实验三 线程同步编程练习
【要求】所有练习题保留题目要求,在题目要求后面作答:
代码要求有注释,代码中适当标注关键代码为红色。
要有运行结果的截图。
每题最后应该有对程序的适当分析和总结!
注意格式排版,内容分析注意列条目,展开清楚地阐述。
1、分析理解多线程执行中的互斥与同步
1)加入合适的sleep语句,运行体验ppt中的案例,重点是要给出运行效果并详细分析过程,没有分析说明的作业没有成绩。

代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
int n;
//设置信号量(生产者和消费者的full与empty)
sem_t product,empty;
void *eat(void *arg){
while(1){
printf("** SON WANT TO EAT FRUIT ");
//在消费者消费之前首先要获取信号量full(product)即确保有产品
sem_wait(&product);
sem_getvalue(&product,&n);
printf("** There are %d fruits now ",n);
//释放空信号量
sem_post(&empty);
//休眠等待
sleep(1);
}//while
}
void *putfruit(void *arg){
while (1) {//main thread ,put fruit
printf("Main thread want to put fruit ");
//在生产者生产之前首先要获取信号量empty即确保产品为空,可继续添加
sem_wait(&empty);
sleep(10);
//释放满信号量
sem_post(&product);
sem_getvalue(&product,&n);
printf("Main: putting fruit in a secs,fruits is %d ",n);
}//while
}
int main(){
pthread_t threadP,threadC;
void *thread_result1,*thread_result2;
int semi,ret1,ret2;
semi = sem_init(&empty, 0, 5); //初始设置5个空资源,生产者可连续放入5次
if (semi == -1) {
printf("sem_init empty failed ");
return -1;
}
semi = sem_init(&product, 0, 0); //初始设置0个产品数
if (semi == -1) {
printf("sem_init product failed ");
return -1;
}
ret1 = pthread_create(&threadC, NULL,eat,NULL);
ret2 = pthread_create(&threadP, NULL,putfruit,NULL);
if (ret1 != 0|ret2!=0) {
printf("pthread_create failed ");
return -1;
}
ret1 = pthread_join(threadC, &thread_result1);
ret2 = pthread_join(threadP, &thread_result2);
if (ret1!=0||ret2!=0){
perror("Thread join failed! ");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}//if error
return 0;
} //main
运行代码截图:

运行分析请详见代码(含分析)。
2)加入合适的sleep语句,运行体验ppt中的案例,重点是要给出运行效果并详细分析过程,没有分析说明的作业没有成绩。

代码:
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
int count=0; //条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond; //互斥量
pthread_mutex_t mutex=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *producer(void *mesgP){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
//互斥锁关锁
count++;
printf("%s produce ont product,count = %d ",mesgP,count);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
//互斥锁开锁
sleep(rand()%3);//0-3
}//while producer
}
void *consumer(void *mesgC){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
//给互斥量mutex加锁
while(count<=0){
//根据count条件决定消费者进程
//是否阻塞在条件变量 (#)
printf("%s wait a condition... ",mesgC);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}//while count
count--;
printf("%s one item,count = %d ",mesgC,count);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand()%10);//0-9
//设置消费者睡眠时间比生产者长,模拟消费速度慢的情况
}//whlie consumer
}
int main(void){
pthread_t threadP,threadC;
char *mesgC = "CONSUMER";
char *mesgP = "PRODUCER";
pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
//初始化条件变量cond
pthread_create(&threadC,NULL, consumer,(void*)mesgC);
pthread_create(&threadP,NULL, producer,(void*)mesgP);
pthread_join(threadC,NULL);
pthread_join(threadP,NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
//销毁条件变量cond
}
运行代码截图:

运行分析请详见代码(含分析)。
2、编写代码模拟实现如下逻辑要求:
1)编写程序让主进程产生两个线程,主进程等待线程共同对共享的进程的长整型变量x做加1操作,当加和到100000时停止工作,主进程在线程结束后输出加和后的结果。如果不加同步控制为什么会加得错的数?
继续给出加入同步控制代码后的实现,使两个线程共同使进程中的x变量做百万次的加法操作但输出得到正确结果。注意不仅要有源码,还要有运行结果,有说明分析!!!!
加入同步互斥限制前:
代码:
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;//条件变量
long x=0,y=0,z=0;
void *thread_function1(void *arg)
{
while(x<100000){
x++;
y++;
}
}
void *thread_function2(void *arg)
{
while(x<100000){
x++;
z++;
}
}
int main()
{
int res,k;
pthread_t thread1;
pthread_t thread2;
void *thread_result;
res=pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,thread_function1,NULL);
res=pthread_create(&thread2,NULL,thread_function2,NULL);
sleep(1);
printf("%lld %lld %lld ",x,y,z);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
运行结果截图:

分析:在上面我们可以看出在不加同步控制条件时可能会出现错误(比如最后一条,这是因为在两个线程中一个线程获取x时x=99999,此时继续运行,但另一线程此时也获取了x=99999继续运行,此时就造成了两个线程同时对x进行++操作导致结果错误)(程序中x未来得及回写就被中断掉(可对比y,z的值得出结论))
加入同步互斥限制后:
代码:
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;//条件变量
long x=0,y=0,z=0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//互斥信号量
void *thread_function1(void *arg)
{
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//互斥锁关锁
if(x==100000)break;
x++;
y++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void *thread_function2(void *arg)
{
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//互斥锁关锁
if(x==100000) break;
x++;
z++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main()
{
int res,k;
pthread_t thread1;
pthread_t thread2;
void *thread_result;
res=pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,thread_function1,NULL);
res=pthread_create(&thread2,NULL,thread_function2,NULL);
sleep(1);
printf("%lld %lld %lld ",x,y,z);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
运行结果截图:

分析:加入同步互斥限制后,我们每次运行都可以得出正确结论,我们可以从x,y,z中的条件关系上得出结论(x=y+z)
2)设两个围棋选手下棋,黑先白后,交替下子,但黑方棋艺较高,开局会让对方3个子。试编程模拟两下棋进程之间的落子过程。要有源码,有运行结果,有说明分析!!!!
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int x=0;
sem_t _empty,product;
pthread_mutex_t mutex=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//互斥信号量
void *white(void *arg){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//互斥锁关锁
sem_wait(&_empty);
if(x<2){
x++;
sem_post(&_empty);
}else if(x==2){
x++;
sem_post(&product);
}else{
sem_post(&product);
}
printf("白子落 ");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
usleep(300);
}
}
void *black(void *arg){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(x>2){
sem_wait(&product);
printf("黑子落 ");
sem_post(&_empty);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
usleep(300);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t threadP,threadC;
sem_init(&_empty,0,1);
sem_init(&product,0,0);
pthread_create(&threadC,NULL,black,NULL);
pthread_create(&threadP,NULL,white,NULL);
pthread_join(threadC,NULL);
pthread_join(threadP,NULL);
}
运行截图:
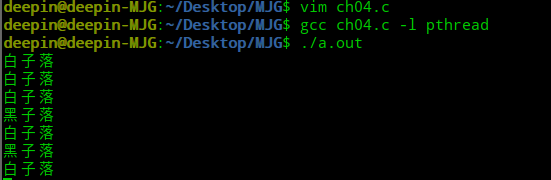
运行分析请详见代码。