定义
/** * A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values, * constructor argument values, and further information supplied by * concrete implementations. * * <p>This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a * {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} to introspect and modify property values * and other bean metadata. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Rob Harrop * @since 19.03.2004 * @see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#getBeanDefinition * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition */ public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
解读:
BeanDefinition相当于一个数据结构,Spring容器对bean的管理是通过BeanDefinition来实现的。
方法
BeanDefinition中的方法如下图所示:

类图

解读:
从上述类图可以得知BeanDefinition有哪些实现类。
调用链路
本部分准备探究一下Spring中解析bean的调用链路,涉及到几个层次,譬如:ApplicationContext -> BeanDefinitionReader -> BeanDefinitionDocumentReader。
可以带着问题阅读:
- 这几个层次之间是怎么关联起来的?
- 最终是如何解析bean的?
ApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh"); // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process"); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); beanPostProcess.end(); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); contextRefresh.end(); } } }
解读:
上述AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh方法调用的obtainFreshBeanFactory方法是整个调用链路的入口。
/** * Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. * @return the fresh BeanFactory instance * @see #refreshBeanFactory() * @see #getBeanFactory() */ protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { refreshBeanFactory(); return getBeanFactory(); }
/** * Subclasses must implement this method to perform the actual configuration load. * The method is invoked by {@link #refresh()} before any other initialization work. * <p>A subclass will either create a new bean factory and hold a reference to it, * or return a single BeanFactory instance that it holds. In the latter case, it will * usually throw an IllegalStateException if refreshing the context more than once. * @throws BeansException if initialization of the bean factory failed * @throws IllegalStateException if already initialized and multiple refresh * attempts are not supported */ protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
解读:
此处refreshBeanFactory方法是抽象方法,由子类实现。
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
/** * This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying * bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and * initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle. */ @Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
/** * Load bean definitions into the given bean factory, typically through * delegating to one or more bean definition readers. * @param beanFactory the bean factory to load bean definitions into * @throws BeansException if parsing of the bean definitions failed * @throws IOException if loading of bean definition files failed * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader */ protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException;
解读:
此处loadBeanDefinitions方法是抽象方法,由子类实现。
AbstractXmlApplicationContext
/** * Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader * @see #initBeanDefinitionReader * @see #loadBeanDefinitions */ @Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
/** * Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory} * method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions. * @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use * @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors * @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found * @see #refreshBeanFactory * @see #getConfigLocations * @see #getResources * @see #getResourcePatternResolver */ protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
解读:
上述loadBeanDefinitions方法最终是调用了AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的loadBeanDefinitions方法,参数是数组类型。
问题:此处loadBeanDefinitions方法的返回值为空,而reader是new出来的变量,reader做什么事情看似跟ApplicationContext没啥关系啊。
实则不然,构造reader时传递了beanFactory,在最终解析bean时用到了该参数,所以说beanfactory承担了关联解析bean的几个层次的作用。
BeanDefinitionReader
类图:
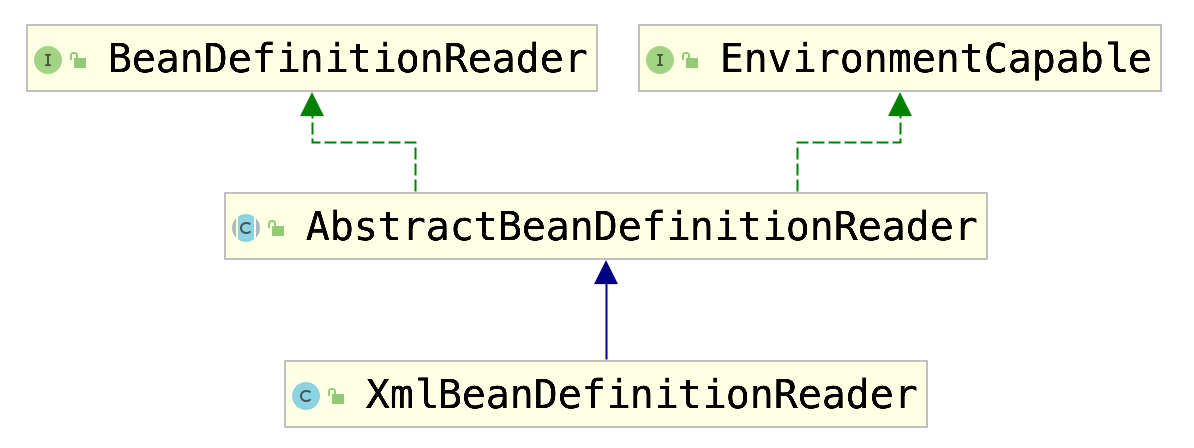
解读:
分析后续流程时可以参照类图继承层次。
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
@Override public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null"); int count = 0; for (Resource resource : resources) { count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } return count; }
解读:
此处算是真正开始进入了解析bean的流程,使用了for循环。
BeanDefinitionReader
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified resource. * @param resource the resource descriptor * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ @Override public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); }
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file, * allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } }
/** * Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors * @see #doLoadDocument * @see #registerBeanDefinitions */ protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource); } return count; } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } }
/** * Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document. * Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}. * <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes * {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it. * @param doc the DOM document * @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information) * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors * @see #loadBeanDefinitions * @see #setDocumentReaderClass * @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions */ public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; }
@Override public final BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry() { return this.registry; }
解读:
此处的registry是什么?
本文前面构造reader变量的代码语句的含义请参见如下代码:
/** * Create new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory. * @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into, * in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry */ public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { super(registry); }
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
/** * Create a new AbstractBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory. * <p>If the passed-in bean factory does not only implement the BeanDefinitionRegistry * interface but also the ResourceLoader interface, it will be used as default * ResourceLoader as well. This will usually be the case for * {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} implementations. * <p>If given a plain BeanDefinitionRegistry, the default ResourceLoader will be a * {@link org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver}. * <p>If the passed-in bean factory also implements {@link EnvironmentCapable} its * environment will be used by this reader. Otherwise, the reader will initialize and * use a {@link StandardEnvironment}. All ApplicationContext implementations are * EnvironmentCapable, while normal BeanFactory implementations are not. * @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into, * in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry * @see #setResourceLoader * @see #setEnvironment */ protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null"); this.registry = registry; // Determine ResourceLoader to use. if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) { this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry; } else { this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(); } // Inherit Environment if possible if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) { this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment(); } else { this.environment = new StandardEnvironment(); } }
解读:
至此可知在构造XmlBeanDefinitionReader类型的变量时,实质是将beanFactory赋值给AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的registry变量。
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
纵观前述代码调用流程可知此流程的核心是前述标记为粉色的代码
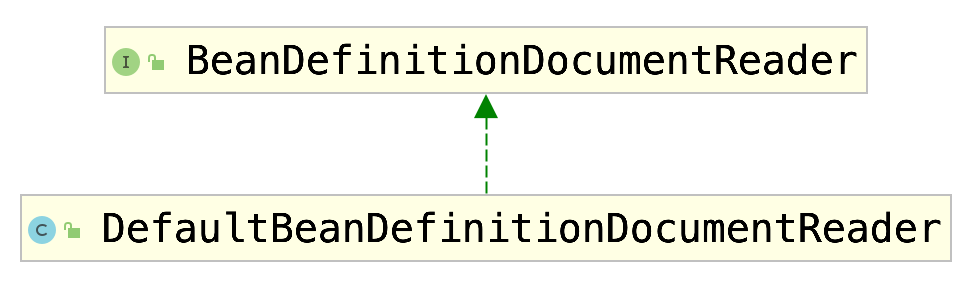
/** * Create the {@link BeanDefinitionDocumentReader} to use for actually * reading bean definitions from an XML document. * <p>The default implementation instantiates the specified "documentReaderClass". * @see #setDocumentReaderClass */ protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() { return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass); }
解读:
上述方法中documentReaderClass的定义如下
private Class<? extends BeanDefinitionDocumentReader> documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class;
registerBeanDefinitions方法
上述方法最终是调用了registerBeanDefinitions方法,对应代码如下
/** * This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD * (or DTD, historically). * <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings * specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions. */ @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { this.readerContext = readerContext; doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement()); }
解读:
BeanDefinitionReader与BeanDefinitionDocumentReader之间的关联是通过readerContext维护的。
后续流程是真正的解析bean配置文件的过程,代码如下:
/** * Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element. */ @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for Environment.acceptsProfiles(String...) protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { // Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); // We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported // in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details. if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); } return; } } } preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; }
/** * Parse the elements at the root level in the document: * "import", "alias", "bean". * @param root the DOM root element of the document */ protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
解读:
查看此方法的注释部分即可明确方法的目的。
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { processAliasRegistration(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { // recurse doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele); } }
解读:
观察上述代码的一个分支,代码如下:
/** * Process the given bean element, parsing the bean definition * and registering it with the registry. */ protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele); if (bdHolder != null) { bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder); try { // Register the final decorated instance. BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" + bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex); } // Send registration event. getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder)); } }
解读:
注意上述代码中着色(蓝色)部分代码,此处拿到了最前面传递的beanFactory。
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils
/** * Register the given bean definition with the given bean factory. * @param definitionHolder the bean definition including name and aliases * @param registry the bean factory to register with * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if registration failed */ public static void registerBeanDefinition( BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { // Register bean definition under primary name. String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName(); registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition()); // Register aliases for bean name, if any. String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases(); if (aliases != null) { for (String alias : aliases) { registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias); } } }
BeanDefinitionRegistry
/** * Register a new bean definition with this registry. * Must support RootBeanDefinition and ChildBeanDefinition. * @param beanName the name of the bean instance to register * @param beanDefinition definition of the bean instance to register * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if the BeanDefinition is invalid * @throws BeanDefinitionOverrideException if there is already a BeanDefinition * for the specified bean name and we are not allowed to override it * @see GenericBeanDefinition * @see RootBeanDefinition * @see ChildBeanDefinition */ void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
解读:
此处registerBeanDefinition方法为抽象方法,由子类(即BeanFactory的具体实现类)实现。
Note:
从上面的分析可知,最终bean的解析是由BeanDefinitionHolder实现的。
/** * Parses the supplied {@code <bean>} element. May return {@code null} * if there were errors during parse. Errors are reported to the * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter}. */ @Nullable public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) { String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE); String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE); List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) { String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr)); } String beanName = id; if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) { beanName = aliases.remove(0); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName + "' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases"); } } if (containingBean == null) { checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele); } AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); if (beanDefinition != null) { if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) { try { if (containingBean != null) { beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName( beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true); } else { beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); // Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible, // if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix. // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility. String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); if (beanClassName != null && beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) { aliases.add(beanClassName); } } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " + "using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]"); } } catch (Exception ex) { error(ex.getMessage(), ele); return null; } } String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases); return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray); } return null; }