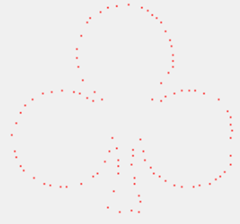
(1)这N个点要在图像边缘上;
(2)最近邻的两点之间要尽量分散开。
如,图像为:
需要设计一个采样算法,使它得到下面的结果:
==== 实现 ====
1,将图像加载,转换为ImageU8类(参见《发布我的高性能纯C#图像处理基本类,顺便也挑战一下极限。:)》),方便下一步处理。
2,获得全部边缘像素的位置。
在《重新认识C#: 玩转指针》的一文基础上新添加一个扩展方法:
 ForEach
ForEach 1 public unsafe delegate void ActionOnPosition(Int32 x, Int32 y, TPixel* p);
2 public unsafe static void ForEach(this UnmanagedImage<TPixel> src, ActionOnPosition handler)
3 {
4 Int32 width = src.Width;
5 Int32 height = src.Height;
6
7 TPixel* p = (TPixel*)src.StartIntPtr;
8 for (Int32 r = 0; r < height; r++)
9 {
10 for (Int32 w = 0; w < width; w++)
11 {
12 handler(w, r, p);
13 p++;
14 }
15 }
16 }
2 public unsafe static void ForEach(this UnmanagedImage<TPixel> src, ActionOnPosition handler)
3 {
4 Int32 width = src.Width;
5 Int32 height = src.Height;
6
7 TPixel* p = (TPixel*)src.StartIntPtr;
8 for (Int32 r = 0; r < height; r++)
9 {
10 for (Int32 w = 0; w < width; w++)
11 {
12 handler(w, r, p);
13 p++;
14 }
15 }
16 }
假设灰度值>0的点是边缘点,通过下面的两行代码就可以取得所有的边缘点:
1 List<Point> points = new List<Point>();
2 img.ForEach((x, y, p) => { if (*p > 0) points.Add(new Point(x, y)); });
2 img.ForEach((x, y, p) => { if (*p > 0) points.Add(new Point(x, y)); });
简洁吧!
3,随机抽样
这一步参考了Jitendra Malik的实现,下面是他的matlab代码:
 matlab
matlab 1 function [xi,yi,ti]=get_samples_1(x,y,t,nsamp);
2 % [xi,yi,ti]=get_samples_1(x,y,t,nsamp);
3 %
4 % uses Jitendra's sampling method
5
6 N=length(x);
7 k=3;
8 Nstart=min(k*nsamp,N);
9
10 ind0=randperm(N);
11 ind0=ind0(1:Nstart);
12
13 xi=x(ind0);
14 yi=y(ind0);
15 ti=t(ind0);
16 xi=xi(:);
17 yi=yi(:);
18 ti=ti(:);
19
20 d2=dist2([xi yi],[xi yi]);
21 d2=d2+diag(Inf*ones(Nstart,1));
22
23 s=1;
24 while s
25 % find closest pair
26 [a,b]=min(d2);
27 [c,d]=min(a);
28 I=b(d);
29 J=d;
30 % remove one of the points
31 xi(J)=[];
32 yi(J)=[];
33 ti(J)=[];
34 d2(:,J)=[];
35 d2(J,:)=[];
36 if size(d2,1)==nsamp
37 s=0;
38 end
39 end
2 % [xi,yi,ti]=get_samples_1(x,y,t,nsamp);
3 %
4 % uses Jitendra's sampling method
5
6 N=length(x);
7 k=3;
8 Nstart=min(k*nsamp,N);
9
10 ind0=randperm(N);
11 ind0=ind0(1:Nstart);
12
13 xi=x(ind0);
14 yi=y(ind0);
15 ti=t(ind0);
16 xi=xi(:);
17 yi=yi(:);
18 ti=ti(:);
19
20 d2=dist2([xi yi],[xi yi]);
21 d2=d2+diag(Inf*ones(Nstart,1));
22
23 s=1;
24 while s
25 % find closest pair
26 [a,b]=min(d2);
27 [c,d]=min(a);
28 I=b(d);
29 J=d;
30 % remove one of the points
31 xi(J)=[];
32 yi(J)=[];
33 ti(J)=[];
34 d2(:,J)=[];
35 d2(J,:)=[];
36 if size(d2,1)==nsamp
37 s=0;
38 end
39 end
这段代码原理是:检查全部点对的距离,每次去除距离最小的点对中的一个点,直至剩下的点的数量达到要取样的点的数量N。如果点的总量M>>N,这样的操作是很费时间的,为了减少计算量,当M>>N时,随机取3N个点,对这3N个点进行操作即可。需要说明的是,即使M<3N,在具体抽样之前,也需要对样本进行随机打乱,这样才能使得后面删除点对中的某一个点这一行为具有随机性,不然的话,一条直线上的点恐怕会删的只剩尾部一个点。
下面是我的实现,实现方法和Jitendra Malik的略有不同,Jitendra Malik是使用矩阵来计算的,我使用List来计算:
 RandomUniformSample
RandomUniformSample 1 public static List<Point> RandomUniformSample(List<Point> srcList, Int32 count)
2 {
3 List<Point> resultList = new List<Point>(count);
4 Int32 numNeedRemoved = srcList.Count - count;
5 if (numNeedRemoved < 1)
6 {
7 resultList.AddRange(srcList);
8 return resultList;
9 }
10
11 // 将序列随机打乱。RandomPermute是扩展方法。
12 srcList.RandomPermute();
13
14 // 如果srcList的数量巨大,则随机抽取部分点。由于上面已经随机大乱了,使用GetRange方法便可。
15 if (srcList.Count > count * 3)
16 {
17 srcList = srcList.GetRange(0, count * 3);
18 numNeedRemoved = srcList.Count - count;
19 }
20
21 // mask 记录点的删除状况。若位于mask[i]=1,则代表第i个点未被删除,若为0,则代表已删除
22 Int32[] mask = new Int32[srcList.Count];
23 for(int i=0; i < mask.Length; i++)
24 {
25 mask[i] = 1;
26 }
27
28 // 计算全部点对,并计算距离的平方
29 List<PairDistance> list = new List<PairDistance>(srcList.Count*(1 + srcList.Count/2));
30 for (int i = 0; i < srcList.Count; i++)
31 {
32 for (int j = i + 1; j < srcList.Count; j++)
33 {
34 Point p0 = srcList[i];
35 Point p1 = srcList[j];
36 Int32 deltaX = p0.X - p1.X;
37 Int32 deltaY = p0.Y - p1.Y;
38 list.Add(new PairDistance{ Index0 = i, Index1= j, DistanceSquare = deltaX*deltaX + deltaY * deltaY});
39 }
40 }
41
42 // 进行排序
43 list.Sort();
44
45 // 遍历list,直至足够的点被移除
46 int startIndex = 0;
47 while (numNeedRemoved > 0)
48 {
49 PairDistance pair = list[startIndex];
50
51 // 如果点对的两点均未被移除,则将其中一点移除。
52 if (mask[pair.Index0] != 0 && mask[pair.Index1] != 0)
53 {
54 mask[pair.Index1] = 0;
55 numNeedRemoved--;
56 }
57 startIndex++;
58 }
59
60 // 根据mask中的记录,得到全部采样点
61 for (int i = 0; i < mask.Length; i++)
62 {
63 if (mask[i] == 1) resultList.Add(srcList[i]);
64 }
65 return resultList;
66 }
2 {
3 List<Point> resultList = new List<Point>(count);
4 Int32 numNeedRemoved = srcList.Count - count;
5 if (numNeedRemoved < 1)
6 {
7 resultList.AddRange(srcList);
8 return resultList;
9 }
10
11 // 将序列随机打乱。RandomPermute是扩展方法。
12 srcList.RandomPermute();
13
14 // 如果srcList的数量巨大,则随机抽取部分点。由于上面已经随机大乱了,使用GetRange方法便可。
15 if (srcList.Count > count * 3)
16 {
17 srcList = srcList.GetRange(0, count * 3);
18 numNeedRemoved = srcList.Count - count;
19 }
20
21 // mask 记录点的删除状况。若位于mask[i]=1,则代表第i个点未被删除,若为0,则代表已删除
22 Int32[] mask = new Int32[srcList.Count];
23 for(int i=0; i < mask.Length; i++)
24 {
25 mask[i] = 1;
26 }
27
28 // 计算全部点对,并计算距离的平方
29 List<PairDistance> list = new List<PairDistance>(srcList.Count*(1 + srcList.Count/2));
30 for (int i = 0; i < srcList.Count; i++)
31 {
32 for (int j = i + 1; j < srcList.Count; j++)
33 {
34 Point p0 = srcList[i];
35 Point p1 = srcList[j];
36 Int32 deltaX = p0.X - p1.X;
37 Int32 deltaY = p0.Y - p1.Y;
38 list.Add(new PairDistance{ Index0 = i, Index1= j, DistanceSquare = deltaX*deltaX + deltaY * deltaY});
39 }
40 }
41
42 // 进行排序
43 list.Sort();
44
45 // 遍历list,直至足够的点被移除
46 int startIndex = 0;
47 while (numNeedRemoved > 0)
48 {
49 PairDistance pair = list[startIndex];
50
51 // 如果点对的两点均未被移除,则将其中一点移除。
52 if (mask[pair.Index0] != 0 && mask[pair.Index1] != 0)
53 {
54 mask[pair.Index1] = 0;
55 numNeedRemoved--;
56 }
57 startIndex++;
58 }
59
60 // 根据mask中的记录,得到全部采样点
61 for (int i = 0; i < mask.Length; i++)
62 {
63 if (mask[i] == 1) resultList.Add(srcList[i]);
64 }
65 return resultList;
66 }
其中:
 PairDistance
PairDistance  RandomPermute
RandomPermute