ax^n while(1) { cout << "输入一组系数和指数(>0)" << endl; cin >> a >> n; if(n<0) break; last = last->InsertAfter(a,n); } return in; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Poly& P) { Node *temp = P.getHead()->next; cout << "结果是:" << endl; int flag = 1; while(temp != NULL) { if(flag==0 && temp->a>0.0) cout <<"+"; flag = 0; cout << *temp; temp = temp->next; } cout << endl; return out; } Poly operator+(Poly& A,Poly& B) { Node *pa,*pb,*pc; Node *p; double temp; Poly C; pc = C.head; pa = A.getHead()->next; pb = B.getHead()->next; while(pa!=NULL && pb!=NULL) { if(pa->n == pb->n) { temp = pa->a + pb->a; if(temp>0) pc = pc->InsertAfter(temp,pa->n); pa = pa->next; pb = pb->next; } else if(pa->n < pb->n) { pc = pc->InsertAfter(pa->a,pa->n); pa = pa->next; } else { pc = pc->InsertAfter(pb->a,pa->n); pb = pb->next; } } if(pa != NULL) p = pa; else p = pb; while(p != NULL) { pc = pc->InsertAfter(p->a,p->n); p = p->next; } return C; } int main() { Poly pa,pb; cin >> pa; cout << pa; cin >> pb; cout << pb; cout << pa+pb; return 0; }
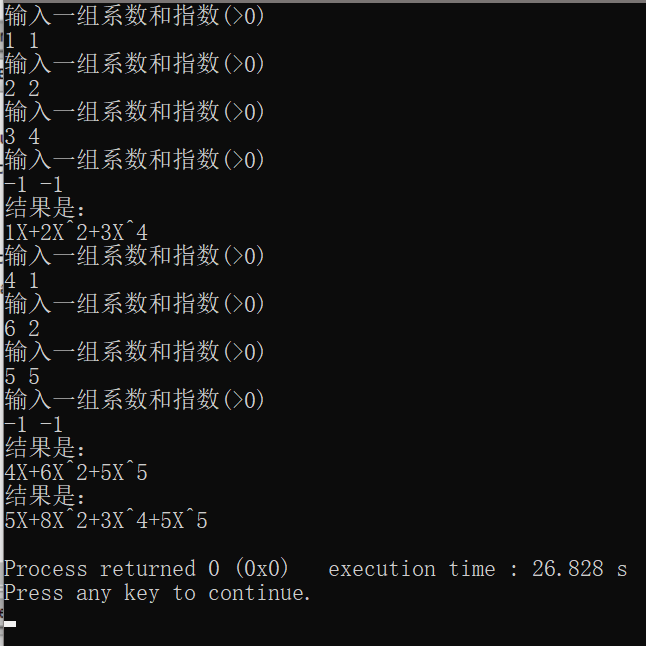
②C++方法二(写的最好的了,可以自动进行排序)
#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; const int defaultSize = 100; typedef struct { int a; int n; } data; template <class T> class SeqList { private: T* da; int maxSize; int last; public: SeqList(int sz = defaultSize); ~SeqList(); int Length()const { return last; } int Search(T& x)const; void Delete(int i); void outPut(); void Insert(const T& x); void operator =(const SeqList<T>& LL); SeqList<T> operator +(const SeqList<T>& LL); }; template <class T> SeqList<T>::SeqList(int sz) { if(sz > 0) { maxSize = sz; last = 0; da = new T[maxSize]; if(da == NULL) { cerr << "wrong!" << endl; exit(1); } } } template <class T> SeqList<T>::~SeqList() { delete[] da; } template <class T> int SeqList<T>::Search(T& x) const { for(int i=0; i<last; ++i) if(da[i].n == x.n) return i; return -1; } template <class T> void SeqList<T>::Delete(int i) { if((i<0) || (i>last-1)) { cout << "not found!" <<endl; exit(0); } for(int j=i; j<=last-2; j++) da[j] = da[j+1]; last--; } template <class T> void SeqList<T>::outPut() { for(int i=0; i<=last-1; i++) { if(da[i].a > 0) cout << "+"; cout << da[i].a << "x^" << da[i].n << " "; } cout << endl; } template <class T> void SeqList<T>::Insert(const T& x) { da[last++] = x; for(int i=last-1;i>0;--i) if(da[i].n < da[i-1].n) swap(da[i],da[i-1]); } template <class T> void SeqList<T>::operator =(const SeqList<T>& LL) { maxSize = LL.maxSize; last = LL.last; for(int i=0;i<last;++i) da[i] = LL.da[i]; } template <class T> SeqList<T> SeqList<T>::operator +(const SeqList<T>& LL) { maxSize += LL.maxSize; int x; for(int i=0; i<LL.last; ++i) { x=Search(LL.da[i]); if(x==-1) { da[last++] = LL.da[i]; for(int j=last-1; j>0; --j) { if(da[j].n < da[j-1].n) swap(da[j],da[j-1]); else break; } } else { if(da[x].a + LL.da[i].a == 0) Delete(x); else da[x].a += LL.da[i].a; } } return *this; } int main () { data poly; SeqList<data> L1,L2,L3; int x,num=1; while(cin >> x) { char ch=cin.get(); if(ch == ' ') { poly.n=x; L1.Insert(poly); break; } else { if(num == 1) { poly.a=x; num++; } else { poly.n=x; L1.Insert(poly); num=1; } } } L1.outPut(); int y,num1=1; while(cin >> y) { char ch=cin.get(); if(ch == ' ') { poly.n=y; L2.Insert(poly); break; } else { if(num1 == 1) { poly.a=y; num1++; } else { poly.n=y; L2.Insert(poly); num1=1; } } } L2.outPut(); L3 = L1+L2; cout << "outcome: " ; L3.outPut(); return 0; }

③C++
#include<iostream> using namespace std; struct Link { int p, e; Link* next; Link(int c, int d, Link* nextValue = NULL) { p = c; e = d; next = nextValue; } Link(Link* nextValue) { next = nextValue; } }; class Lnklist { private: Link* head,*tail; Link* curlenth; public: Lnklist() { head = new Link(0,-1); tail = new Link(0,-1); } ~Lnklist() { Link* tmp; while (head != NULL) { tmp = head; head = head->next; delete tmp; } } void Attach(int x, int y) { Link*t=new Link(x,y,NULL); if (head->next == NULL) { head->next = t; tail = t; t->next = NULL; } else { tail->next = t; tail = t; } } Link* setPos(int i) { int count = 0; if (i == -1) return head; Link* p = new Link(head->next); while (p != NULL && count < i) { p = p->next; count++; } return p; } bool getvalue(const int p,int &c,int &d) { Link* temp = setPos(p); if (temp->next == NULL || temp->next == head) { c = 0, d = 0; return false; } c = (temp->next)->p; d = (temp->next)->e; return true; } void print() { Link* P; for (P = head->next; P != NULL; P = P->next) { cout << P->p << ' ' << P->e << ' '; } } }; Lnklist add( Lnklist&t1, Lnklist& t2,int num1,int num2) { int a = 1; int b = 1; int p1 = 0, e1 = 0, p2 = 0, e2 = 0; Lnklist arr3; while (a<=num1 && b<=num2) { t1.getvalue(a - 1, p1, e1); t2.getvalue(b - 1, p2, e2); if (e1 == e2) { arr3.Attach(p1 + p2, e1); a++; b++; } else { if (e1 > e2) { arr3.Attach( p1, e1); a++; } else { arr3.Attach(p2, e2); } } } while(a < num1) { arr3.Attach(p1, e1); a++; } while (b < num2) { arr3.Attach(p2, e2); b++; } return arr3; } int main() { int num1,num2,i; cout << "Please input the number of terms of polynomial" << endl; cout << "polynomial 1: "; cin >> num1; cout << "polynomial 2: "; cin >> num2; Lnklist arr1; cout << "Please input polynomial 1" << endl; for (i = 0; i < num1; i++) { int x, y; cin >> x>>y; arr1.Attach(x, y); } arr1.print(); cout << endl; Lnklist arr2; cout << "Please input polynomial 2" << endl; for (i = 0; i < num2; i++) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; arr2.Attach(x, y); } arr2.print(); cout << endl; Lnklist arr3; arr3 = add(arr1, arr2, num1,num2); arr3.print(); return 0; }