一:线性表的简单回顾
上一篇写了顺序存储,通过实验,可以比较清楚的看到,在头部插入需要移动n次,网上很多往往以此来判断顺序存储效率低(当然我们可以通过代码控制每次添加元素都加入链表的尾部),其实一种数据结构两种实现方法,效率高低主要取决内存模型。
二:链表名词解释
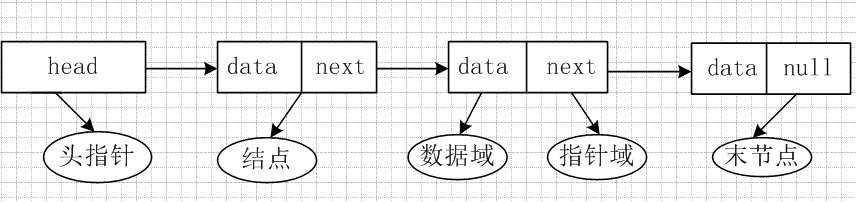
1、链表的“每个节点”都包含一个”数据域“和”指针域“;
2、”数据域“中包含当前的数据;
3、”指针域“中包含下一个节点的指针;
4、”头指针”也就是head,指向头结点数据;
5、“末节点“作为单向链表,因为是最后一个节点,通常设置指针域为null;
如下示例图
代码段如下
1 /* 2 * LNode.h 3 * 4 * Created on: Mar 18, 2013 5 * Author: sunysen 6 */ 7 8 #ifndef LNODE_H_ 9 #define LNODE_H_ 10 11 template<class T> struct LNode{ 12 public: 13 T data;//数据域 14 LNode<T> *next;//指针域 15 LNode(T value):data(value),next(0){} 16 17 }; 18 19 #endif /* LNODE_H_ */
三:链表的优缺点
链表最大的一个缺点,就是查找一个元素,必须整个链表遍历,也可以看出这种数据结构便于插入或者删除一个接点;
四:应用范围
链表用来构建许多其它数据结构,如堆栈,队列和他们的派生;
五:代码分析
1、插入节点
在头结点或者未节点插入一个新的节点比较简单、在一个有前后驱节点位置插入比较困难(1、需要找到相应的位置;2、修改前驱节点指针域值和新加入节点指针域)。如下图

代码段如下:
1 bool Insert(const int i,const T e){ 2 3 int j = 0; 4 LNode<T> *p = head.get(); 5 6 //找到要插入节点位置前节点 7 while(p != 0 && j < i -1){ 8 ++j; 9 p = p->next; 10 } 11 if(p == 0 || j > i-1){ 12 return false; 13 } 14 15 //新创建一个节点,当频繁插入和删除数据, 16 //下面这样内存操作方式是非常低效的(频繁分配内存和释放内存已经非常低效, 17 //而且会造成内存碎片),大多算情况list里边存储都小对象,这样应用场景适合 18 //在系统加载时候分配很多小内存装入内存池,需要直接从内存池拿,释放时放回内存池 19 //更多关于stl内存分配问题请参考侯捷<<STL源码剖析>> 20 LNode<T> *q = new LNode<T>(e); 21 if(q == 0){ 22 return false; 23 } 24 //更新新创建的指针域 25 q->next = p->next; 26 //前节点指针域指向新创建节点 27 p->next = q; 28 29 return true; 30 }
2、删除节点
每次想到自己能搞懂数据结构一部分知识,都在心里默默感谢发明图的人(推荐大家看看<<打开餐巾纸>>),如下图

代码段如下:
1 /** 2 *删除指定位置链表元素 3 */ 4 bool Delete(const int i) const{ 5 int j = 0; 6 LNode<T> *p = head.get(); 7 8 //找到要删除的节点 9 while(p->next != 0 && j < i -1){ 10 j++; 11 p = p->next; 12 } 13 14 if(p->next == 0 || j > i){ 15 return false; 16 } 17 18 //释放删除节点占用内存 19 std::auto_ptr<LNode<T> > new_ptr(p->next); 20 //更新删除节点前一个节点指针域 21 p->next = new_ptr->next; 22 return true; 23 }
3、清空链表代码段如下:
1 /** 2 *清空链表数据并且释放内存 3 */ 4 void Clear(){ 5 LNode<T> *p = head->next; 6 7 while(p != 0){ 8 //更多关于auto_ptr知识,请阅读memory里auto_ptr源码, 9 std::auto_ptr<LNode<T> > new_ptr(p); 10 p = new_ptr->next; 11 } 12 13 head->next = 0; 14 15 }
4、判断是否为空代码段如下:
1 /** 2 * 判断链表是否为空 3 */ 4 bool Empty() const{ 5 return head->next == 0; 6 }
5、反转链表代码段如下:
1 /** 2 *链表反转,网上看到很多人面试的时候都让写这个,写一个练练手,以防万一 3 *基本思路,就是用两个节点指针,保证一个节点指针是另个节点指针前驱节点 4 *最简单方法,用一个只有两个节点链表,反推效果 5 */ 6 void Invert(){ 7 LNode<T> *head_ptr = head.get(); 8 //p是head_ptr前驱节点,q和r指针都是中间变量 9 LNode<T> *p = head_ptr,*q = head_ptr,*r=0; 10 head_ptr = head_ptr->next; 11 12 while(head_ptr){ 13 r = head_ptr->next; 14 head_ptr->next = p; 15 p = head_ptr; 16 head_ptr = r; 17 } 18 head_ptr = p; 19 q->next = 0; 20 21 while(p != 0){ 22 std::cout<<"p is value = "<<p->data<<"\n"; 23 p = p->next; 24 } 25 }
6、计算链表长度代码段如下:
1 /** 2 * 计算链表元素的长度 3 */ 4 int Length() const{ 5 int i = 0; 6 LNode<T> *p = head.get()->next; 7 //操作是O(N),相对来说效率已经很高 8 while(p != 0){ 9 p = p->next; 10 ++i; 11 } 12 return i; 13 }
7、测试代码段如下:
1 /** 2 * 测试链表各个方法 3 */ 4 void test(){ 5 std::cout<<"-----------insert begin------------"<<std::endl; 6 for(int i = 1; i < 5; i++){ 7 Insert(1,i); 8 } 9 std::cout<<"-----------insert end------------"<<std::endl; 10 11 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length begin----------"<<std::endl; 12 std::cout<<"frist list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 13 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length end----------"<<std::endl; 14 15 std::cout<<"-----------delete begin----------"<<std::endl; 16 Delete(1); 17 std::cout<<"-----------delete end----------"<<std::endl; 18 19 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length begin----------"<<std::endl; 20 std::cout<<"second list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 21 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length end----------"<<std::endl; 22 23 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns begin----------"<<std::endl; 24 LNode<int> *p = head->next; 25 26 while(p != 0){ 27 if(p->data){ 28 std::cout<<"p is value = "<<p->data<<std::endl; 29 } 30 p = p->next; 31 } 32 33 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns end----------"<<std::endl; 34 35 std::cout<<"--------------------list begin------------------"<<std::endl; 36 Clear(); 37 std::cout<<"--------------------list end------------------"<<std::endl; 38 39 std::cout<<"----------------------------------------------------"<<std::endl; 40 41 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length begin----------"<<std::endl; 42 std::cout<<"third list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 43 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length end----------"<<std::endl; 44 45 std::cout<<"------------万恶的分割线-------------------"<<std::endl; 46 for(int i = 1; i < 5; i++){ 47 Insert(1,i); 48 } 49 std::cout<<"------------insert end--------------------------"<<std::endl; 50 51 std::cout<<"--------------calculated length begin-----------------"<<std::endl; 52 std::cout<<"fourth list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 53 std::cout<<"--------------calculated length end-----------------"<<std::endl; 54 55 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns begin----------"<<std::endl; 56 LNode<int> *p1 = head->next; 57 58 while(p1 != 0){ 59 if(p1->data){ 60 std::cout<<"p is value = "<<p1->data<<std::endl; 61 } 62 p1 = p1->next; 63 } 64 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns end----------"<<std::endl; 65 66 std::cout<<"-----------invert of the elemetns begin----------"<<std::endl; 67 Invert(); 68 std::cout<<"-----------invert of the elemetns end----------"<<std::endl; 69 }
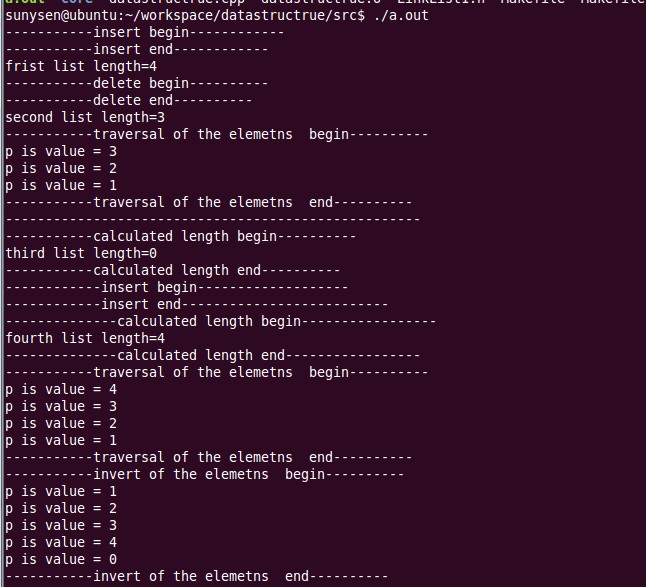
8、运行结果
9、完整代码
 View Code
View Code
1 #include "core/node/LNode.h" 2 //#include "memory.h" 3 //#include <iostream> 4 5 /** 6 * 下面类用到模板相关知识(更多模板知识请参考Effective C++第七章或者C++_Templates完全导引) 7 * 正常运行下面的方法还需要两个头文件(#include "memory.h" #include <iostream>), 8 * 一般项目开发中头文件都在一个公共文件中(更多请参考参考Effective C++里边条款31) 9 */ 10 template <class T> 11 class LinkList { 12 private: 13 //获取资源立即放入管理对象(参考Effective C++里边条款13) 14 //tr1::shared_ptr(引用计数智慧指针)管理对象比auto_ptr更强大 15 std::auto_ptr<LNode<T> > head; 16 public: 17 LinkList():head(new LNode<T>(0)){ 18 head->next = 0; 19 } 20 /** 21 * 析构函数释放资源 22 */ 23 ~LinkList(){ 24 Clear(); 25 } 26 27 /** 28 *清空链表数据并且释放内存 29 */ 30 void Clear(){ 31 LNode<T> *p = head->next; 32 33 while(p != 0){ 34 //更多关于auto_ptr知识,请阅读memory里auto_ptr源码, 35 std::auto_ptr<LNode<T> > new_ptr(p); 36 p = new_ptr->next; 37 } 38 39 head->next = 0; 40 41 } 42 /** 43 * 判断链表是否为空 44 */ 45 bool Empty() const{ 46 return head->next == 0; 47 } 48 49 /** 50 *删除指定位置链表元素 51 */ 52 bool Delete(const int i) const{ 53 int j = 0; 54 LNode<T> *p = head.get(); 55 56 //找到要删除的节点 57 while(p->next != 0 && j < i -1){ 58 j++; 59 p = p->next; 60 } 61 62 if(p->next == 0 || j > i){ 63 return false; 64 } 65 66 //释放删除节点占用内存 67 std::auto_ptr<LNode<T> > new_ptr(p->next); 68 //更新删除节点前一个节点指针域 69 p->next = new_ptr->next; 70 return true; 71 } 72 73 bool Insert(const int i,const T e){ 74 75 int j = 0; 76 LNode<T> *p = head.get(); 77 78 //找到要插入节点位置前节点 79 while(p != 0 && j < i -1){ 80 ++j; 81 p = p->next; 82 } 83 if(p == 0 || j > i-1){ 84 return false; 85 } 86 87 //新创建一个节点,当频繁插入和删除数据, 88 //下面这样内存操作方式是非常低效的(频繁分配内存和释放内存已经非常低效, 89 //而且会造成内存碎片),大多算情况list里边存储都小对象,这样应用场景适合 90 //在系统加载时候分配很多小内存装入内存池,需要直接从内存池拿,释放时放回内存池 91 //更多关于stl内存分配问题请参考侯捷<<STL源码剖析>> 92 LNode<T> *q = new LNode<T>(e); 93 if(q == 0){ 94 return false; 95 } 96 //更新新创建的指针域 97 q->next = p->next; 98 //前节点指针域指向新创建节点 99 p->next = q; 100 101 return true; 102 } 103 104 105 /** 106 * 计算链表元素的长度 107 */ 108 int Length() const{ 109 int i = 0; 110 LNode<T> *p = head.get()->next; 111 //操作是O(N),相对来说效率已经很高 112 while(p != 0){ 113 p = p->next; 114 ++i; 115 } 116 return i; 117 } 118 /** 119 *链表反转,网上看到很多人面试的时候都让写这个,写一个练练手,以防万一 120 *基本思路,就是用两个节点指针,保证一个节点指针是另个节点指针前驱节点 121 *最简单方法,用一个只有两个节点链表,反推效果 122 */ 123 void Invert(){ 124 125 LNode<T> *head_ptr = head.get(); 126 //p是head_ptr前驱节点,q和r指针都是中间变量 127 LNode<T> *p = head_ptr,*q = head_ptr,*r=0; 128 head_ptr = head_ptr->next; 129 130 while(head_ptr){ 131 r = head_ptr->next; 132 head_ptr->next = p; 133 p = head_ptr; 134 head_ptr = r; 135 std::cout<<"invert is value="<<p->data<<std::endl; 136 } 137 head_ptr = p; 138 q->next = 0; 139 140 } 141 /** 142 * 测试链表各个方法 143 */ 144 void test(){ 145 std::cout<<"-----------insert begin------------"<<std::endl; 146 for(int i = 1; i < 5; i++){ 147 Insert(1,i); 148 } 149 std::cout<<"-----------insert end------------"<<std::endl; 150 151 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length begin----------"<<std::endl; 152 std::cout<<"frist list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 153 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length end----------"<<std::endl; 154 155 std::cout<<"-----------delete begin----------"<<std::endl; 156 Delete(1); 157 std::cout<<"-----------delete end----------"<<std::endl; 158 159 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length begin----------"<<std::endl; 160 std::cout<<"second list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 161 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length end----------"<<std::endl; 162 163 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns begin----------"<<std::endl; 164 LNode<int> *p = head->next; 165 166 while(p != 0){ 167 if(p->data){ 168 std::cout<<"p is value = "<<p->data<<std::endl; 169 } 170 p = p->next; 171 } 172 173 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns end----------"<<std::endl; 174 175 std::cout<<"--------------------list begin------------------"<<std::endl; 176 Clear(); 177 std::cout<<"--------------------list end------------------"<<std::endl; 178 179 std::cout<<"----------------------------------------------------"<<std::endl; 180 181 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length begin----------"<<std::endl; 182 std::cout<<"third list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 183 std::cout<<"-----------calculated length end----------"<<std::endl; 184 185 std::cout<<"------------万恶的分割线-------------------"<<std::endl; 186 for(int i = 1; i < 5; i++){ 187 Insert(1,i); 188 } 189 std::cout<<"------------insert end--------------------------"<<std::endl; 190 191 std::cout<<"--------------calculated length begin-----------------"<<std::endl; 192 std::cout<<"fourth list length="<<Length()<<std::endl; 193 std::cout<<"--------------calculated length end-----------------"<<std::endl; 194 195 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns begin----------"<<std::endl; 196 LNode<int> *p1 = head->next; 197 198 while(p1 != 0){ 199 if(p1->data){ 200 std::cout<<"p is value = "<<p1->data<<std::endl; 201 } 202 p1 = p1->next; 203 } 204 std::cout<<"-----------traversal of the elemetns end----------"<<std::endl; 205 206 std::cout<<"-----------invert of the elemetns begin----------"<<std::endl; 207 Invert(); 208 std::cout<<"-----------invert of the elemetns end----------"<<std::endl; 209 } 210 };
单向链表在查询很多操作时间复杂度为O(N),这在对查询要求比较高情况,就不太合适,所以就有了很多的优化方案,比如:双向链表,循环链表(都是以空间换取时间)等等,后面会给出各自实现代码,和大家一起学习。
六:环境
1、运行环境:Ubuntu 10.04 LTS+VMware8.0.4+gcc4.4.3;
2、开发工具:Eclipse+make
七:题记
1、上面的代码难免有bug,如果你发现代码写的有问题,请你帮忙指出,让我们一起进步,让代码变的更漂亮和更健壮;
2、我自己能手动写上面代码,离不开郝斌、高一凡、侯捷、严蔚敏等老师的书籍和视频指导,在这里感谢他们;
3、鼓励自己能坚持把更多数据结构方面的知识写出来,让自己掌握更深刻,也顺便冒充下"小牛";
欢迎继续阅读“启迪思维:数据结构和算法”系列
