 CF768B
CF768B题目链接:
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/768/B
题目:
Initially Sam has a list with a single element n. Then he has to perform certain operations on this list. In each operation Sam must remove any element x, such that x > 1, from the list and insert at the same position  ,
, 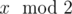 ,
,  sequentially. He must continue with these operations until all the elements in the list are either 0 or 1.
sequentially. He must continue with these operations until all the elements in the list are either 0 or 1.
Now the masters want the total number of 1s in the range l to r (1-indexed). Sam wants to become a maester but unfortunately he cannot solve this problem. Can you help Sam to pass the eligibility test?
The first line contains three integers n, l, r (0 ≤ n < 2^50, 0 ≤ r - l ≤ 10^5, r ≥ 1, l ≥ 1) – initial element and the range lto r.
It is guaranteed that r is not greater than the length of the final list.
Output the total number of 1s in the range l to r in the final sequence.
分析:
非常有趣的一道题,就是说我们有一个数n我们把它打散为一串0,1序列,方式如上所述,问l到r中有多少个1。
打散方式:比如说7, 。
。
先通过找规律我们可以发现以下两条结论:
1,数x打散后的序列中有x个1。
2,数x打散后的序列有 2n-1位数,其中2n-1为刚好大于等于x的数。
现在给你l,r,问从第l位到第r位有多少个1.
那么这个问题,我们就可以转化为第x位以前有多少个1,然后再相减,就是答案了。
我们可以采用线段树的思想,
这样我们就可以利用第2条确定向左走还是向右走,第1条来确定有多少个1了。

题目链接:
http://codeforces.com/contest/896/problem/A
题目:
s0 = "What are you doing at the end of the world? Are you busy? Will you save us?".
si = "What are you doing while sending "si - 1"? Are you busy? Will you send "si - 1"?" ( i ≥ 1)
给你一个n(n<=105)和k(k<=1018),问你在fn中第k个字符是什么,如果没有就输出 '.'。
分析:
我们可以算出每个fi包含多少个字符。我们算出来:
f0=75
fn=34+fn-1+32+fn-1+2(n>=1)
我们还是利用到与上面一个类似的思想就可以做。
但要注意n特别大的时候的讨论,当时RE了好几发。
代码:

1 // 很重要!!hack点n>tot 2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 long long f[100]; 5 int tot=0; 6 char s[4][100]={ 7 "What are you doing while sending "", 8 ""? Are you busy? Will you send "", 9 ""?" 10 }; 11 char s1[100]="What are you doing at the end of the world? Are you busy? Will you save us?"; 12 void init(){ 13 /*for(int i=0;i<3;++i){ 14 int len=strlen(s[i]); 15 printf("len%d=%d ",i,len); 16 }*/ 17 //printf("len:%d ",strlen(s1)); 18 f[0]=75; 19 for(int i=1;;++i){ 20 f[i]=2*f[i-1]+68; 21 tot=i; 22 if(f[i]>1e18)break; 23 } 24 //printf("f[tot]=%lld ",f[tot]); 25 } 26 char ans[20]; 27 int cnt=0; 28 int main(){ 29 init(); 30 int q;scanf("%d",&q); 31 while(q--){ 32 int n;long long k; 33 scanf("%d%lld",&n,&k); 34 if(n>=tot||k<=f[n]){ 35 while(1){ 36 if(n==0){ 37 ans[cnt++]=s1[k-1]; 38 break; 39 } 40 if(k<=34){ 41 ans[cnt++]=s[0][k-1]; 42 break; 43 }else if((k-=34)&&(n>tot||k<=f[n-1])){ 44 n--; 45 }else if((k-=f[n-1])&&k<=32){ 46 ans[cnt++]=s[1][k-1]; 47 break; 48 }else if((k-=32)&&k<=f[n-1]){ 49 n--; 50 }else if((k-=f[n-1])){ 51 ans[cnt++]=s[2][k-1]; 52 break; 53 } 54 } 55 56 }else{ 57 ans[cnt++]='.'; 58 } 59 ans[cnt+1]='�'; 60 } 61 printf("%s ",ans); 62 return 0; 63 }
题目链接:
http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1081
题意:
Input
Output
Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
3 1
|
000
|
分析:
求第K小的字符串。
我们假设dp[i][0]:为以0开头的长度为i的合法串的个数,dp[i][1]:为以1开头的长度为i的个数。
所以有dp[1][0]=1,dp[1][1]=1;
dp[i+1][1]=dp[i][0];
dp[i+1][0]=dp[i][1]+dp[i][0];
然后也是一样的思想,就可以做了。
代码:

1 #include<cstdio> 2 long long dp[50][2]; 3 int main(){ 4 int N,K; 5 scanf("%d%d",&N,&K); 6 dp[1][0]=1;dp[1][1]=1; 7 for(int i=1;i<N;++i){ 8 dp[i+1][1]=dp[i][0]; 9 dp[i+1][0]=dp[i][0]+dp[i][1]; 10 } 11 /*for(int i=1;i<=N;++i){ 12 printf("dp[%d][1]=%lld ",i,dp[i][1]); 13 printf("dp[%d][0]=%lld ",i,dp[i][0]); 14 }*/ 15 if(K>dp[N][1]+dp[N][0]){ 16 printf("-1 "); 17 return 0; 18 } 19 for(int i=N;i>=1;--i){ 20 if(K<=dp[i][0]){ 21 printf("0"); 22 23 }else{ 24 printf("1"); 25 K-=dp[i][0]; 26 } 27 } 28 printf(" "); 29 return 0; 30 }
