一、深浅拷贝
深浅拷贝的前置知识:
- 变量的三大属性:id、type、value
- 可变数据类型与不可变数据类型:
- 可变数据类型:value发生变化,id不变,具体有列表、字典、集合
- 不可变数据类型:value发生变化,id也发生变化,具体有数字(int、float)、字符串、元组
浅拷贝
以列表为例,进行展开:
list_1 = ['egon','lxx',[11,22]] list_2 = list_1.copy() list_1[0] = 'EGON' list_1[1] = 'LXX' list_1[2][0] = 111 list_1[2][1] = 222
如下图所示
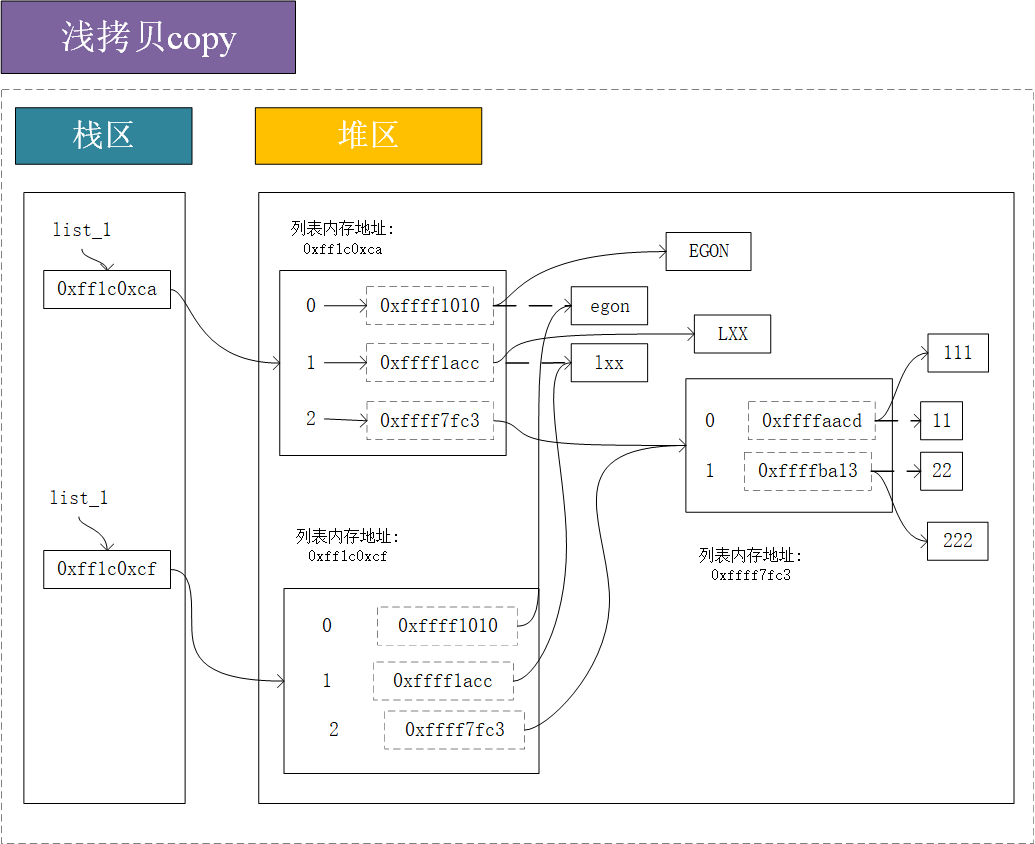
浅拷贝:是将拷贝对象的第一层元素的内存地址进行复制,开辟一个新的内存空间进行存储,对于可变类型的写操作不会造成影响;对于不可变类型(比如一些容器对象,列表、字典、集合)进行写操作,元素的内存地址不会发生改变(改变的仅仅是子元素的地址)
深拷贝
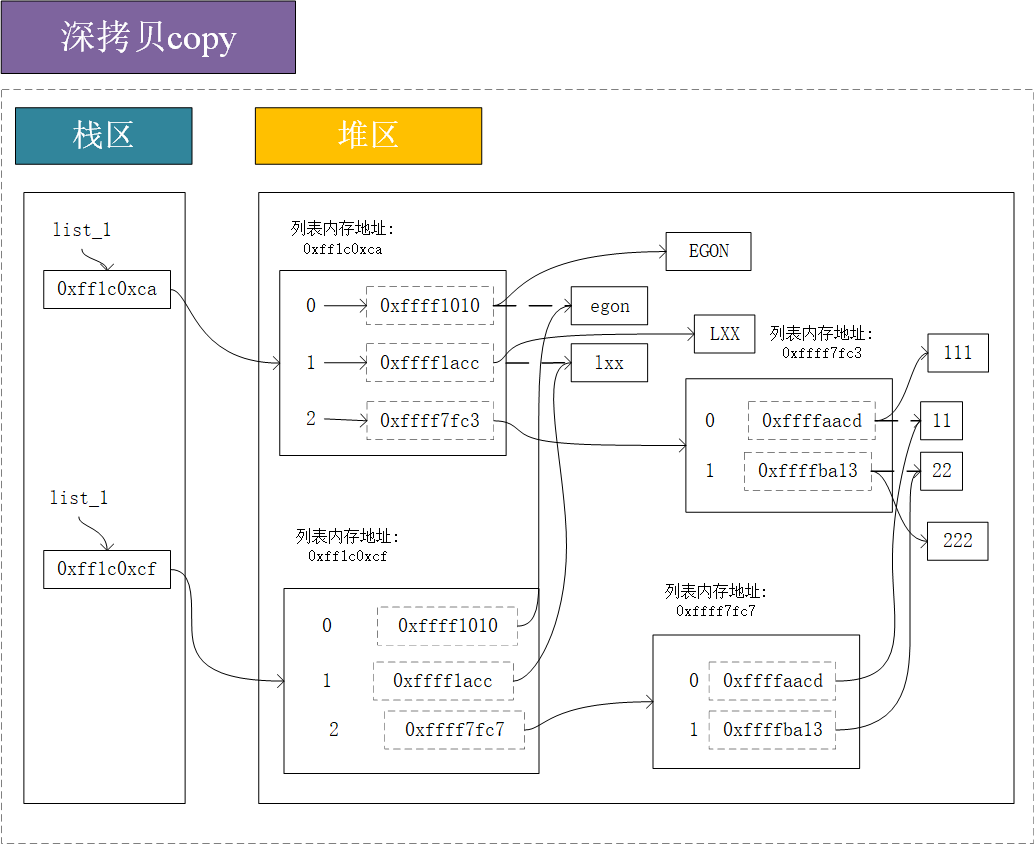
深拷贝:就是将拷贝对象的第一层可变类型元素的内存地址进行复制,不可变类型元素重新开辟一个内存空间(将其子元素的内存地址存进去),并将两者(可变类型与不可变类型)存放进新开辟的内存空间里。对原对象进行写操作,不会对新对象产生影响,即两者是独立的。
二、流程控制之while循环
- while循环语法
while 条件: 代码1 代码2 代码3 ''' while的运行步骤: 步骤1:如果条件为真,则自上而下的执行代码1、2、3... 步骤2:执行完最后一条代码时再次判断条件,如果条件为Treu则重复步骤1,如果条件为False,则结束循环 '''
- while+break的案例
# 如果while循环嵌套了很多层,要想退出每一层循环则需要在每一层循环都有一个break username = "jason" password = "123" count = 0 while count < 3: # 第一层循环 inp_name = input("请输入用户名:") inp_pwd = input("请输入密码:") if inp_name == username and inp_pwd == password: print("登陆成功") while True: # 第二层循环 cmd = input('>>: ') if cmd == 'quit': break # 用于结束本层循环,即第二层循环 print('run <%s>' % cmd) break # 用于结束本层循环,即第一层循环 else: print("输入的用户名或密码错误!") count += 1
- 使用tag退出多层循环
''' 让所有while循环的条件都用同一个变量,该变量的初始值为True, 一旦在某一层将该变量的值改成False,则所有层的循环都结束 ''' username = "jason" password = "123" count = 0 tag = True while tag: inp_name = input("请输入用户名:") inp_pwd = input("请输入密码:") if inp_name == username and inp_pwd == password: print("登陆成功") while tag: cmd = input('>>: ') if cmd == 'quit': tag = False # tag变为False, 所有while循环的条件都变为False break print('run <%s>' % cmd) break # 用于结束本层循环,即第一层循环 else: print("输入的用户名或密码错误!") count += 1
- while+continue的使用
# 打印1到10之间,除7以外的所有数字 number=11 while number>1: number -= 1 if number==7: continue print(number)
- while+else的使用
# 无break count = 0 while count <= 5 : count += 1 print("Loop",count) else: print("循环正常执行完啦") print("-----out of while loop ------") 输出 Loop 1 Loop 2 Loop 3 Loop 4 Loop 5 Loop 6 循环正常执行完啦 #没有被break打断,所以执行了该行代码 -----out of while loop ------ # 有break count = 0 while count <= 5 : count += 1 if count == 3: break print("Loop",count) else: print("循环正常执行完啦") print("-----out of while loop ------") 输出 Loop 1 Loop 2 -----out of while loop ------ #由于循环被break打断了,所以不执行else后的输出语句
三、流程控制之for循环
- for循环语法
for 变量名 in 可迭代对象(字符串、列表、字典): 代码1 代码2 ... #例1 for item in ['a','b','c']: print(item) # 运行结果 a b c # 参照例1来介绍for循环的运行步骤 # 步骤1:从列表['a','b','c']中读出第一个值赋值给item(item=‘a’),然后执行循环体代码 # 步骤2:从列表['a','b','c']中读出第二个值赋值给item(item=‘b’),然后执行循环体代码 # 步骤3: 重复以上过程直到列表中的值读尽
- for+continue(同while)
- for+break(同while)
- for+else(同while)
for循环的经典练习:
- 打印金字塔
 View Code
View Code#!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- import sys import argparse class Pyramid: def __init__(self,row,direction): self.row = row self.direction = direction def run(self): str_base = '*' str_none = ' ' if self.direction == 'p': for i in range(self.row): str_obj = (self.row-i-1)*str_none + (2*i+1)*str_base + (self.row-i-1)*str_none print(str_obj,end = ' ') elif self.direction == 'n': for i in range(self.row): str_obj = i*str_none + (2*self.row-2*i-1)*str_base + i*str_none print(str_obj,end = ' ') if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser( description = 'Print the pyramid') parser.add_argument('--row', action = 'store', dest = 'row', type = int, required = True, help = 'The row number to print pyramid') parser.add_argument('--dire', action = 'store', dest = 'dire', choices = ['n','p'], help = 'Choose positive(p) or negative(n)') parser.add_argument('--version', action = 'version', version = '%(prog)s 1.0') args = parser.parse_args() if args.dire: P = Pyramid(args.row,args.dire) P.run() else: print("please use '%s -h or %s --help' to obtain the help information" % (sys.argv[0],sys.argv[0]))
