灯塔(LightHouse)
Description
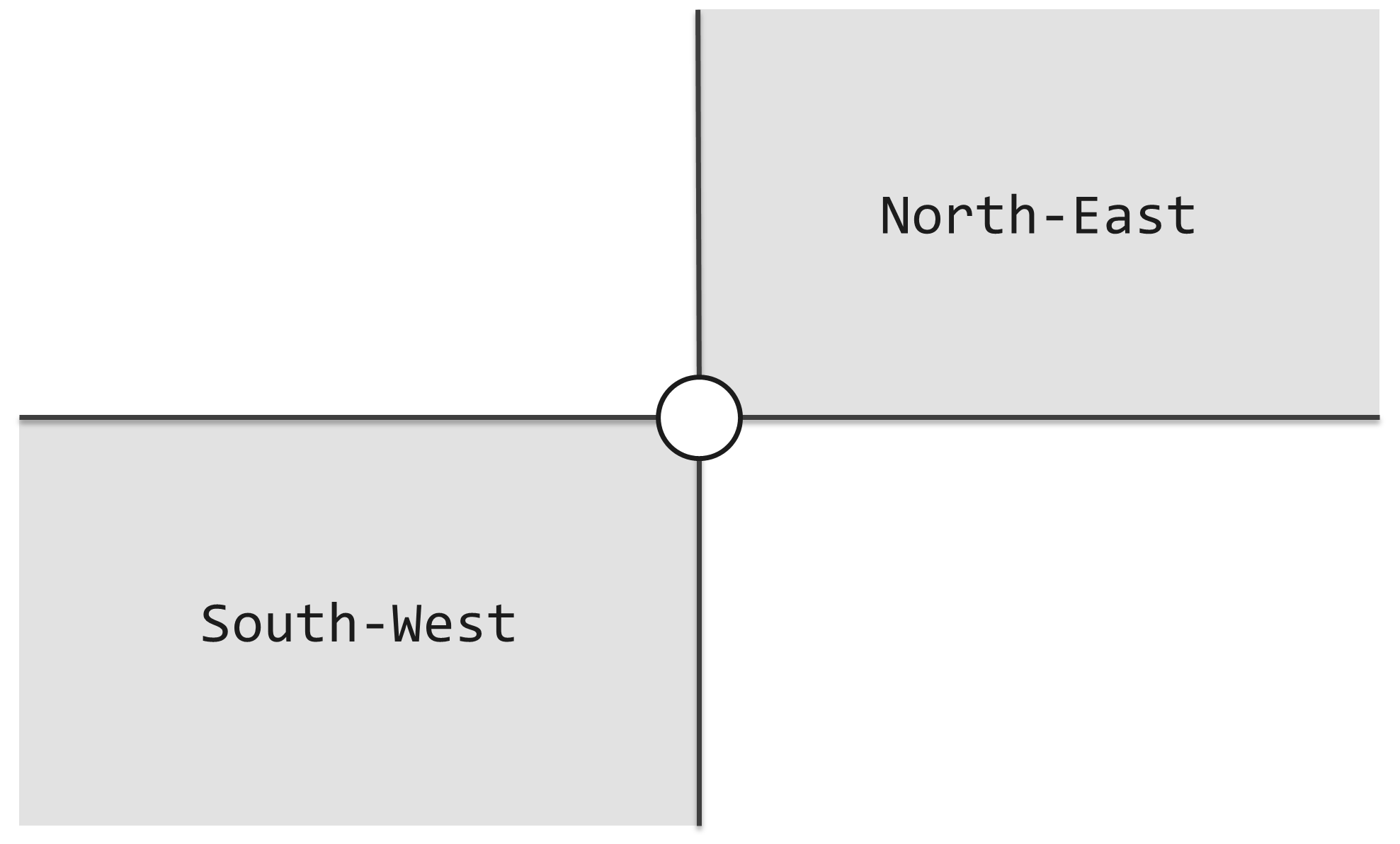
As shown in the following figure, If another lighthouse is in gray area, they can beacon each other.
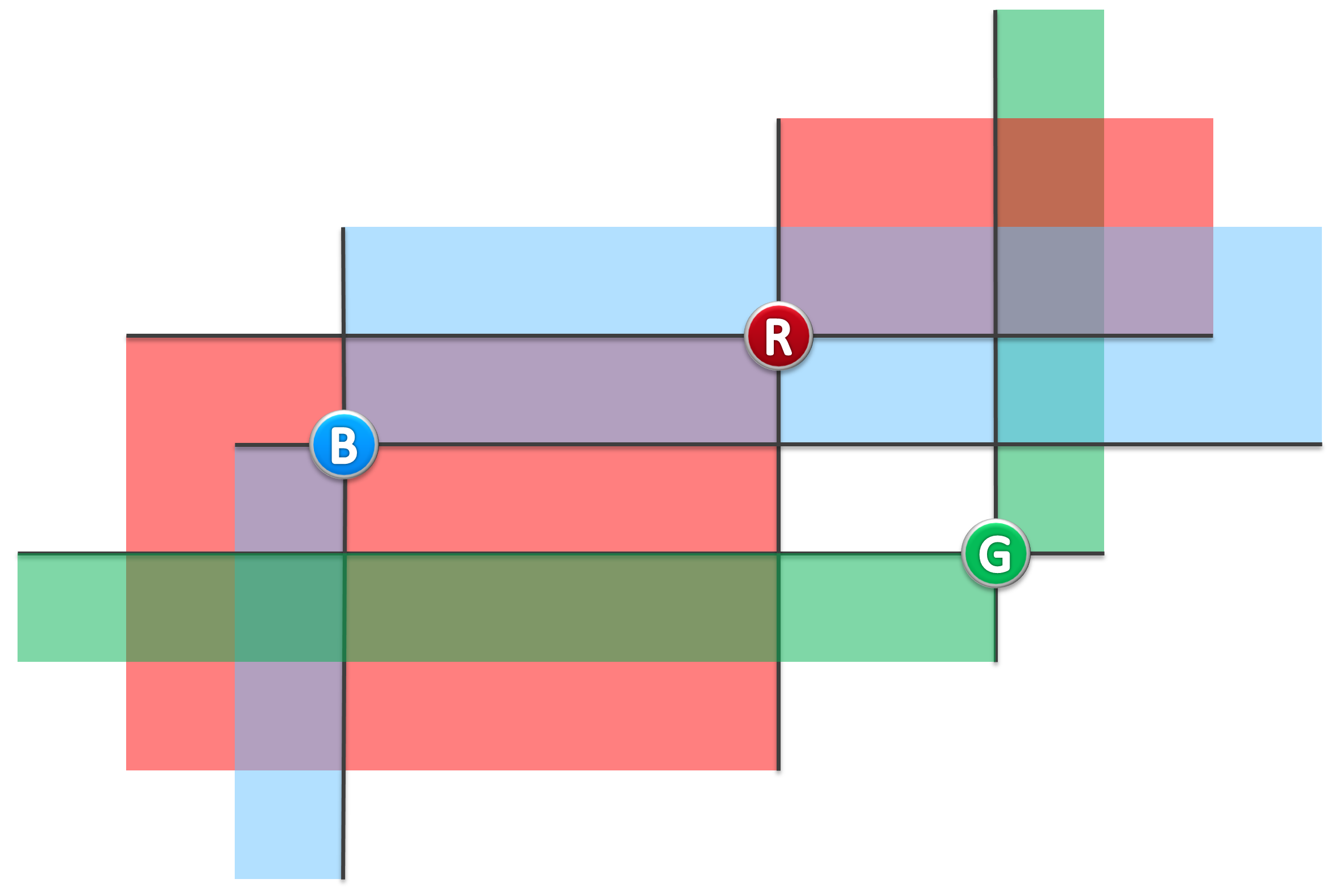
For example, in following figure, (B, R) is a pair of lighthouse which can beacon each other, while (B, G), (R, G) are NOT.
Input
1st line: N
2nd ~ (N + 1)th line: each line is X Y, means a lighthouse is on the point (X, Y).
Output
How many pairs of lighthourses can beacon each other
( For every lighthouses, X coordinates won't be the same , Y coordinates won't be the same )
Example
Input
3
2 2
4 3
5 1
Output
1
Restrictions
For 90% test cases: 1 <= n <= 3 * 105
For 95% test cases: 1 <= n <= 106
For all test cases: 1 <= n <= 4 * 106
For every lighthouses, X coordinates won't be the same , Y coordinates won't be the same.
1 <= x, y <= 10^8
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
Hints
The range of int is usually [-231, 231 - 1], it may be too small.
描述
海上有许多灯塔,为过路船只照明。

(图一)
如图一所示,每个灯塔都配有一盏探照灯,照亮其东北、西南两个对顶的直角区域。探照灯的功率之大,足以覆盖任何距离。灯塔本身是如此之小,可以假定它们不会彼此遮挡。

(图二)
若灯塔A、B均在对方的照亮范围内,则称它们能够照亮彼此。比如在图二的实例中,蓝、红灯塔可照亮彼此,蓝、绿灯塔则不是,红、绿灯塔也不是。
现在,对于任何一组给定的灯塔,请计算出其中有多少对灯塔能够照亮彼此。
输入
共n+1行。
第1行为1个整数n,表示灯塔的总数。
第2到n+1行每行包含2个整数x, y,分别表示各灯塔的横、纵坐标。
输出
1个整数,表示可照亮彼此的灯塔对的数量。
样例
见英文题面
限制
对于90%的测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 3×105
对于95%的测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 106
全部测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 4×106
灯塔的坐标x, y是整数,且不同灯塔的x, y坐标均互异
1 ≤ x, y ≤ 10^8
时间:2 sec
内存:256 MB
提示
注意机器中整型变量的范围,C/C++中的int类型通常被编译成32位整数,其范围为[-231, 231 - 1],不一定足够容纳本题的输出。
题目来源——清华OJ——数据结构与算法实验(中国石油大学)
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #define N 4005000 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int c[N]={0}; 7 8 void updata(int pos,int w) 9 { 10 for(int i=pos;i<N;i+=i&(-i))c[i]+=w; 11 } 12 13 int Sum(int pos) 14 { 15 int ans=0; 16 for(int i=pos;i>0;i-=i&(-i))ans+=c[i]; 17 return ans; 18 } 19 20 struct ss 21 { 22 int x,y; 23 bool operator < (const ss &s)const 24 { 25 if(x!=s.x)return x<s.x; 26 return y<s.y; 27 } 28 }; 29 30 void sort(ss arr[],ss ls[],int l,int r) 31 { 32 if(l==r)return; 33 int mid=(l+r)/2; 34 sort(arr,ls,l,mid); 35 sort(arr,ls,mid+1,r); 36 37 int c1=l,c2=mid+1; 38 int c=l; 39 40 while(c1<=mid&&c2<=r) 41 { 42 if(arr[c1]<arr[c2])ls[c++]=arr[c1++]; 43 else 44 ls[c++]=arr[c2++]; 45 } 46 47 while(c1<=mid)ls[c++]=arr[c1++]; 48 while(c2<=r)ls[c++]=arr[c2++]; 49 for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)arr[i]=ls[i]; 50 } 51 52 void sort(int arr[],int ls[],int l,int r) 53 { 54 if(l==r)return; 55 int mid=(l+r)/2; 56 sort(arr,ls,l,mid); 57 sort(arr,ls,mid+1,r); 58 59 int c1=l,c2=mid+1; 60 int c=l; 61 62 while(c1<=mid&&c2<=r) 63 { 64 if(arr[c1]<arr[c2])ls[c++]=arr[c1++]; 65 else 66 ls[c++]=arr[c2++]; 67 } 68 69 while(c1<=mid)ls[c++]=arr[c1++]; 70 while(c2<=r)ls[c++]=arr[c2++]; 71 for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)arr[i]=ls[i]; 72 } 73 74 ss arr[N],ls1[N]; 75 int lsh[N],sum_lsh=0; 76 77 int f(int x) 78 { 79 int ans; 80 81 int l=0,r=sum_lsh-1; 82 while(l<=r) 83 { 84 int mid=(l+r)/2; 85 if(lsh[mid]>=x) 86 { 87 ans=mid; 88 r=mid-1; 89 } 90 else 91 { 92 l=mid+1; 93 } 94 } 95 return ans+1; 96 } 97 98 int ls[N]; 99 100 int read() 101 { 102 int now=0; 103 char ch=getchar(); 104 while(!(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'))ch=getchar(); 105 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') 106 { 107 now=now*10+ch-'0'; 108 ch=getchar(); 109 } 110 return now; 111 } 112 113 int main() 114 { 115 int n; 116 //scanf("%d",&n); 117 n=read(); 118 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 119 { 120 arr[i].x=read(); 121 arr[i].y=read(); 122 //scanf("%d %d",&arr[i].x,&arr[i].y); 123 lsh[sum_lsh++]=arr[i].y; 124 } 125 126 sort(lsh,ls,0,sum_lsh-1); 127 int c1=1; 128 for(int i=1;i<sum_lsh;i++) 129 { 130 if(lsh[i]!=lsh[i-1])lsh[c1++]=lsh[i]; 131 } 132 sum_lsh=c1; 133 134 long long ans=0; 135 sort(arr,ls1,0,n-1); 136 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 137 { 138 int now=f(arr[i].y); 139 ans+=Sum(now); 140 updata(now,1); 141 } 142 printf("%lld\n",ans); 143 return 0; 144 }