字符串(String)的不可变性
String类在java.lang包下面,是Object类的直接子类,通过API或者源码可以看到,String类是final修饰的,这说明String类不能被继承。
字符串一旦创建好之后,里面的内容是不能被修改的,jvm会将双引号””中的内容存放在字符串常量池里面,常量池中的对象内容是不可修改的。
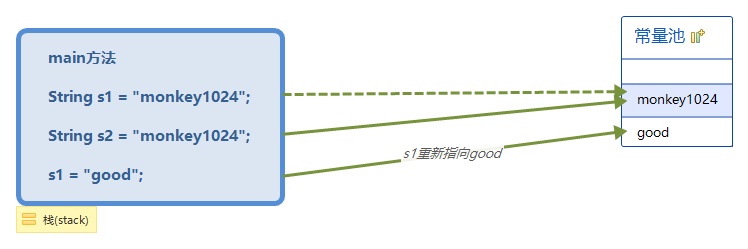
String s1 = "monkey1024";
String s2 = "monkey1024";
s1 = "good";
上面代码中,创建s1时,jvm会在常量池中创建一个monkey1024字符串对象,创建s2时,jvm会去常量池中搜索,此时常量池中有monkey024,所以就不创建了,直接让s2指向之前创建的monkey1024。当执行到最后一行时,jvm会在常量池中创建一个good,然后让s1指向这个good,而不是将常量池中的monkey1024修改为good,所以说常量池中的对象内容是不可修改的。
字符串为什么被设计成不可变的?
还是上面的代码
String s1 = "monkey1024";
String s2 = "monkey1024";
s1 = "good";
String是引用数据类型,s1和s2指向的是同一块内存区域。如果String类型是可变的,那上面代码的第三行的s1的修改就会导致s2变化,但这可能并不是程序员的本意。
String的两种创建方式及区别
可以使用下面两种方式创建String类型的对象:
String s3 = "hello";
String s4 = new String("monkey");
这两种方式的区别:
s3:系统会在常量池里面创建一个hello的字符串对象。
s4:系统会在常量池里面创建一个monkey字符串对象,然后在堆内存里面再创建一个monkey字符串对象。
请看下面程序的打印结果:
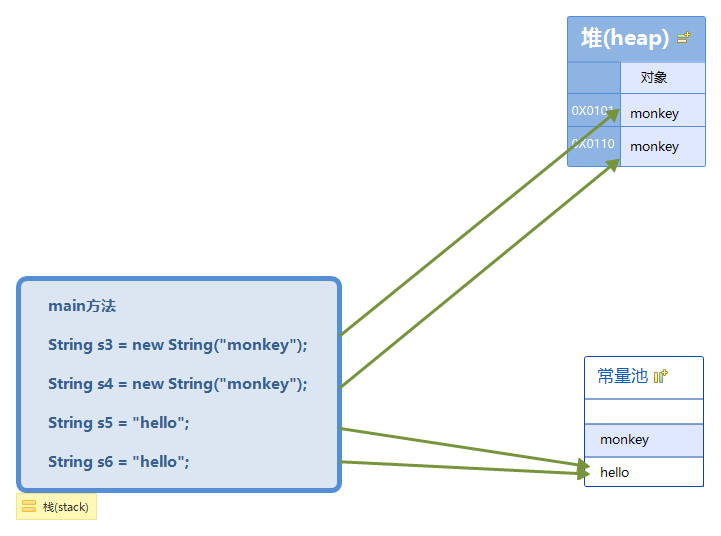
String s3 = new String("monkey");
String s4 = new String("monkey");
String s5 = "hello";
String s6 = "hello";
System.out.println(s3 == s4);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));
System.out.println(s5== s6);
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));
打印机的结果是
false
true
true
true
s3和s4分别使用了new关键词来创建String类型的对象,系统会在堆内存中分配两块不同的空间地址来分别存放monkey,s3和s4分别指向这两块不同的地址,所以s3s4的结果是false。
String类中已经重写了equals方法,所以s3.equals(s4)的结果是true
因为s5和s6指向的是同一块常量池中hello所在的内存地址,所以s5s6的结果是true。
String类中已经重写了equals方法,所以s5.equals(s6)的结果也是true
开发中建议使用String s = “monkey1024”;这种方式创建字符串对象,可以减少堆内存的使用。
注意:比较两个字符串是否一致最好使用equals方法
String中的intern方法
在String类中有一个intern方法,当这个方法被调用的时候,如果在字符串常量池中存在与当前String相同的字符串时(equals),就会将该字符串返回,如果不存在时,就会将该字符串字面量放到字符串常量池中并返回该字符串的引用。
//下面代码可能在不同的jdk版本中执行的结果不一样
String s1 = new String("hello");
//false,一个指向堆内存中,一个指向字符串常量池
System.out.println(s1.intern() == s1);
//true,都指向字符串常量池
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s2.intern() == s2);
练习
下面代码创建了几个对象?
String s1 = new String("www.monkey1024.com");
String s2 = new String("www.monkey1024.com");
答案
一共创建了三个对象,常量池中一个,堆内存上面有两个
使用String时需要注意的问题
在工作中尽量不要做字符串频繁的拼接操作。因为字符串一旦创建不可改变,如果频繁拼接,就会在字符串常量池中创建大量的字符串对象,给垃圾回收带来问题。
如果需要做字符串频繁的拼接操作,最好使用StringBuffer或者StringBuilder,这两个类在后面会讲到。
String s1 = "";
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
s1 += i;//避免频繁的字符串拼接操作
}
System.out.println(s1);
String s2 = "a";
String s3 = "b";
String s4 = s2 + s3;
String s5 = "ab";
System.out.println(s5 == s4);
上面程序最后打印的结果是false,因为在做字符串拼接时会在堆内存中创建新的对象。
String类常用方法
char charAt(int index);获取index位置的字符
boolean contains(CharSequence s);判断字符串中是否包含某个字符串
boolean endsWith(String endStr);判断是否是以某个字符串结尾
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString);忽略大小写比较两个字符串是否相等
byte[] getBytes();转换成byte数组
int indexOf(String str);取得指定字符在字符串的位置
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex);从指定的下标开始取得指定字符在字符串的位置
int lastIndexOf(String str);从后面开始取得指定字符在字符串最后出现的的位置
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex);从后面开始指定的下标开始取得指定字符在字符串的位置
int length();获取字符串的长度
String replaceAll(String s1,String s2);替换字符串中的内容
String[] split(String s);根据指定的表达式拆分字符串
boolean startsWith(String s);判断是否是以某个字符串开始
String substring(int begin);根据传入的索引位置截子串
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex);根据传入的起始和结束位置截子串
char[] toCharArray();将字符串转换为char数组
void toUpperCase();转换为大写
void toLowerCase();转换为小写
String trim();去除首尾空格
String valueOf(Object obj);将其他类型转换为字符串类型
package com.monkey1024.string;
public class StringTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "monkey1024";
// char charAt(int index);获取index位置的字符
System.out.println(s1.charAt(5));
// boolean contains(CharSequence s);判断字符串中是否包含某个字符串
System.out.println(s1.contains("key"));
// boolean endsWith(String endStr);判断是否是以某个字符串结尾
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("1028"));
// boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString);忽略大小写比较两个字符串是否相等
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase("Monkey1024"));
// byte[] getBytes();转换成byte数组
String s2 = "abc";
byte[] b1 = s2.getBytes();
for(int i=0; i<b1.length; i++){
System.out.print(b1[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// int indexOf(String str);取得指定字符在字符串的位置
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("y"));
// int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex);从指定的下标开始取得指定字符在字符串的位置
String s3 = "monkey1024monkeyy";
System.out.println(s3.indexOf("y", 6));
// int lastIndexOf(String str);从后面开始取得指定字符在字符串最后出现的的位置
System.out.println(s3.lastIndexOf("y"));
// int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex);从后面开始指定的下标开始取得指定字符在字符串的位置
System.out.println(s3.lastIndexOf("y", 14));
// int length();获取字符串的长度
System.out.println(s3.length());
// String replaceAll(String s1,String s2);替换字符串中的内容
String s4 = "monkeymonkey1024monkey";
System.out.println(s4.replaceAll("key", "YYY"));
// String[] split(String s);根据指定的表达式拆分字符串
String s5 = "a,b,c,d";
String[] array1 = s5.split(",");
for(int i=0; i<array1.length; i++){
System.out.print(array1[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// boolean startsWith(String s);判断是否是以某个字符串开始
System.out.println(s3.startsWith("m1"));
// String substring(int begin);根据传入的索引位置截子串
System.out.println(s3.substring(5));
// String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex);根据传入的起始和结束位置截子串
System.out.println(s3.substring(6, 10));
// char[] toCharArray();将字符串转换为char数组
char[] array2 = s5.toCharArray();
for(int i=0; i<array2.length; i++){
System.out.print(array2[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// void toUpperCase();转换为大写
System.out.println(s5.toUpperCase());
// void toLowerCase();转换为小写
System.out.println(s5.toLowerCase());
// String trim();去除首尾空格
String s6 = " java good ok ";
System.out.println(s6.trim());
// String valueOf(Object obj);将其他类型转换为字符串类型
Object o = new Object();
o = null;
System.out.println(String.valueOf(o));//建议使用这种方法转换字符串
//System.out.println(o.toString());//报出空指针错误
}
}