首先声明一点,springboot获取资源文件,需要看是
1》从spring boot默认的application.properties资源文件中获取
2》还是从自定义的资源文件中获取
带着这个想法去看下面几种方式
===============================================================================================
1》从spring boot默认的application.properties资源文件中获取
先给出来application.properties的内容
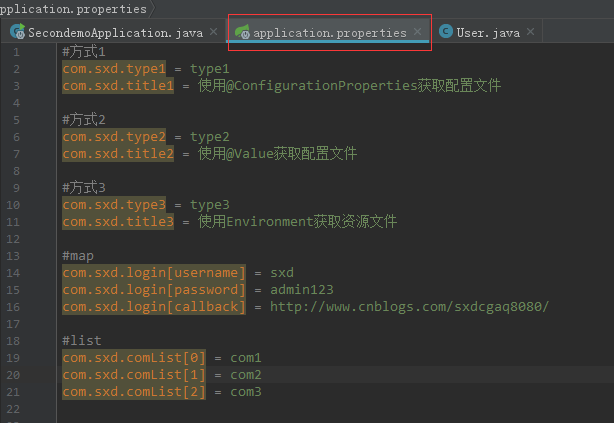

#方式1
com.sxd.type1 = type1
com.sxd.title1 = 使用@ConfigurationProperties获取配置文件
#方式2
com.sxd.type2 = type2
com.sxd.title2 = 使用@Value获取配置文件
#方式3
com.sxd.type3 = type3
com.sxd.title3 = 使用Environment获取资源文件
#map
com.sxd.login[username] = sxd
com.sxd.login[password] = admin123
com.sxd.login[callback] = http://www.cnblogs.com/sxdcgaq8080/
#list
com.sxd.comList[0] = com1
com.sxd.comList[1] = com2
com.sxd.comList[2] = com3
①===第一种方式:使用@ConfigurationProperties获取配置文件
先搞一个绑定资源文件的bean
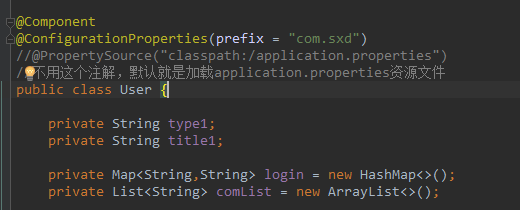
注意属性名和资源文件中的属性名相一致。

package com.sxd.beans; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "com.sxd") //@PropertySource("classpath:/application.properties") //不用这个注解,默认就是加载application.properties资源文件 public class User { private String type1; private String title1; private Map<String,String> login = new HashMap<>(); private List<String> comList = new ArrayList<>(); public String getType1() { return type1; } public void setType1(String type1) { this.type1 = type1; } public String getTitle1() { return title1; } public void setTitle1(String title1) { this.title1 = title1; } public Map<String, String> getLogin() { return login; } public void setLogin(Map<String, String> login) { this.login = login; } public List<String> getComList() { return comList; } public void setComList(List<String> comList) { this.comList = comList; } }
然后在启动类中使用
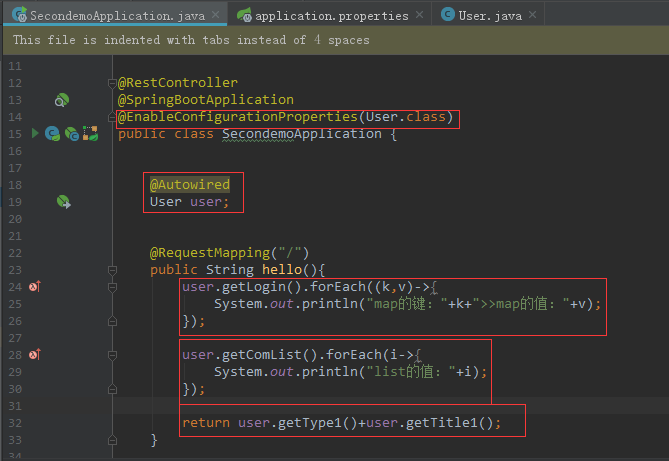

package com.sxd.secondemo; import com.sxd.beans.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigurationProperties(User.class) public class SecondemoApplication { @Autowired User user; @RequestMapping("/") public String hello(){ user.getLogin().forEach((k,v)->{ System.out.println("map的键:"+k+">>map的值:"+v); }); user.getComList().forEach(i->{ System.out.println("list的值:"+i); }); return user.getType1()+user.getTitle1(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SecondemoApplication.class, args); } }
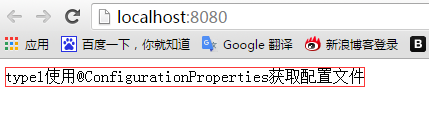
结果如下:
控制台打印:
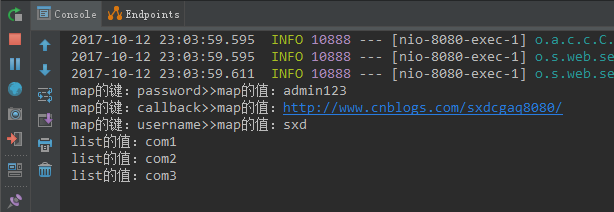
访问地址:
②===第二种方式:使用@Value获取配置文件
这里不用搞一个绑定资源文件的bean了。
只需要在你想用的地方使用@Value调用你想要的属性名对应的值即可。
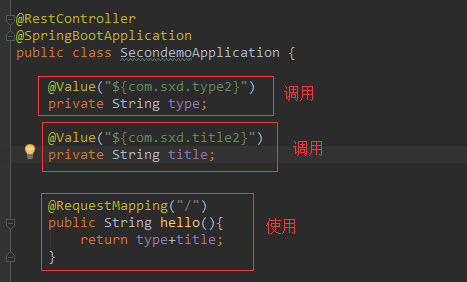

package com.sxd.secondemo; import com.sxd.beans.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication public class SecondemoApplication { @Value("${com.sxd.type2}") private String type; @Value("${com.sxd.title2}") private String title; @RequestMapping("/") public String hello(){ return type+title; } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SecondemoApplication.class, args); } }
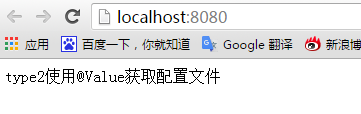
访问结果:
③===第三种方式:使用Environment获取资源文件
也不用提前做什么使用,Environment就是一个全局的资源池,application.properties中的属性值都可以从这里获取到。
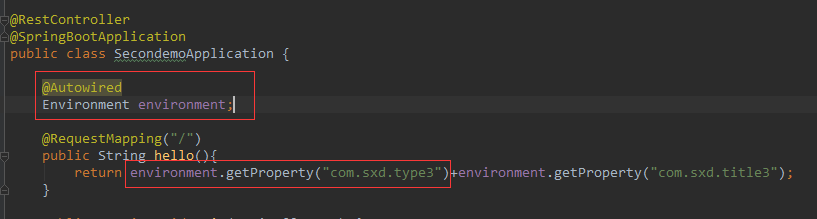

package com.sxd.secondemo; import com.sxd.beans.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication public class SecondemoApplication { @Autowired Environment environment; @RequestMapping("/") public String hello(){ return environment.getProperty("com.sxd.type3")+environment.getProperty("com.sxd.title3"); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SecondemoApplication.class, args); } }
运行结果:
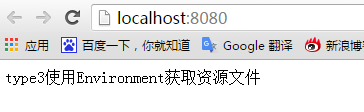
================================================================================================
2》从自定义的资源文件中获取属性值
①===第一种方式:使用@ConfigurationProperties获取配置文件
自定义资源文件如下:
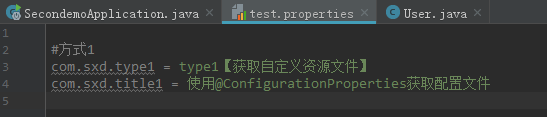
然后指定绑定自定义资源文件
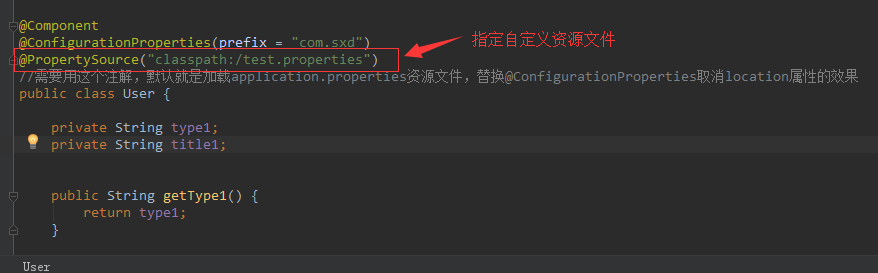

package com.sxd.beans; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "com.sxd") @PropertySource("classpath:/test.properties") //需要用这个注解,默认就是加载application.properties资源文件,替换@ConfigurationProperties取消location属性的效果 public class User { private String type1; private String title1; public String getType1() { return type1; } public void setType1(String type1) { this.type1 = type1; } public String getTitle1() { return title1; } public void setTitle1(String title1) { this.title1 = title1; } }
最后在启动类中使用一下
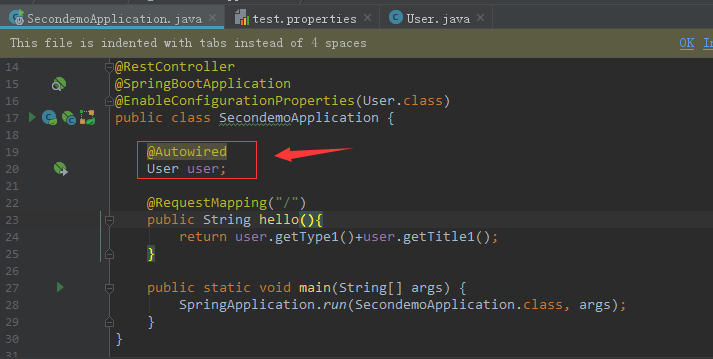

package com.sxd.secondemo; import com.sxd.beans.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigurationProperties(User.class) public class SecondemoApplication { @Autowired User user; @RequestMapping("/") public String hello(){ return user.getType1()+user.getTitle1(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SecondemoApplication.class, args); } }
运行结果:
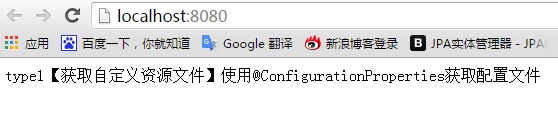
②===第二种方式:使用@Value获取配置文件
先设定一个自定义资源文件
如下,自定义资源文件需要满足application-{profile}.properties格式
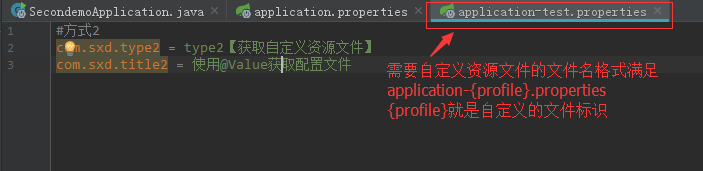
然后在application.properties文件中指明加载这个资源文件
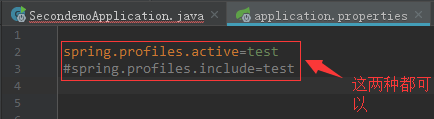
spring.profiles.active=test
#spring.profiles.include=test
这两种哪种都可以加载上自定义的资源文件,后面的test就是上面{profile}的值
最后在启动类中使用@Value获取自定义资源文件中的属性,这个时候自定义的资源文件已经在application,properties文件中被指明要被加载了,因此是可以被获取到的
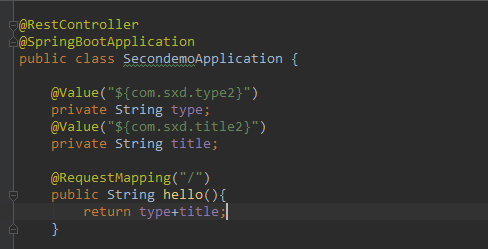

package com.sxd.secondemo; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication public class SecondemoApplication { @Value("${com.sxd.type2}") private String type; @Value("${com.sxd.title2}") private String title; @RequestMapping("/") public String hello(){ return type+title; } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SecondemoApplication.class, args); } }
运行结果:
③===第三种方式:使用Environment获取资源文件
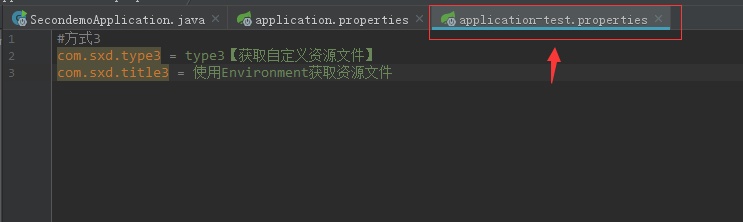
首先还是写一个自定义的资源文件,文件命名同上面第二种方式一样
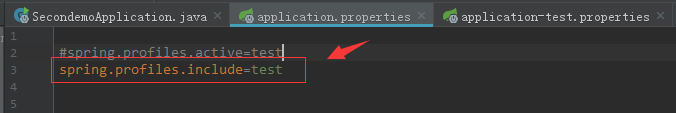
接着,在application.properties中声明加载这个自定义的资源文件
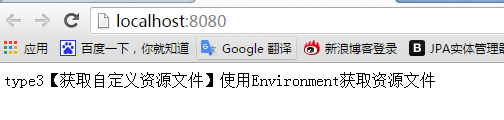
最后在启动类中,也就是哪里使用就在那里自动注入Environment.
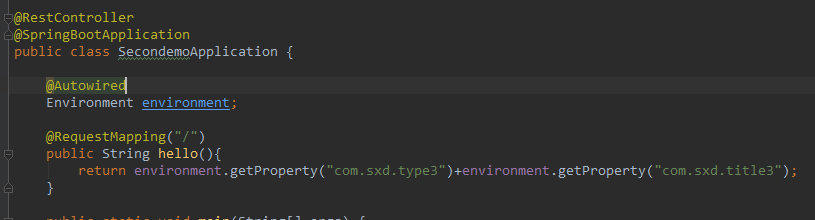

package com.sxd.secondemo; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication public class SecondemoApplication { @Autowired Environment environment; @RequestMapping("/") public String hello(){ return environment.getProperty("com.sxd.type3")+environment.getProperty("com.sxd.title3"); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SecondemoApplication.class, args); } }
运行结果:
==================================================================================================================
===================================================完成============================================================
