当两个元素同时设置,position属性,后写的元素会覆盖先写的。
<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>博客</title> <style> .pre{ width:500px; height:500px; position:relative; } .test1{ width:100px; height:100px; position:absolute; top:100px; background:black; } .test2{ width:100px; height:100px; position:absolute; top:50px; background:blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="pre"> <div class="test1"></div><div class="test2"></div> <div> </body> </html>
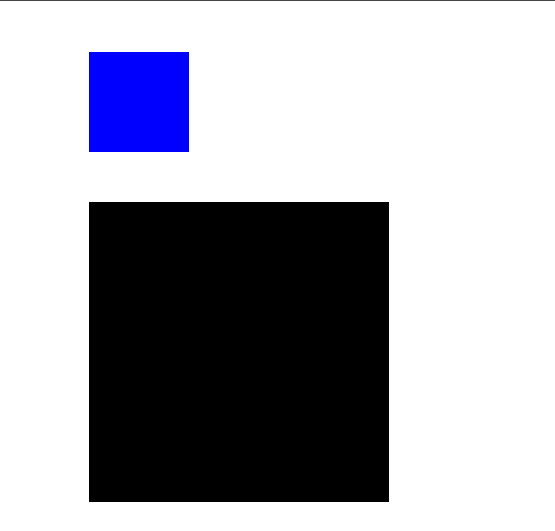
 如图所示,后写的蓝色覆盖了先写的黑色部分。这是因为默认的层级关系,文档中后写的层级大于先写的。
如图所示,后写的蓝色覆盖了先写的黑色部分。这是因为默认的层级关系,文档中后写的层级大于先写的。
2.Position:fixed;不受制于父元素。固定于页面的相应位置。
<style> .pre{ width:300px; height:300px; position:absolute; top:200px; left:300px; background:black; } .test2{ width:100px; height:100px; position:fixed; top:50px; background:blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="pre"> <div class="test2"></div> <div>
3.position:inherit;