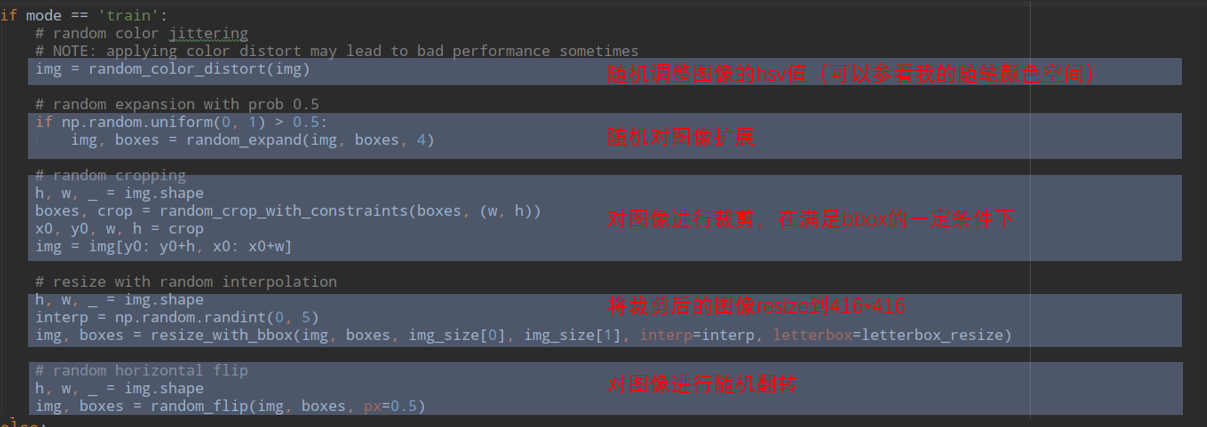
先说一下,做data augmentation的目的是为了减少噪声对模型的影响,希望模型真正学习到目标的特征,由于yolov3的该模块特别典型,故以此说明,就是包括以下部分:
在这之前先进行了图像融合,就是随机对图像融合,:
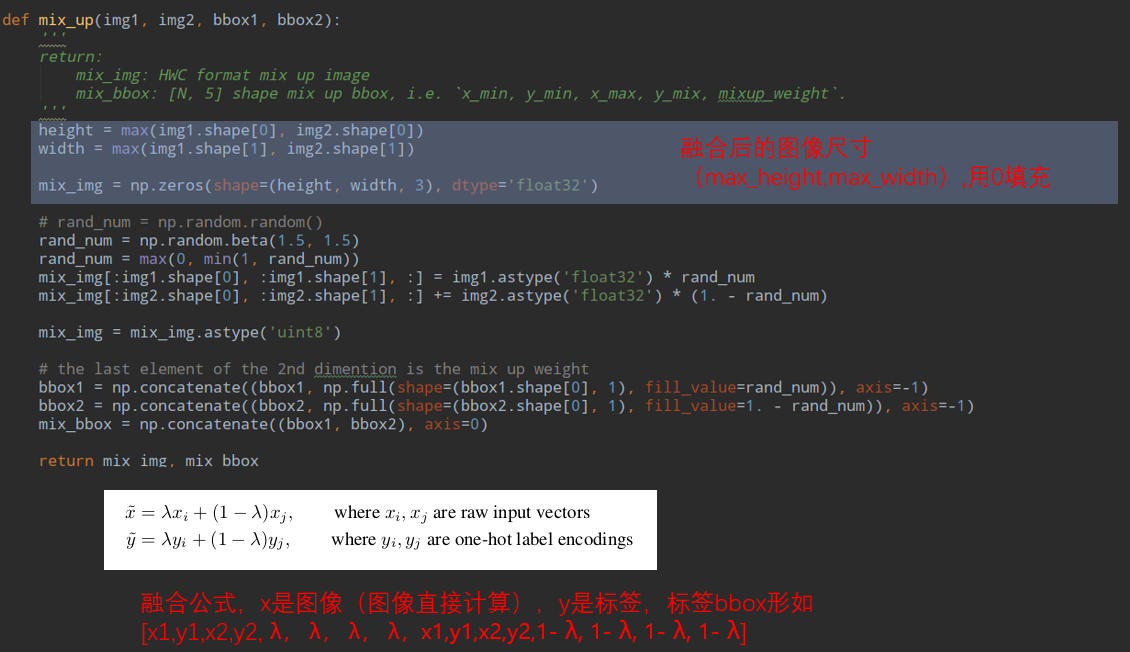
我们只看图像操作部分先确定融合后的图像为两个图像最大的w和h,然后以比例λ进行计算:

除了v3采用的这种mixup,还有两种是别的论文中的:
cutmix和Mosaic
论文名称:CutMix: Regularization Strategy to Train Strong Classifiers with Localizable Features
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.04899
开源地址:https://github.com/clovaai/CutMix-PyTorch
简单来说cutmix相当于cutout+mixup的结合,可以应用于各种任务中:

而Mosaic增强是本文提出的,属于cutmix的扩展,cutmix是两张图混合,而马赛克增强是4张图混合,好处非常明显是一张图相当于4张图,等价于batch增加了,可以显著减少训练需要的batch size大小。

然后是调整图像的hsv值,关于图像的颜色空间参照博客:

接下来随机比例扩展图像,多余的部分用固定颜色填充:

然后对图像进行随机裁剪(可能会丢掉一些box,留下那些满足iou界限的box):

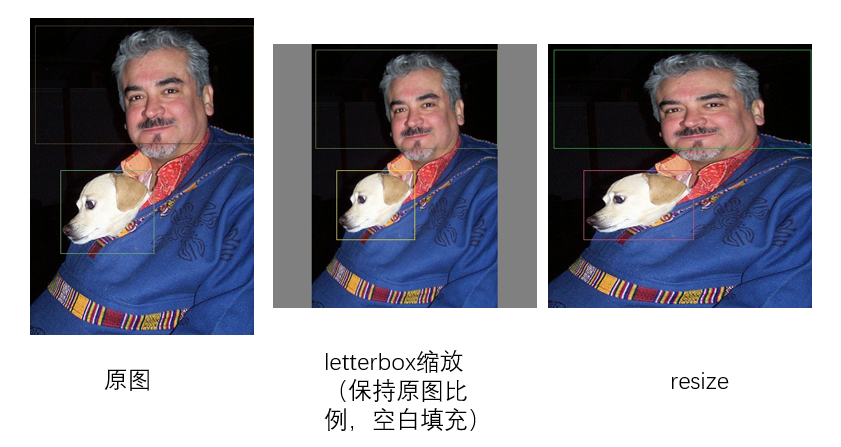
然后就可以把图像resize到固定的尺寸(416*416),有两种方式可以选择:

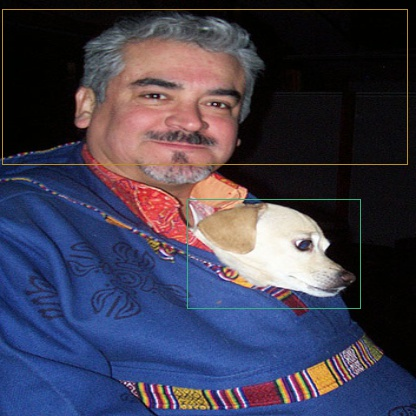
最后还能随机进行翻转操作,比如变成这样:

以上就是yolov3所有的data augmentation过程,代码在下面。
1 import numpy as np 2 import cv2 3 import random 4 5 def mix_up(img1, img2): 6 ''' 7 return: 8 mix_img: HWC format mix up image 9 mix_bbox: [N, 5] shape mix up bbox, i.e. `x_min, y_min, x_max, y_mix, mixup_weight`. 10 ''' 11 height = max(img1.shape[0], img2.shape[0]) 12 width = max(img1.shape[1], img2.shape[1]) 13 14 mix_img = np.zeros(shape=(height, width, 3), dtype='float32') 15 16 # rand_num = np.random.random() 17 rand_num = np.random.beta(1.5, 1.5) 18 rand_num = max(0, min(1, rand_num)) 19 rand_num = 1 20 mix_img[:img1.shape[0], :img1.shape[1], :] = img1.astype('float32') * rand_num 21 mix_img[:img2.shape[0], :img2.shape[1], :] += img2.astype('float32') * (1. - rand_num) 22 23 mix_img = mix_img.astype('uint8') 24 25 return mix_img 26 27 def random_color_distort(img, brightness_delta=32, hue_vari=18, sat_vari=0.5, val_vari=0.5): 28 ''' 29 randomly distort image color. Adjust brightness, hue, saturation, value. 30 param: 31 img: a BGR uint8 format OpenCV image. HWC format. 32 ''' 33 34 def random_hue(img_hsv, hue_vari, p=0.5): 35 if np.random.uniform(0, 1) > p: 36 hue_delta = np.random.randint(-hue_vari, hue_vari) 37 img_hsv[:, :, 0] = (img_hsv[:, :, 0] + hue_delta) % 180 38 return img_hsv 39 40 def random_saturation(img_hsv, sat_vari, p=0.5): 41 if np.random.uniform(0, 1) > p: 42 sat_mult = 1 + np.random.uniform(-sat_vari, sat_vari) 43 img_hsv[:, :, 1] *= sat_mult 44 return img_hsv 45 46 def random_value(img_hsv, val_vari, p=0.5): 47 if np.random.uniform(0, 1) > p: 48 val_mult = 1 + np.random.uniform(-val_vari, val_vari) 49 img_hsv[:, :, 2] *= val_mult 50 return img_hsv 51 52 def random_brightness(img, brightness_delta, p=0.5): 53 if np.random.uniform(0, 1) > p: 54 img = img.astype(np.float32) 55 brightness_delta = int(np.random.uniform(-brightness_delta, brightness_delta)) 56 img = img + brightness_delta 57 return np.clip(img, 0, 255) 58 59 # brightness 60 img = random_brightness(img, brightness_delta) 61 img = img.astype(np.uint8) 62 63 # color jitter 64 img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV).astype(np.float32) 65 66 if np.random.randint(0, 2): 67 img_hsv = random_value(img_hsv, val_vari) 68 img_hsv = random_saturation(img_hsv, sat_vari) 69 img_hsv = random_hue(img_hsv, hue_vari) 70 else: 71 img_hsv = random_saturation(img_hsv, sat_vari) 72 img_hsv = random_hue(img_hsv, hue_vari) 73 img_hsv = random_value(img_hsv, val_vari) 74 75 img_hsv = np.clip(img_hsv, 0, 255) 76 img = cv2.cvtColor(img_hsv.astype(np.uint8), cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR) 77 78 return img 79 80 def random_expand(img, bbox, max_ratio=4, fill=255, keep_ratio=True): 81 ''' 82 Random expand original image with borders, this is identical to placing 83 the original image on a larger canvas. 84 param: 85 max_ratio : 86 Maximum ratio of the output image on both direction(vertical and horizontal) 87 fill : 88 The value(s) for padded borders. 89 keep_ratio : bool 90 If `True`, will keep output image the same aspect ratio as input. 91 ''' 92 h, w, c = img.shape 93 ratio_x = random.uniform(1, max_ratio) 94 if keep_ratio: 95 ratio_y = ratio_x 96 else: 97 ratio_y = random.uniform(1, max_ratio) 98 99 oh, ow = int(h * ratio_y), int(w * ratio_x) 100 off_y = random.randint(0, oh - h) 101 off_x = random.randint(0, ow - w) 102 103 dst = np.full(shape=(oh, ow, c), fill_value=fill, dtype=img.dtype) 104 105 dst[off_y:off_y + h, off_x:off_x + w, :] = img 106 107 # correct bbox 108 bbox[:, :2] += (off_x, off_y) 109 bbox[:, 2:4] += (off_x, off_y) 110 111 return dst, bbox 112 113 def plot_one_box(img, coord, label=None, color=None, line_thickness=None): 114 ''' 115 coord: [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max] format coordinates. 116 img: img to plot on. 117 label: str. The label name. 118 color: int. color index. 119 line_thickness: int. rectangle line thickness. 120 ''' 121 tl = line_thickness or int(round(0.002 * max(img.shape[0:2]))) # line thickness 122 color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] 123 c1, c2 = (int(coord[0]), int(coord[1])), (int(coord[2]), int(coord[3])) 124 cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl) 125 if label: 126 tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness 127 t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=float(tl) / 3, thickness=tf)[0] 128 c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3 129 cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1) # filled 130 cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, float(tl) / 3, [0, 0, 0], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA) 131 132 def bbox_crop(bbox, crop_box=None, allow_outside_center=True): 133 """Crop bounding boxes according to slice area. 134 This method is mainly used with image cropping to ensure bonding boxes fit 135 within the cropped image. 136 Parameters 137 ---------- 138 bbox : numpy.ndarray 139 Numpy.ndarray with shape (N, 4+) where N is the number of bounding boxes. 140 The second axis represents attributes of the bounding box. 141 Specifically, these are :math:`(x_{min}, y_{min}, x_{max}, y_{max})`, 142 we allow additional attributes other than coordinates, which stay intact 143 during bounding box transformations. 144 crop_box : tuple 145 Tuple of length 4. :math:`(x_{min}, y_{min}, width, height)` 146 allow_outside_center : bool 147 If `False`, remove bounding boxes which have centers outside cropping area. 148 Returns 149 ------- 150 numpy.ndarray 151 Cropped bounding boxes with shape (M, 4+) where M <= N. 152 """ 153 bbox = bbox.copy() 154 if crop_box is None: 155 return bbox 156 if not len(crop_box) == 4: 157 raise ValueError( 158 "Invalid crop_box parameter, requires length 4, given {}".format(str(crop_box))) 159 if sum([int(c is None) for c in crop_box]) == 4: 160 return bbox 161 162 l, t, w, h = crop_box 163 164 left = l if l else 0 165 top = t if t else 0 166 right = left + (w if w else np.inf) 167 bottom = top + (h if h else np.inf) 168 crop_bbox = np.array((left, top, right, bottom)) 169 170 if allow_outside_center: 171 mask = np.ones(bbox.shape[0], dtype=bool) 172 else: 173 centers = (bbox[:, :2] + bbox[:, 2:4]) / 2 174 mask = np.logical_and(crop_bbox[:2] <= centers, centers < crop_bbox[2:]).all(axis=1) 175 176 # transform borders 177 bbox[:, :2] = np.maximum(bbox[:, :2], crop_bbox[:2]) 178 bbox[:, 2:4] = np.minimum(bbox[:, 2:4], crop_bbox[2:4]) 179 bbox[:, :2] -= crop_bbox[:2] 180 bbox[:, 2:4] -= crop_bbox[:2] 181 182 mask = np.logical_and(mask, (bbox[:, :2] < bbox[:, 2:4]).all(axis=1)) 183 bbox = bbox[mask] 184 return bbox 185 186 def bbox_iou(bbox_a, bbox_b, offset=0): 187 """Calculate Intersection-Over-Union(IOU) of two bounding boxes. 188 Parameters 189 ---------- 190 bbox_a : numpy.ndarray 191 An ndarray with shape :math:`(N, 4)`. 192 bbox_b : numpy.ndarray 193 An ndarray with shape :math:`(M, 4)`. 194 offset : float or int, default is 0 195 The ``offset`` is used to control the whether the width(or height) is computed as 196 (right - left + ``offset``). 197 Note that the offset must be 0 for normalized bboxes, whose ranges are in ``[0, 1]``. 198 Returns 199 ------- 200 numpy.ndarray 201 An ndarray with shape :math:`(N, M)` indicates IOU between each pairs of 202 bounding boxes in `bbox_a` and `bbox_b`. 203 """ 204 if bbox_a.shape[1] < 4 or bbox_b.shape[1] < 4: 205 raise IndexError("Bounding boxes axis 1 must have at least length 4") 206 207 tl = np.maximum(bbox_a[:, None, :2], bbox_b[:, :2]) 208 br = np.minimum(bbox_a[:, None, 2:4], bbox_b[:, 2:4]) 209 210 area_i = np.prod(br - tl + offset, axis=2) * (tl < br).all(axis=2) 211 area_a = np.prod(bbox_a[:, 2:4] - bbox_a[:, :2] + offset, axis=1) 212 area_b = np.prod(bbox_b[:, 2:4] - bbox_b[:, :2] + offset, axis=1) 213 return area_i / (area_a[:, None] + area_b - area_i) 214 215 def random_crop_with_constraints(bbox, size, min_scale=0.3, max_scale=1, 216 max_aspect_ratio=2, constraints=None, 217 max_trial=50): 218 """Crop an image randomly with bounding box constraints. 219 This data augmentation is used in training of 220 Single Shot Multibox Detector [#]_. More details can be found in 221 data augmentation section of the original paper. 222 .. [#] Wei Liu, Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Christian Szegedy, 223 Scott Reed, Cheng-Yang Fu, Alexander C. Berg. 224 SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. ECCV 2016. 225 Parameters 226 ---------- 227 bbox : numpy.ndarray 228 Numpy.ndarray with shape (N, 4+) where N is the number of bounding boxes. 229 The second axis represents attributes of the bounding box. 230 Specifically, these are :math:`(x_{min}, y_{min}, x_{max}, y_{max})`, 231 we allow additional attributes other than coordinates, which stay intact 232 during bounding box transformations. 233 size : tuple 234 Tuple of length 2 of image shape as (width, height). 235 min_scale : float 236 The minimum ratio between a cropped region and the original image. 237 The default value is :obj:`0.3`. 238 max_scale : float 239 The maximum ratio between a cropped region and the original image. 240 The default value is :obj:`1`. 241 max_aspect_ratio : float 242 The maximum aspect ratio of cropped region. 243 The default value is :obj:`2`. 244 constraints : iterable of tuples 245 An iterable of constraints. 246 Each constraint should be :obj:`(min_iou, max_iou)` format. 247 If means no constraint if set :obj:`min_iou` or :obj:`max_iou` to :obj:`None`. 248 If this argument defaults to :obj:`None`, :obj:`((0.1, None), (0.3, None), 249 (0.5, None), (0.7, None), (0.9, None), (None, 1))` will be used. 250 max_trial : int 251 Maximum number of trials for each constraint before exit no matter what. 252 Returns 253 ------- 254 numpy.ndarray 255 Cropped bounding boxes with shape :obj:`(M, 4+)` where M <= N. 256 tuple 257 Tuple of length 4 as (x_offset, y_offset, new_width, new_height). 258 """ 259 # default params in paper 260 if constraints is None: 261 constraints = ( 262 (0.1, None), 263 (0.3, None), 264 (0.5, None), 265 (0.7, None), 266 (0.9, None), 267 (None, 1), 268 ) 269 270 w, h = size 271 272 candidates = [(0, 0, w, h)] 273 for min_iou, max_iou in constraints: 274 min_iou = -np.inf if min_iou is None else min_iou 275 max_iou = np.inf if max_iou is None else max_iou 276 277 for _ in range(max_trial): 278 scale = random.uniform(min_scale, max_scale) 279 aspect_ratio = random.uniform( 280 max(1 / max_aspect_ratio, scale * scale), 281 min(max_aspect_ratio, 1 / (scale * scale))) 282 crop_h = int(h * scale / np.sqrt(aspect_ratio)) 283 crop_w = int(w * scale * np.sqrt(aspect_ratio)) 284 285 crop_t = random.randrange(h - crop_h) 286 crop_l = random.randrange(w - crop_w) 287 crop_bb = np.array((crop_l, crop_t, crop_l + crop_w, crop_t + crop_h)) 288 289 if len(bbox) == 0: 290 top, bottom = crop_t, crop_t + crop_h 291 left, right = crop_l, crop_l + crop_w 292 return bbox, (left, top, right-left, bottom-top) 293 294 iou = bbox_iou(bbox, crop_bb[np.newaxis]) 295 if min_iou <= iou.min() and iou.max() <= max_iou: 296 top, bottom = crop_t, crop_t + crop_h 297 left, right = crop_l, crop_l + crop_w 298 candidates.append((left, top, right-left, bottom-top)) 299 break 300 301 # random select one 302 while candidates: 303 crop = candidates.pop(np.random.randint(0, len(candidates))) 304 new_bbox = bbox_crop(bbox, crop, allow_outside_center=False) 305 if new_bbox.size < 1: 306 continue 307 new_crop = (crop[0], crop[1], crop[2], crop[3]) 308 return new_bbox, new_crop 309 return bbox, (0, 0, w, h) 310 311 def letterbox_resize(img, new_width, new_height, interp=0): 312 ''' 313 Letterbox resize. keep the original aspect ratio in the resized image. 314 ''' 315 ori_height, ori_width = img.shape[:2] 316 317 resize_ratio = min(new_width / ori_width, new_height / ori_height) 318 319 resize_w = int(resize_ratio * ori_width) 320 resize_h = int(resize_ratio * ori_height) 321 322 img = cv2.resize(img, (resize_w, resize_h), interpolation=interp) 323 image_padded = np.full((new_height, new_width, 3), 128, np.uint8) 324 325 dw = int((new_width - resize_w) / 2) 326 dh = int((new_height - resize_h) / 2) 327 328 image_padded[dh: resize_h + dh, dw: resize_w + dw, :] = img 329 330 return image_padded, resize_ratio, dw, dh 331 332 def resize_with_bbox(img, bbox, new_width, new_height, interp=0, letterbox=False): 333 ''' 334 Resize the image and correct the bbox accordingly. 335 ''' 336 337 if letterbox: 338 image_padded, resize_ratio, dw, dh = letterbox_resize(img, new_width, new_height, interp) 339 340 # xmin, xmax 341 bbox[:, [0, 2]] = bbox[:, [0, 2]] * resize_ratio + dw 342 # ymin, ymax 343 bbox[:, [1, 3]] = bbox[:, [1, 3]] * resize_ratio + dh 344 345 return image_padded, bbox 346 else: 347 ori_height, ori_width = img.shape[:2] 348 349 img = cv2.resize(img, (new_width, new_height), interpolation=interp) 350 351 # xmin, xmax 352 bbox[:, [0, 2]] = bbox[:, [0, 2]] / ori_width * new_width 353 # ymin, ymax 354 bbox[:, [1, 3]] = bbox[:, [1, 3]] / ori_height * new_height 355 356 return img, bbox 357 358 def random_flip(img, bbox, px=0, py=0): 359 ''' 360 Randomly flip the image and correct the bbox. 361 param: 362 px: 363 the probability of horizontal flip 364 py: 365 the probability of vertical flip 366 ''' 367 height, width = img.shape[:2] 368 if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < px: 369 img = cv2.flip(img, 1) 370 xmax = width - bbox[:, 0] 371 xmin = width - bbox[:, 2] 372 bbox[:, 0] = xmin 373 bbox[:, 2] = xmax 374 375 if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < py: 376 img = cv2.flip(img, 0) 377 ymax = height - bbox[:, 1] 378 ymin = height - bbox[:, 3] 379 bbox[:, 1] = ymin 380 bbox[:, 3] = ymax 381 return img, bbox 382 383 384 if __name__ == "__main__": 385 # img1 = cv2.imread("1.png") 386 # img2 = cv2.imread("2.png") 387 # mix_img = mix_up(img1,img2) 388 # hsv_img = random_color_distort(img2) 389 img = cv2.imread("data/000001.jpg") 390 img2 = img.copy() 391 boxes = np.array([[48,240,195,371],[8,12,352,198]]) 392 # plot_one_box(img,boxes[0]) 393 # plot_one_box(img, boxes[1]) 394 # cv2.imshow("1",img) 395 # cv2.imwrite("ori.jpg",img) 396 # cv2.waitKey(0) 397 # img1, boxes1 = random_expand(img2,np.array(boxes)) 398 h, w, _ = img2.shape 399 # boxes, crop = random_crop_with_constraints(boxes, (w, h)) 400 # x0, y0, w, h = crop 401 # img2 = img2[y0: y0 + h, x0: x0 + w] 402 interp = np.random.randint(0, 5) 403 img, boxes = resize_with_bbox(img, boxes, 416, 416, interp=interp, letterbox=False) 404 img, boxes = random_flip(img, boxes, px=0.5) 405 for i in range(len(boxes)): 406 407 plot_one_box(img, boxes[i]) 408 # plot_one_box(img1, boxes[1]) 409 cv2.imshow("1", img) 410 cv2.imwrite("crop.jpg", img) 411 cv2.waitKey(0)