初识ConcurrentHashMap
针对并发容器中的ConcurrentHashMap,《java并发编程实战》一书有如下这样一段文字:

ConcurrentHashMap的定义如下:
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable {
进而可得到如下类图:
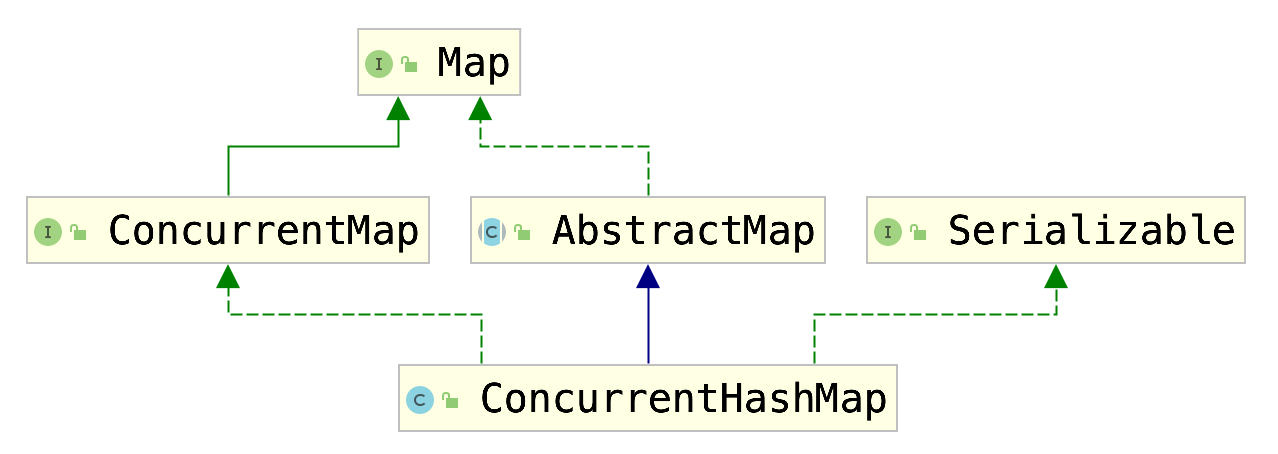
详述ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap利用了与HashMap相同的原则,但它是为多线程应用设计的,因此它不需要显式的同步。
此处先给出ConcurrentHashMap中数据的存储结构,如下图:

ConcurrentHashMap的锁分离技术
HashTable容器在竞争激烈的并发环境下效率低下,原因是所有访问HashTable的线程都必须竞争同一把锁。
若容器中有多把锁,每一把锁用于锁定容器其中一部分数据,那么当多线程访问容器里不同数据段的数据时,线程间就不会存在锁竞争,从而可以有效提高并发访问效率,这就是所谓的锁分段技术。
ConcurrentHashMap将数据分成一段一段,然后给每一段数据配一把锁,当一个线程占用锁并访问其中数据的时候,其他段的数据能被其他线程访问。

对比上图(该图摘自网络),同步容器HashTable实现锁的方式是锁整个hash表,而并发容器ConcurrentHashMap的实现方式是锁桶(简单理解就是将整个hash表想象成一大缸水,现在将这大缸里的水分到了几个水桶里,hashTable每次都锁定这个大缸,而ConcurrentHashMap则每次只锁定其中一个 桶)。
ConcurrentHashMap将hash表分为16个桶(默认值),get、put、remove等常用操作只锁当前需要用到的桶。
试想,原来只能一个线程进入,现在却能同时16个线程进入,并发性的提升是显而易见的。
源码解读
无参构造函数的定义如下:
/** * Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16). */ public ConcurrentHashMap() { }
指定初始容量的构造函数如下:
/** * Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size * accommodating the specified number of elements without the need * to dynamically resize. * * @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal * sizing to accommodate this many elements. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of * elements is negative */ public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, LOAD_FACTOR, 1); }
/** * Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on * the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), initial * table density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently * updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation * performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements, * given the specified load factor. * @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for * establishing the initial table size * @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently * updating threads. The implementation may use this value as * a sizing hint. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is * negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are * nonpositive */ public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor); int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size); this.sizeCtl = cap; }
put方法的定义如下:
/** * Maps the specified key to the specified value in this table. * Neither the key nor the value can be null. * * <p>The value can be retrieved by calling the {@code get} method * with a key that is equal to the original key. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or * {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key} * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null */ public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(key, value, false); }
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */ final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; K fk; V fv; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) tab = initTable(); else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else if (onlyIfAbsent // check first node without acquiring lock && fh == hash && ((fk = f.key) == key || (fk != null && key.equals(fk))) && (fv = f.val) != null) return fv; else { V oldVal = null; synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) { pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value); break; } } } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } else if (f instanceof ReservationNode) throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update"); } } if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } } addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
解释:
(1)concurrentHashMap不允许Key或者Value为null
(2)初次调用put方法时初始化table,table的定义如下:
/** * The array of bins. Lazily initialized upon first insertion. * Size is always a power of two. Accessed directly by iterators. */ transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
table中结点的定义如下:
/** * Key-value entry. This class is never exported out as a * user-mutable Map.Entry (i.e., one supporting setValue; see * MapEntry below), but can be used for read-only traversals used * in bulk tasks. Subclasses of Node with a negative hash field * are special, and contain null keys and values (but are never * exported). Otherwise, keys and vals are never null. */ static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V val; volatile Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V val) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.val = val; } Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { this(hash, key, val); this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return val; } public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); } public final String toString() { return Helpers.mapEntryToString(key, val); } public final V setValue(V value) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public final boolean equals(Object o) { Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e; return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) && (k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null && (v = e.getValue()) != null && (k == key || k.equals(key)) && (v == (u = val) || v.equals(u))); } /** * Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses. */ Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { Node<K,V> e = this; if (k != null) { do { K ek; if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } return null; } }
初始化代码如下:
/** * Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl. */ private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc; while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin else if (U.compareAndSetInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { try { if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; table = tab = nt; sc = n - (n >>> 2); } } finally { sizeCtl = sc; } break; } } return tab; }
(3)
/* ---------------- Table element access -------------- */ /* * Atomic access methods are used for table elements as well as * elements of in-progress next table while resizing. All uses of * the tab arguments must be null checked by callers. All callers * also paranoically precheck that tab's length is not zero (or an * equivalent check), thus ensuring that any index argument taking * the form of a hash value anded with (length - 1) is a valid * index. Note that, to be correct wrt arbitrary concurrency * errors by users, these checks must operate on local variables, * which accounts for some odd-looking inline assignments below. * Note that calls to setTabAt always occur within locked regions, * and so require only release ordering. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) { return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectAcquire(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE); } static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) { return U.compareAndSetObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v); } static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) { U.putObjectRelease(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v); }
ConcurrentHashMap的remove操作
当对ConcurrentHashMap进行remove操作时,并不是进行简单的结点删除操作

根据上图,当对ConcurrentHashMap的一个元素(也就是一个桶中的节点)进行remove,例如:删除结点C,结点C实际并没有被销毁,而是将结点C前面的元素反转并拷贝到新的链表中,结点C后面的不需要被克隆。
这样的操作使读线程不受并发的写线程的干扰,例如,现在有一个读线程读到了结点A,写线程把C删掉了,读线程仍然可以继续读下去;当然,如果在删除C之前读线程读到的是D,那么更不会有影响。
由于在ConcurrentHashMap中删除一个结点并不会立刻被读线程感受到,所以ConcurrentHashMap的迭代器是弱一致性迭代器。