一. javascript
JavaScript基础分为三个部分:
-
ECMAScript:JavaScript的语法标准。包括变量、表达式、运算符、函数、if语句、for语句等。
-
DOM:操作网页上的元素的API。比如让盒子移动、变色、轮播图等。
-
BOM:操作浏览器部分功能的API。比如让浏览器自动滚动。
PS:JS机械重复性的劳动几乎为0,基本都是创造性的劳动。而不像HTML、CSS中margin、padding都是机械重复劳动。
console 相当于解释器
//两条斜杠是单行注释 /**/多行注释 ctrl+shift+/多行注释 ctrl+/单行注释
声明变量使用 var 关键字
变量可以用$
测试语句:
1. console.log() 会在浏览器控制台打印出信息
2. console.alert() 弹出提示框
3. console.dir() 可以显示一个对象的所有属性和方法

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script type="text/javascript"> //console相当于解释器 //两条斜杠是单行注释 /**/多行注释 ctrl+shift+/多行注释 ctrl+/单行注释 // 声明变量使用 var 关键字 var $ = '2'; // $ = 字符串2 var a = 2; // a是数字2 //检索 console.log(a); console.log($); console.log(a==$); // 解释器自动将字符串的数字与2比对,true, ==比较的是值,不是内存地址 var str = '哈哈'; //全局对象 window.str = '哈哈' </script> <!--外接式--> <script src="js/index.js"></script> </head> <body> <!--一般js操作不写在行内--> <!--行内的js alert() console.log()是测试语句--> <button onclick='alert("点我了")'>点击</button> <button onclick="console.log('点我了')"> 点击</button> </body> </html>
二. 基本数据类型
1. number 数字(包括整数和小数)
2. string 字符串
3. boolean 布尔值
4. null 相当于none, 空
5. undefined 未定义的
字符串的拼接

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var name = '伊拉克'; var am = '美军'; var str = '2003年3月20日,' +name+ '战争爆发,以美军为主的联合部队仅用20多天就击溃了萨达姆的军队。这是继十多年前的海湾战争后,' + am + '又一次取得的大规模压倒性军事胜利。'; console.log(str); var str2 = `2003年3月20日,${name}战争爆发,以美军为主的联合部队仅用20多天就击溃了萨达姆的军队。这是继十多年前的海湾战争后,${am}又一次取得的大规模压倒性军事胜利。` console.log(str2); var num = 1111; console.log(typeof num); console.log(typeof (num+'')); console.dir(name); </script> </body> </html>
数据类型的转换

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var a = 5; console.log(String(a)); // 转换成字符串类型 console.log(a.toString()); // 转换成字符串类型 var numStr = '63.32426444'; // console.log(Number(numStr)); // console.log(parseFloat(numStr)); var b = 7 / 0; // 结果是无穷大 Infinity console.log(b); console.log(typeof b); var b1 = '123'; var b2 = 0; var b3 = -123; var b4 = Infinity; //无穷大 var b5 = NaN; var b6; //false var b7 = null; //false console.log(Boolean(b1)); </script> </body> </html>
三. 引用数据类型
Function 函数
Object 对象
Array 数组,列表
String 字符串
Date 日期

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var a = '2', b=4, c = true; console.log(a); // 打印a console.log(typeof a); //判断a的类型 console.log(typeof b); console.log(typeof c); var str = '23哈5喽'; console.log(parseInt(str)); //解析出字符串中的整数 var str1 = '你好啊'; console.log(typeof parseInt(str)); //判断从字符串解析出的整数的类型 number console.log(parseInt(str1)); // NaN Not a Number 不是一个数字 console.log(isNaN(2)); // false 判断是否不是一个数字 console.log(parseFloat('5.8哈哈哈')); // 解析出小数,这里整数也能出来 </script> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var person = null; console.log(person); console.log(typeof person); var a; console.log(a); console.log(typeof a); </script> </body> </html>
四. 运算符
1. 赋值运算符
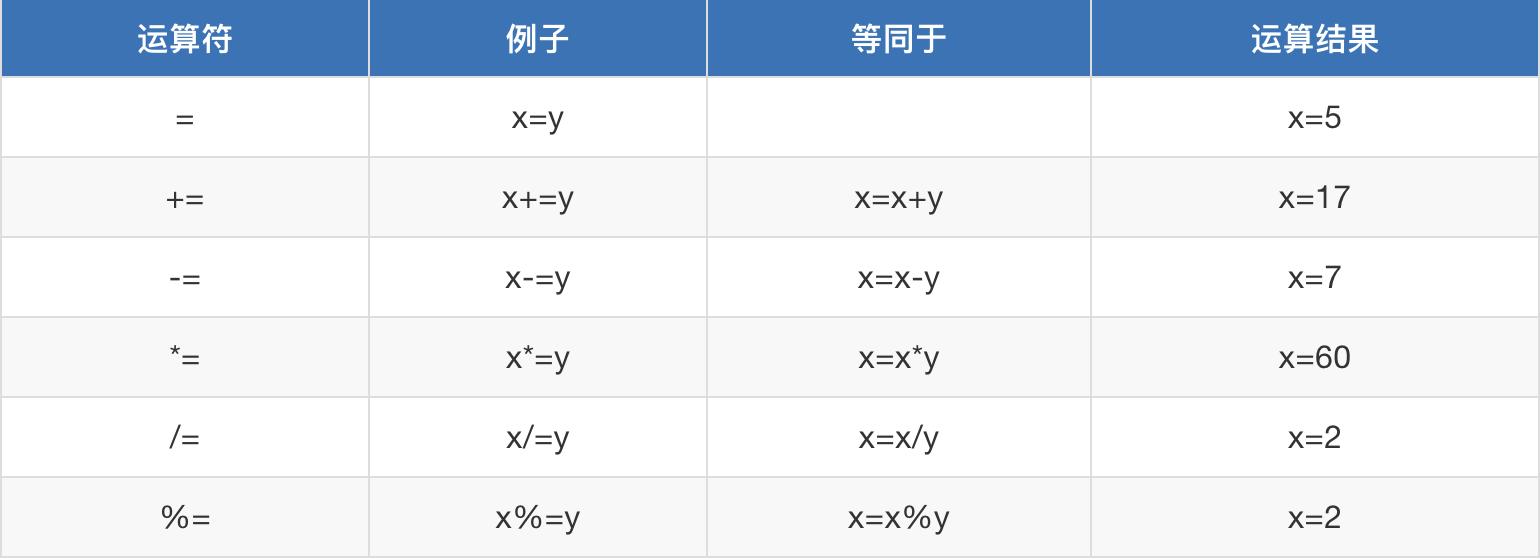
2. 算数运算符
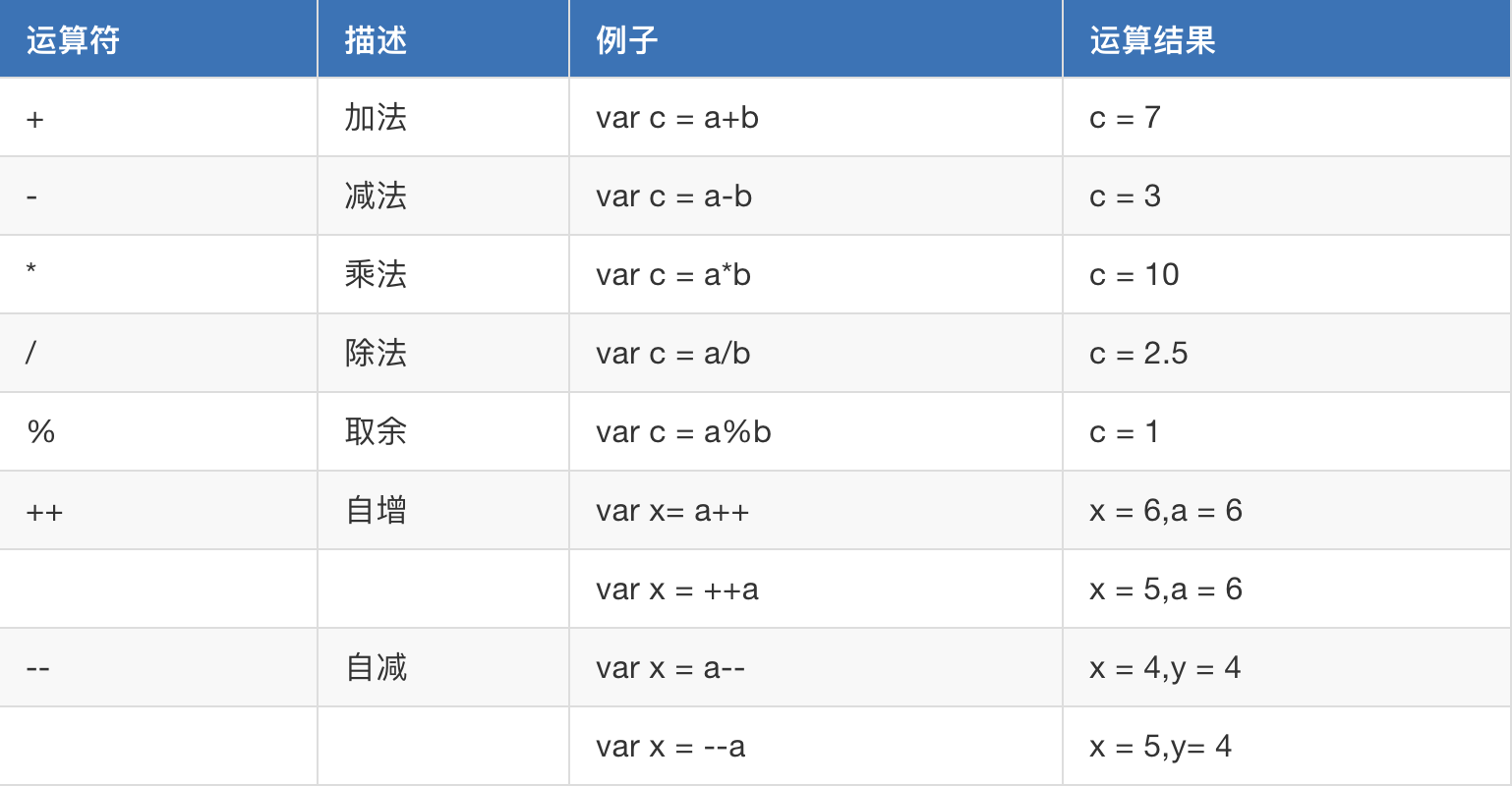
3. 比较运算符
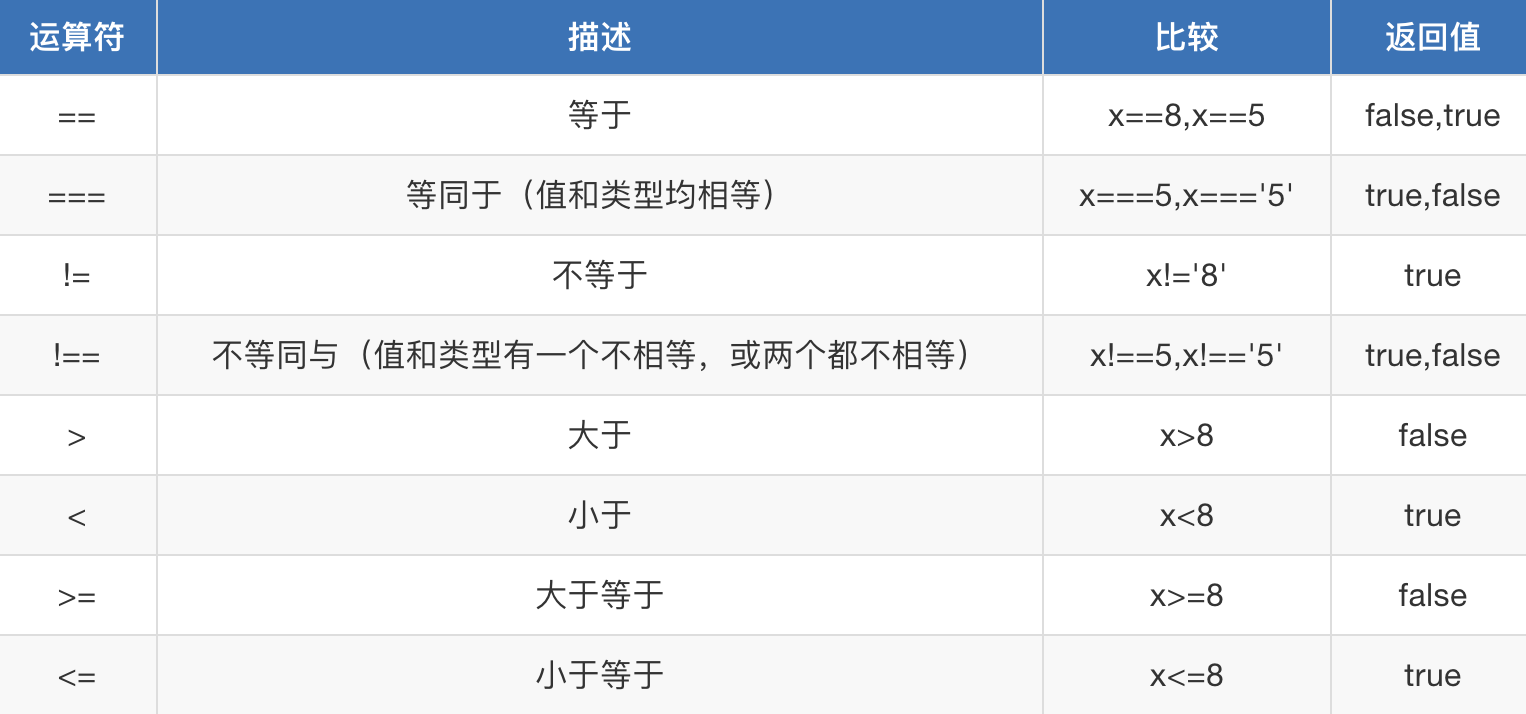

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var a = 5; a++; var b = ++a; console.log(a); console.log(b); var x = 6; var y = '6'; // 比较的是值 console.log(x==y); // 相当于python中is, 比较内存地址 console.log(x===y); </script> </body> </html>
五. if else 流程控制

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var age = 1; if(age > 18){ alert('可以进'); }else if(age > 16){ alert('禁止入内'); }else{ alert('小孩回家玩去!'); } </script> </body> </html>
六. switch

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var weather = '下雪'; switch (weather){ case '晴天': console.log('今天天气很好'); break; //如果不写break, 符合条件的话会打印到下一个break结束 case '雨天': console.log('天气不太好啊'); break; case '下雪': console.log('天气严寒,多添衣物哦~'); break; default: console.log('未知天气') } </script> </body> </html>
七. while循环

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var i = 1; while (i <=10){ console.log(i); i++; } //不管有没有满足while中的条件do里面的代码都会走一次 // var a = 3; // do{ // console.log(a); // a++; // }while (a<10) var j = 5; do{ console.log(j); j++ }while (j < 11) </script> </body> </html>
八. for循环

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> // for (var i = 0;i< 10; i++){ // console.log(i) // } // var arr = ['张三', '李四']; // for(var i=0; i< arr.length; i++){ // console.log(arr[i]) // } // arr.forEach(function (item, index){ // console.log(item,index) // }) // for (var i=0; i<12; i++){ // console.log(i) // } var arr=['张三', '李四']; // for (i=0; i<arr.length; i++){ // console.log(arr[i]) // } // arr.forEach(function (item,index) { // console.log(item,index); // }) arr.forEach(function (item, index) { console.log(item,index) }) </script> </body> </html>
for循环的嵌套

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> // document.write('<h1>呵呵哒</h1>'); // document.write('*****') for(var i=0; i<6; i++){ for (var j = 0; j<16; j++){ document.write('*') } document.write('<br>') } </script> </body> </html>
九. 常用内置对象
1. Array

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var colors = ['red', 'green', 'yellow']; console.log(colors); var colors2 = new Array('a', 'b'); // new 一个数组对象 var colors3 = new Array(); colors3[0] = 'alex'; // 和列表一样用 console.log(colors2); console.log(colors3); var newArr = colors2.concat(colors3); </script> </body> </html>
2. date

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var date = new Date(); console.log(date); // 打印日期 Thu Nov 08 2018 16:57:37 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间) console.log(date.getDate()); // 一个月的第几天 console.log(date.getMonth()+1); // 月份 console.log(date.getDay()); // 一周中的第几天 周日用0表示 // 本地时间 console.log(date.toLocaleString()); // 本地时间 2018/11/8 下午4:57:37 </script> </body> </html>
3. Math对象

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> var a = 3.003; console.log(Math.floor(a)); // 取整数位置 3 console.log(Math.ceil(a)); // 取整数进一位 4 console.log(Math.random()); // 0-1随机数 console.log(Math.random()*100); // 自定义随机数 </script> </body> </html>
4. 函数

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> function add(x,y){ return console.log(x+y) } add(1,2) </script> </body> </html>
5. 伪数组

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> function fn(){ console.log(arguments); // 参数 var arr = []; for(var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++){ console.log(arguments[i]); arr.push(arguments[i]); } console.log(arr); } fn('alex', 'wusir') </script> </body> </html>
6. 匿名函数

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> function add2(){ alert(2) } var add = function(){ alert('匿名函数') } add() add2() </script> </body> </html>
7. DOM操作

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /*DOM Document Object Model 文档对象模型*/ #box{ width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <button id="btn">隐藏</button> <div id="box"></div> <script> // 1. 找开关 var oDiv = document.getElementById('box'); var oBtn = document.getElementById('btn'); var isRed = true; var isShow = true; // 2. 点一下 动作 oDiv.onclick = function () { if (isRed){ // 3. 灯亮了 oDiv.style.backgroundColor = 'blue'; isRed = false; }else{ oDiv.style.backgroundColor = 'red'; isRed = true; } alert(1) }; function hidden() { if (isShow){ oDiv.style.display = 'none'; isShow = false; oBtn.innerText = '显示'; } else{ oDiv.style.display = 'block'; isShow = true; oBtn.innerText = '隐藏'; } } oBtn.onclick = hidden </script> </body> </html>
