IoC概念
-
IoC(Inversion Of Control)控制反转,Spring反向控制应用程序所需要使用的外部资源。举例
-
Spring控制的资源将全部放置在Spring容器中,该容器称为IoC容器
-
IoC是面向对象编程的一种设计原则,可以用来降低代码之间的耦合度
bean
-
名称:bean
-
类型:标签
-
归属:beans标签
-
作用:定义spring中的资源,受此标签定义的资源将受到spring控制
-
基本属性:
<bean id="userService" name="userService1, userService2" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"/>id:bean的名称,通过id值获取bean
class:bean的类型
name:bean的名称,可以通过name值获取bean,用于多人共同开发时给bean起别名
set注入(重点)
-
名称:property
-
类型:标签
-
归属:bean标签
-
作用:使用set方法的形式为bean提供资源
-
格式:
<bean>
<property />
</bean> -
基本属性:
-
引用类型:自定义类产生的对象,使用ref指定
-
非引用类型:基本数据类型(int, char,...)和特殊类型String,使用value指定
<!--非引用类型注入-->
<property name="propertyName" value="propertyValue" />
<!--引用类型注入-->
<property name="propertyName" ref="beanId"/> -
name:对应bean中的属性名,要求该属性必须提供可访问的set方法(严格规范:此名称是set方法对应名称)
value:设定非引用类型属性对应的值,不能与ref同时使用
ref:设定引用类型属性对应bean的id ,不能与value同时使用
集合类型数据注入
-
名称:array,list,set,map,props
-
类型:标签
-
归属:property标签 或 constructor-arg标签
-
作用:注入集合数据类型属性
-
格式:
(1)集合类型数据注入——list
<!--setAl()-->
<property name="al">
<list>
<value>itheima</value>
<value>66666</value>
</list>
</property>
(2)集合类型数据注入——props
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="name">itheima666</prop>
<prop key="value">666666</prop>
</props>
</property>
综合案例(重点)(.xml格式)
案例介绍
-
使用spring整合mybatis技术,完成账户模块(Account)的基础增删改查功能
-
账户模块对应字段
-
编号:id
-
账户名:name
-
余额:money
-
案例分析
下图中标红部分需要咱们来实现
-
环境准备:导入Spring坐标,MyBatis坐标,MySQL坐标,Druid坐标
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> -
业务类与接口准备
-
创建数据库表,并制作相应的实体类Account
-
定义业务层接口与数据层接口
-
在业务层调用数据层接口,并实现业务方法的调用
-
-
基础配置文件
-
jdbc.properties
-
MyBatis映射配置文件
-
整合准备工作
1.spring配置文件,加上context命名空间,用于加载properties文件
2.开启加载properties文件
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
3.配置数据源Druid
<!--加载druid资源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
4.定义service层bean,并使用property标签注入dao
<!--配置service作为spring的bean,注入dao-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
5.dao的bean无需定义,MyBatis会自动生成代理对象
整合工作
1.导入Spring整合MyBatis坐标
<!--Spring整合MyBatis坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2.将mybatis配置成spring管理的bean(SqlSessionFactoryBean),并将类型别名交由spring处理
<!--spring整合mybatis后控制的创建连接用的对象-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.itheima.domain"/>
</bean>
3.通过spring加载mybatis的映射配置文件到spring环境中(映射Mapper扫描工作交由spring处理)
<!--加载mybatis映射配置的扫描,将其作为spring的bean进行管理-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itheima.dao"/>
</bean>
4.使用spring环境获取业务层bean,执行操作
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ctx.getBean("accountService");
//查询
Account ac = accountService.findById(13);
System.out.println(ac);
//保存
Account account = new Account();
account.setName("jack");
account.setMoney(123456.78);
accountService.save(account);
}
}
注解方式开发
常用注解(重点)
启动注解功能
-
启动注解扫描,加载类中配置的注解项
<!--注解总开关-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/> -
说明:
-
在进行包所扫描时,会对配置的包及其子包中所有文件进行扫描
-
扫描过程是以文件夹递归迭代的形式进行的
-
扫描过程仅读取合法的java文件
-
扫描时仅读取spring可识别的注解
-
扫描结束后会将可识别的有效注解转化为spring对应的资源加入IoC容器
-
-
注意:
-
无论是注解格式还是XML配置格式,最终都是将资源加载到IoC容器中,差别仅仅是数据读取方式不同
-
从开发效率上来说注解优于XML配置文件
-
bean的定义
-
名称:@Component
-
类型:类注解
-
位置:类定义上方
-
作用:设置该类为spring管理的bean
-
范例:
加载第三方资源
-
名称:@Bean
-
类型:方法注解
-
位置:方法定义上方
-
作用:设置该方法的返回值作为spring管理的bean
-
范例:
@Bean("dataSource") public DruidDataSource createDataSource() { return ……; }
-
bean的非引用类型属性注入
-
名称:@Value
-
类型:属性注解、方法注解
-
位置:属性定义上方,set方法定义上方
-
作用:设置对应属性的值或对方法进行传参
-
范例:
@Value("zhangsan") private String username;
bean的引用类型属性注入
-
名称:@Autowired、@Qualifier
-
类型:属性注解、方法注解
-
位置:属性定义上方,方法定义上方
-
作用:设置对应属性的对象或对方法进行引用类型传参
-
范例:
@Autowired(required = false) private UserDao userDao;
加载properties文件
-
名称:@PropertySource
-
类型:类注解
-
位置:类定义上方
-
作用:加载properties文件中的属性值
-
范例:
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:jdbc.properties","classpath:abc.properties"},ignoreResourceNotFound = true) public class ClassName { @Value("${propertiesAttributeName}") private String attributeName; }
纯注解格式
-
名称:@Configuration、@ComponentScan
-
类型:类注解
-
位置:类定义上方
-
作用:设置当前类为spring核心配置加载类
-
范例:
@Configuration @ComponentScan("scanPackageName") public class SpringConfigClassName{ } -
说明:
-
核心配合类用于替换spring核心配置文件,此类可以设置空的,不设置变量与属性
-
bean扫描工作使用注解@ComponentScan替代
-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
-
加载纯注解格式上下文对象,需要使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
-
当配置类作为 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 对象创建的参数时,@Configuration注解可以不写
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
第三方bean配置与管理(重点)
-
名称:@Import
-
类型:类注解
-
位置:类定义上方
-
作用:导入第三方bean作为spring控制的资源
-
范例:
@Configuration @Import(OtherClassName.class) public class ClassName { }注解整合MyBatis步骤
1.修改mybatis外部配置文件格式为注解格式
public interface AccountDao { @Insert("insert into account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money})") void save(Account account); @Delete("delete from account where id = #{id} ") void delete(Integer id); @Update("update account set name = #{name} , money = #{money} where id = #{id} ") void update(Account account); @Select("select * from account") List<Account> findAll(); @Select("select * from account where id = #{id} ") Account findById(Integer id); }2.业务类使用@Service声明bean,使用@Autowired注入对象
@Service("accountService") public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; }3.编写Spring配置类:SpringConfig,并加载properties文件
@Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") public class SpringConfig { }4.建立配置文件JDBCConfig与MyBatisConfig类,并将其导入到核心配置类SpringConfig
数据源配置类:JDBCConfig
public class JDBCConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String userName; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean(value = "dataSource") public DataSource getDataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(driver); ds.setUrl(url); ds.setUsername(userName); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; } }MyBatis配置类:MyBatisConfig
public class MyBatisConfig { @Bean public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSessionFactoryBean(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){ SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.itheima.domain"); ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource); return ssfb; } @Bean public MapperScannerConfigurer getMapperScannerConfigurer(){ MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer(); msc.setBasePackage("com.itheima.dao"); return msc; } }5.开启注解扫描,将JDBCConfig与MyBatisConfig类导入到核心配置类SpringConfig中
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima") @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") @Import({JDBCConfig.class,MyBatisConfig.class}) public class SpringConfig { }6.使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象加载配置项
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ctx.getBean("accountService"); Account ac = accountService.findById(3); System.out.println(ac); } }
采用注解开发的时候会在testjava下运行测试
注解整合Junit
1.导入Spring整合Junit坐标,从Spring5.0以后,要求Junit的版本必须是4.12及以上
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2.Spring接管Junit的运行权,使用Spring专用的Junit类加载器
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
3.加载Spring配置类
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class UserServiceTest {
@Test
public void testSave() {}
}
AOP(重点是注解格式)
AOP概念
-
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programing)面向切面编程,是一种编程范式,隶属于软件工程范畴。
-
AOP基于OOP基础之上进行横向开发,是对 OOP 编程方式的一种补充,并非是取而代之。
-
AOP不是由Spring提出的,最佳开源实现是AspectJ;Spring集成了AspectJ 实现AOP
AOP作用和优势
-
AOP能够将那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的功能,比如
-
日志记录
-
性能监控
-
事务管理
-
权限控制
减少系统的重复代码,降低模块之间的耦合度,并有利于将来维护。
-
AOP核心概念
-
Joinpoint(连接点):就是方法
-
Pointcut(切入点):就是挖掉共性功能的方法
-
Advice(通知):就是共性功能,最终以一个方法的形式呈现
-
Aspect(切面):就是共性功能与挖的位置的对应关系
-
Target(目标对象):就是挖掉功能的方法对应的类产生的对象,这种对象是无法直接完成最终工作的
-
Weaving(织入):就是将挖掉的功能回填的动态过程
-
Proxy(代理):目标对象无法直接完成工作,需要对其进行功能回填,通过创建原始对象的代理对象实现
入门案例制作
下面使用XML方式来开发:
1.导入aspectj的坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
2.确认要抽取的功能:并将其制作成方法保存到专用的类中,最后删除原始业务中对应的功能
3.引入apo命名空间,然后将所有进行AOP操作的资源加载到IoC容器中
-
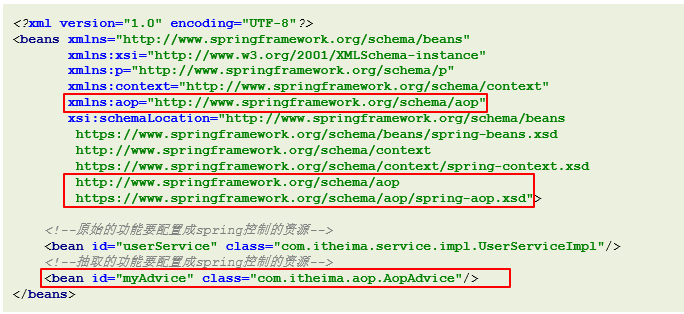
引入aop命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--3.开启AOP命名空间--> -
在applicationContextx.xml中配置userService和通知类AOPAdvice
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"/> <!--2.配置共性功能成为spring控制的资源--> <bean id="myAdvice" class="com.itheima.aop.AOPAdvice"/> -
对比之前新增的改动
4.使用配置的方式描述被抽取功能的位置,并描述被抽取功能与对应位置的关系
<!--aop配置-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* *..*(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<!--通知与切入点之间的关系-->
<aop:before method="logAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
5.运行App类
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService");
userService.save();
AOP配置
aop:config
-
名称:aop:config
-
类型:标签
-
归属:beans子标签
-
作用:设置AOP
-
格式:
<beans> <aop:config>……</aop:config> <aop:config>……</aop:config> </beans> -
说明:一个beans标签中可以配置多个aop:config标签
aop:aspect
-
名称:aop:aspect
-
类型:标签
-
归属:aop:config标签
-
作用:设置具体的AOP通知对应的切入点
-
格式:
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.itheima.aop.AOPAdvice"/> <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pt"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> -
说明:
一个aop:config标签中可以配置多个aop:aspect标签
-
基本属性:
-
ref :通知类的beanId
-
aop:pointcut
-
名称:aop:pointcut
-
类型:标签
-
归属:aop:config标签、aop:aspect标签
-
作用:设置切入点
-
格式:
<aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* *..*(..))"/> <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pt"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
切入点表达式的组成
-
切入点表达式是一个快速匹配方法描述的通配格式,类似于正则表达式
关键字([访问修饰符] 返回值 包名.类名.方法名(参数) [异常名]) #简写方式,省略(访问修饰符、异常名) 关键字(返回值 包名.类名.方法名(参数))
关键字:描述表达式的匹配模式(参看关键字列表) 常用execution
访问修饰符:方法的访问控制权限修饰符,public、 protected、private,可以省略不写
类名:方法所在的类(此处可以配置接口名称)
异常:方法定义中指定抛出的异常,可以省略不写
切入点表达式——逻辑运算符
-
&& :连接两个切入点表达式,表示两个切入点表达式同时成立的匹配
-
|| :连接两个切入点表达式,表示两个切入点表达式成立任意一个的匹配
-
! :连接单个切入点表达式,表示该切入点表达式不成立的匹配
切入点表达式——范例
execution(* *(..))
execution(* *..*(..))
execution(* *..*.*(..))
execution(public * *..*.*(..))
execution(public int *..*.*(..))
execution(public void *..*.*(..))
execution(public void com..*.*(..))
execution(public void com..service.*.*(..))
execution(public void com.itheima.service.*.*(..))
execution(public void com.itheima.service.User*.*(..))
execution(public void com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))
execution(public void com.itheima.service.UserService.*(..))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.find*(..))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.*Id(..))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.findById(..))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.findById(int))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.findById(int,int))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.findById(int,*))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.findById(*,int))
execution(public User com.itheima.service.UserService.findById())
execution(List com.itheima.service.*Service+.findAll(..))
通知类型(重点)
aop:before
-
名称:aop:before
-
类型:标签
-
归属:aop:aspect标签
-
作用:设置前置通知
-
格式:
<aop:aspect ref="adviceId"> <!--直接配置切入点--> <aop:before method="logAdvice" pointcut="execution(* *(..))"/> </aop:aspect><aop:aspect ref="adviceId"> <!--使用公共切入点--> <aop:before method="logAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/> </aop:aspect>
aop:after
-
名称:aop:after
-
类型:标签
-
归属:aop:aspect标签
-
作用:设置后置通知
-
格式:
<aop:aspect ref="adviceId"> <aop:after method="methodName" pointcut="……"/> </aop:aspect>
aop:after-returning
-
名称:aop:after-returning
-
类型:标签
-
归属:aop:aspect标签
-
作用:设置返回后通知
-
格式:
<aop:aspect ref="adviceId"> <aop:after-returning method="methodName" pointcut="……"/> </aop:aspect>
aop:after-throwing
-
名称:aop:after-throwing
-
类型:标签
-
归属:aop:aspect标签
-
作用:设置抛出异常后通知
-
格式:
<aop:aspect ref="adviceId"> <aop:after-throwing method="methodName" pointcut="……" throwing="t"/> </aop:aspect> -
说明:一个aop:aspect标签中可以配置多个aop:after-throwing标签
-
基本属性:
-
method :在通知类中设置当前通知类别对应的方法
-
pointcut :设置当前通知对应的切入点表达式,与pointcut-ref属性冲突
-
pointcut-ref :设置当前通知对应的切入点id,与pointcut属性冲突
-
aop:around(重点)
-
名称:aop:around
-
类型:标签
-
归属:aop:aspect标签
-
作用:设置环绕通知
-
格式:
<aop:aspect ref="adviceId"> <aop:around method="methodName" pointcut="……"/> </aop:aspect> -
说明:一个aop:aspect标签中可以配置多个aop:around标签
-
基本属性:
-
method :在通知类中设置当前通知类别对应的方法
-
pointcut :设置当前通知对应的切入点表达式,与pointcut-ref属性冲突
-
pointcut-ref :设置当前通知对应的切入点id,与pointcut属性冲突
-
环绕通知的开发方式:
-
环绕通知可以在原始方法的前后分别添加功能,因此必须在在环绕通知中对原始方法进行显式调用
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("原始方法执行前执行...") Object ret = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("原始方法执行后执行...") return ret; } -
注意事项
-
方法的第一个参数必须是ProceedingJoinPoint,通过该对象的proceed()方法,实现对原始方法的调用
-
使用proceed()方法调用原始方法时,因无法预知原始方法运行过程中是否会出现异常,需要强制抛出Throwable对象,封装原始方法中可能出现的异常信息
-
通知中获取数据
获取参数数据
第一种方式:
-
设定通知方法第一个参数为JoinPoint,通过该对象调用getArgs()方法,获取原始方法运行的参数数组
public void before(JoinPoint jp) { //通过JoinPoint参数获取调用原始方法所携带的参数 Object[] args = jp.getArgs(); System.out.println("before..." + Arrays.toString(args)); }public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ... userService.save(666, 888); } }
获取返回值数据
第一种:适用于返回后通知(after-returning)
-
设定返回值变量名
-
原始方法
public int update() { System.out.println("user service update running...."); return 100; } -
AOP配置
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <aop:pointcut id="pt3" expression="execution(* *(..)) "/> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pt3" returning="ret"/> </aop:aspect> -
通知类
public void afterReturning(Object ret) { System.out.println("afterReturning..." + ret); } -
在main方法中执行userService.update(),查看执行结果
第二种:适用于环绕通知(around)
-
在通知类的环绕方法中调用原始方法获取返回值
-
编写带返回值的原始方法
public int upate() { System.out.println("user service running..."); return 100; } -
AOP配置
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <aop:pointcut id="pt2" expression="execution(* *(..)) "/> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pt2" /> </aop:aspect> -
通知类
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { Object ret = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("around after..." + ret); return ret; } -
在main方法中执行userService.update(),查看执行结果
通知获取异常数据-视频11
第一种:通知类的方法中调用原始方法捕获异常,适用于环绕通知(around)
-
原始方法:模拟抛出除0异常
public void save() { System.out.println("user service running..."); int i = 1/0; } -
AOP配置
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <aop:pointcut id="pt4" expression="execution(* *(..)) "/> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pt4" /> </aop:aspect> -
通知类
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) { System.out.println("around before..."); Object ret = null; try { //对原始方法的调用 ret = pjp.proceed(); } catch (Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("around...exception...." + throwable.getMessage()); } System.out.println("around after..." + ret); return ret; }
AOP配置(注解格式)
AOP注解驱动
-
名称:@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
-
类型:注解
-
位置:Spring注解配置类定义上方
-
作用:设置当前类开启AOP注解驱动的支持,加载AOP注解
综合案例
5.1)案例介绍
对项目业务层接口执行监控,统计业务层接口的执行效率
public interface AccountService {
void save(Account account);
void delete(Integer id);
void update(Account account);
List<Account> findAll();
Account findById(Integer id);
}
5.2)案例分析
-
测量接口执行效率:接口方法执行前后获取执行时间,求出执行时长
使用System.currentTimeMillis( )获取系统时间
-
对项目进行监控:项目中所有查询方法,使用AOP的环绕通知,在proceed()方法执行前后获取系统时间
5.3)案例制作步骤
-
制作AOP环绕通知
@Component
@Aspect
public class RunTimeMonitorAdvice {
public Object runtimeAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
}
}
-
在通知类RunTimeMonitorAdvice中:定义切入点,绑定到接口上
//拦截所有的业务层接口中查询操作的执行
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.find*(..))")
public void pt(){}
-
完善runtimeAround()方法实现,完成测量功能
@Around("pt()") public Object runtimeMonitor(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { //获取执行签名信息 Signature signature = pjp.getSignature(); //通过签名获取执行类型(接口名) String targetClass = signature.getDeclaringTypeName(); //通过签名获取执行操作名称(方法名) String targetMethod = signature.getName(); //获取操作前系统时间beginTime long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object ret = pjp.proceed(pjp.getArgs()); //获取操作后系统时间endTime long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(targetClass+" 中 "+targetMethod+" 运行时长 "+(endTime-beginTime)+"ms"); return ret; } -
开启注解驱动支持:@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima") @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") @Import({JDBCConfig.class,MyBatisConfig.class}) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class SpringConfig { } -
运行UserServiceTest单元测试
//设定spring专用的类加载器 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //设定加载的spring上下文对应的配置 @ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class) public class UserServiceTest { @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Test public void testFindById(){ Account ac = accountService.findById(13); System.out.println(ac); } @Test public void testFindAll(){ List<Account> list = accountService.findAll(); System.out.println(list); } @Test public void testUpdate() { Account ac = accountService.findById(13); ac.setMoney(0.01); ac.setName("没钱了"); accountService.update(ac); } }
Spring事务
事务的作用
事务特征(ACID)
-
原子性(Atomicity)指事务是一个不可分割的整体,其中的操作要么全执行或全不执行
-
一致性(Consistency)事务前后数据的完整性必须保持一致。比如:张三向李四转100元,转账前和转账后的数据是正确状态这叫一致性,如果出现张三转出100元,李四账户没有增加100元这就出现了数据错误,就没有达到一致性。
-
隔离性(Isolation)事务的隔离性是多个用户并发访问数据库时,数据库为每一个用户开启的事务,不能被其他事务的操作数据所干扰,多个并发事务之间要相互隔离
-
持久性(Durability)持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就是永久性的,接下来即使数据库发生故障也不应该对其有任何影响
四种隔离级
未提交读(Read Uncommitted) - 允许脏读,会去读到其他事务中未提交的数据
提交读(Read Committed) ----- 解决了脏读
可重复读(Repeatable Read) ------消除了不可重复读
串行读(Serializable) ------- 解决了幻读
Spring事务核心对象
Spring提供如下三个接口为业务层提供了整套的事务解决方案
-
事务定义对象:TransactionDefinition
-
事务状态:TransactionStatus
-
平台事务管理器:PlatformTransactionManager
TransactionDefinition(事务对象)
此接口定义了事务的基本信息
-
获取事务定义名称
String getName() -
获取事务的读写属性
boolean isReadOnly() -
获取事务隔离级别
int getIsolationLevel() -
获事务超时时间
int getTimeout() -
获取事务传播行为特征
int getPropagationBehavior()
TransactionStatus(事务状态)
PlatformTransactionManager:事务管理器
DataSourceTransactionManager(事务管理器的实现类) 适用于Spring JDBC或MyBatis
声明式事务(XML)
使用声明式事务需要引入tx命名空间:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
tx:advice
-
名称:tx:advice
-
类型:标签
-
归属:beans标签
-
作用:配置事务专属通知类
-
格式:
<beans> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager"> </tx:advice> </beans> -
基本属性:
-
id :用于配置aop时指定通知类的id
-
transaction-manager :指定事务管理器bean
-
tx:attributes
-
名称:tx:attributes
-
类型:标签
-
归属:tx:advice标签
-
作用:定义通知属性
-
格式:
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="*" read-only="false" /> <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice>
aop:advisor
使用aop:advisor在AOP配置中引用事务专属通知类
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
</aop:config>
使用XML配置事务
-
设置事务管理器
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> -
配置专用事务通知器
<!--定义事务管理的通知类--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager"> <!--定义控制的事务--> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="*" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="transfer" read-only="false"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> -
AOP配置切面,使用通知器绑定切入点
<aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/> </aop:config> -
测试转账
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ctx.getBean("accountService"); accountService.transfer("tom","itheima",100D); } }
声明式事务(纯注解驱动)
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
jdbc.properties配置文件
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
Dao包接口SQL语句采用注解格式
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 入账操作
* @param name 入账用户名
* @param money 入账金额
*/
@Update( "update account set money = money + #{money} where name = #{name}")
void inMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);
/**
* 出账操作
* @param name 出账用户名
* @param money 出账金额
*/
@Update( "update account set money = money - #{money} where name = #{name}")
void outMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);
}
domain包
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double money;
省略set方法和toString...
}
service接口
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账操作
* @param outName 出账用户名
* @param inName 入账用户名
* @param money 转账金额
*/
//代表切入点和事务的一系列默认值
@Transactional
public void transfer(String outName,String inName, Double money);
}
service实现类
//注解代表配置文件里面的Bean:id
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void transfer(String outName, String inName, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(outName, money);
// int a = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(inName, money);
}
}
JDBCConfig类
//扫描配置文件,并且加载
@Component
public class JDBCConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
//连接池
@Bean("dataSource")
public DruidDataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
//事务管理器
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
MyBatisConfig类
public class MyBatisConfig {
//定义SqlSessionFactoryBean的时候,dataSource属性是必须指定的,它表示用于连接数据库的数据源
//spring整合mybatis后控制的创建连接用的对象
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSessionFactoryBean(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb=new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.itheima.domain");
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
return ssfb;
}
//整合dao接口所有的操作,不用再去为dao配Bean了
//加载mybatis映射配置的扫描,将其作为spring的bean进行管理
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer getMapperScannerConfigurer(){
MapperScannerConfigurer msc=new MapperScannerConfigurer();
//basePackage:这个属性就是映射接口的包,这个包里面的所有的接口扫描到
msc.setBasePackage("com.itheima.dao");
return msc;
}
}
SpringConfig类(重点)
//纯注解格式
@Configuration
//设置当前类为spring核心配置加载类
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
//加载properties文件中的属性值
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
//导入写配置的两个类,事务管理器也在JDBCConfig类里面
@Import({JDBCConfig.class,MyBatisConfig.class})
//注解 @EnableTransactionManagement 开启事务支持
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfig {
}
主方法测试类UserServiceTest
//设定Spring专用的类加载器
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//设定加载Spring上下文对应的配置
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class UserServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
accountService.transfer("Mike","Jock",500D);
}
}