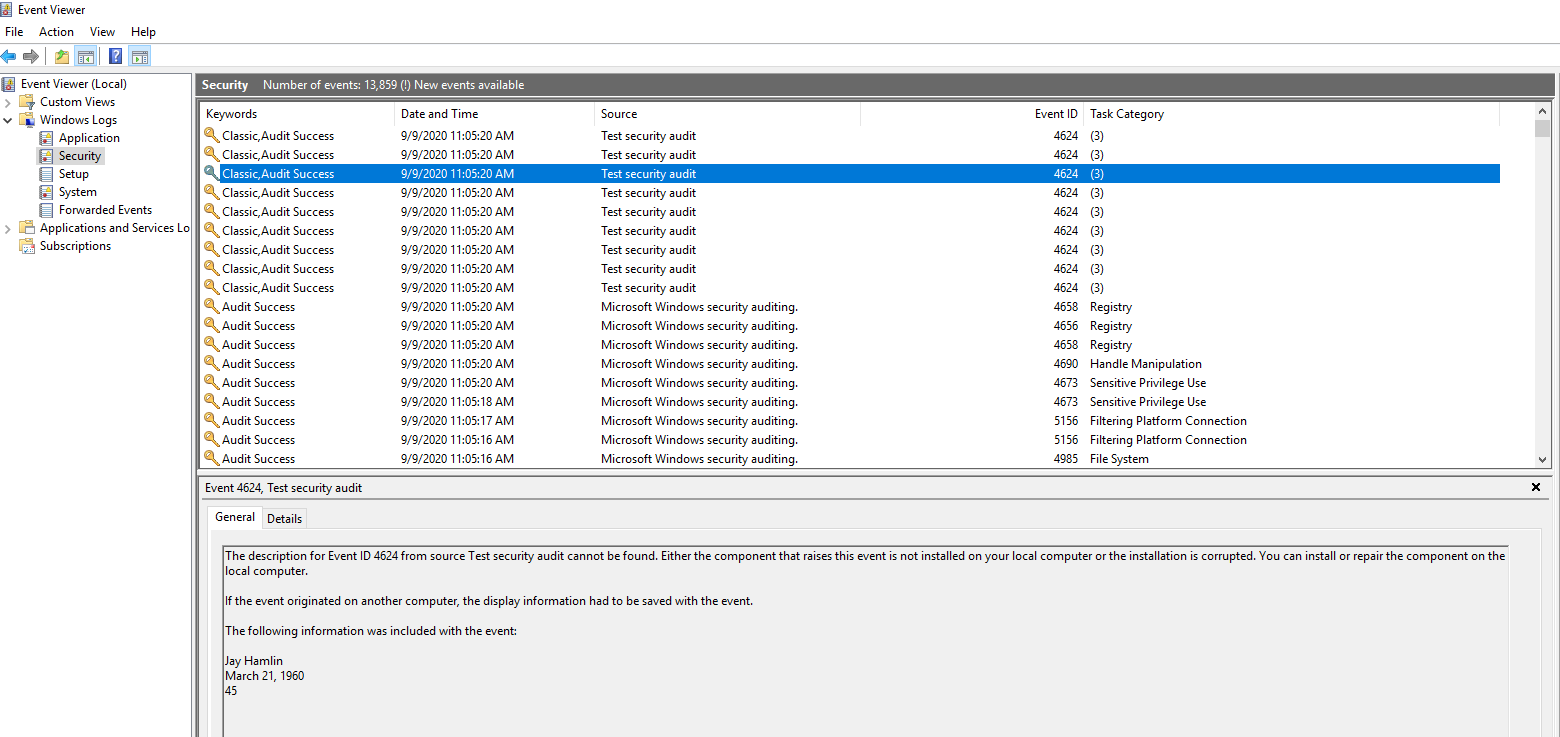
微软文档介绍说,
安全日志在其他两个重要方面与其他日志不同。首先,在默认配置中,它受到强大的访问控制列表(ACL)和特权检查的保护,这将可以读取其内容的个人的范围限制为本地系统,管理员和安全特权的持有者。其次,也是最重要的一点,只允许一个实体(本地安全机构(LSA))写入安全日志。这实际上意味着,每次尝试为安全日志调用RegisterEventSource API时,即使您以本地系统身份运行,也会收到ACCESS_DENIED错误!这种设计可确保安全日志仅包含来自受信任来源的信息。
在Windows Server 2003中,安全日志写访问限制在某种程度上得到了放松,而没有通过引入一组特殊的API来更改基本设计(请参见图2)。这些API在内部使用本地过程调用(LPC)与LSA进行交互,指示LSA代表应用程序生成审核日志。该机制优雅而简单。
首先,应用程序通过调用AuthzRegisterSecurityEventSource向LSA注册安全事件源句柄。此API唯一感兴趣的参数是事件源的名称,该名称可以是几乎任何内容,并受一些限制。例如,它不能命名为“ Security”,因为该名称保留供系统使用。在以下步骤中使用此调用返回的安全事件源句柄。
接下来,通过调用两个紧密相关的API之一来生成事件:AuthzReportSecurityEvent或AuthzReportSecurityEventFromParams。最后,当应用程序关闭时,它将通过调用AuthzUnregisterSecurityEventSource取消注册安全事件源句柄。
在编译代码之前,我们需要赋予当前用户相关的权限,也就是Generate Security audits
具体步骤:
在开始菜单中,打开Local Security Policy,如下图,
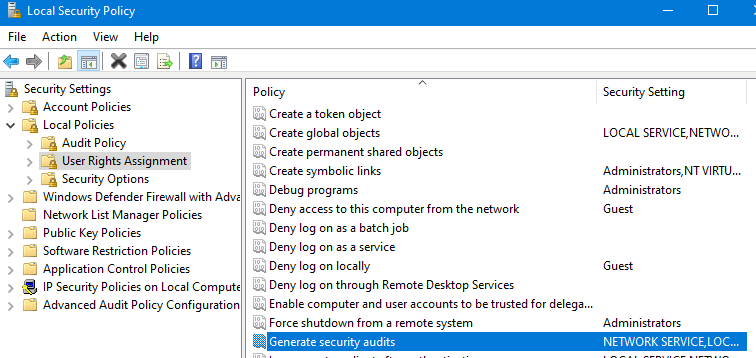
找到Generate Security audits, 在里面添加当前用户,我们的计算机一般是以管理员身份运行的,所以可以将管理员也添加进来(添加完需要将电脑重启,以使组策略生效)。
如果是以管理员身份运行的,那么我们在编译代码时,也需要以管理员身份运行代码。不然还是无法获取SeAuditPrivilege权限。
另外,我们还需要在Audit Policy中Enable Audit object access的Success,Failure, 见下图,

代码示例:
#include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <strsafe.h> #include <windows.h> #include <Authz.h> #include <Ntsecapi.h> #define STATUS_SUCCESS ((NTSTATUS)0x00000000L) #pragma comment(lib,"Authz.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"Advapi32.lib") void print_privileges(HANDLE hToken); BOOL SetPrivilege( HANDLE hToken, // access token handle LPCTSTR lpszPrivilege, // name of privilege to enable/disable BOOL bEnablePrivilege // to enable or disable privilege ) { TOKEN_PRIVILEGES tp; LUID luid; if (!LookupPrivilegeValue( NULL, // lookup privilege on local system lpszPrivilege, // privilege to lookup &luid)) // receives LUID of privilege { printf("LookupPrivilegeValue error: %u ", GetLastError()); return FALSE; } tp.PrivilegeCount = 1; tp.Privileges[0].Luid = luid; if (bEnablePrivilege) tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED; else tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = 0; // Enable the privilege or disable all privileges. if (!AdjustTokenPrivileges( hToken, FALSE, &tp, sizeof(TOKEN_PRIVILEGES), (PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES)NULL, (PDWORD)NULL)) { printf("AdjustTokenPrivileges error: %u ", GetLastError()); return FALSE; } if (GetLastError() == ERROR_NOT_ALL_ASSIGNED) { printf("The token does not have the specified privilege. "); return FALSE; } printf("Get the specified privilege! "); return TRUE; } int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) { // Declare and initialize variables. BOOL bResult = TRUE; DWORD event_id = 4624; AUTHZ_SECURITY_EVENT_PROVIDER_HANDLE hEventProvider = NULL; PAUDIT_PARAMS p; std::string Source_Name = "Test security audit"; std::wstring ws; std::string pbuf = "What is your purpose ?"; std::wstring ws_buf; int return_code = 0; int i = 0; // Register the audit provider. HANDLE token; HANDLE hevent_source; ws.assign(Source_Name.begin(), Source_Name.end()); ws_buf.assign(pbuf.begin(), pbuf.end()); if (!OpenProcessToken(GetCurrentProcess(), TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES | TOKEN_QUERY, &token)) return FALSE; SetPrivilege(token, L"SeAuditPrivilege", true); print_privileges(token); AUTHZ_SOURCE_SCHEMA_REGISTRATION ar; memset(&ar, 0, sizeof(ar)); ar.dwFlags = AUTHZ_ALLOW_MULTIPLE_SOURCE_INSTANCES; ar.szEventSourceName = &ws[0]; ar.szEventMessageFile = &ws_buf[0]; ar.szEventSourceXmlSchemaFile = NULL; ar.szEventAccessStringsFile = &ws_buf[0]; ar.szExecutableImagePath = NULL; AuthzInstallSecurityEventSource(0, &ar); bResult = AuthzRegisterSecurityEventSource(0, ws.c_str(), &hEventProvider); int err = GetLastError(); if (!bResult) { printf("AuthzRegisterSecurityEventSource failed, error is %d ", err); return_code = -1; } SID id; if (hEventProvider) { // Generate the audit. while (i < 10) { bResult = AuthzReportSecurityEvent( APF_AuditSuccess, hEventProvider, event_id, NULL, 3, APT_String, L"Jay Hamlin", APT_String, L"March 21, 1960", APT_Ulong, 45); int err1 = GetLastError(); if (!bResult) { printf("AuthzReportSecurityEvent failed, error is %d ", err1); return_code = -2; break; } i++; } AuthzUnregisterSecurityEventSource(0, &hEventProvider); AuthzUninstallSecurityEventSource(0, &ws[0]); } std::cout << "Exit : " << return_code << std::endl; getchar(); } void print_privileges(HANDLE hToken) { DWORD size = 0; if (!GetTokenInformation(hToken, TokenPrivileges, NULL, 0, &size) && GetLastError() == ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER) { PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES tp = (PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES)malloc(size); if (tp != NULL && GetTokenInformation(hToken, TokenPrivileges, tp, size, &size)) { size_t i; for (i = 0; i < tp->PrivilegeCount; ++i) { char name[64] = "?"; DWORD name_size = sizeof name; LookupPrivilegeNameA(0, &tp->Privileges[i].Luid, name, &name_size); PRIVILEGE_SET ps = { 1, PRIVILEGE_SET_ALL_NECESSARY, { { { tp->Privileges[i].Luid.LowPart, tp->Privileges[i].Luid.HighPart } } } }; BOOL fResult; PrivilegeCheck(hToken, &ps, &fResult); printf("%-*s %s ", 32, name, fResult ? "Enabled" : "Disabled"); } } free(tp); } }
在运行过程中,首先确定是否获取了我们需要的权限。
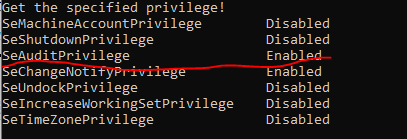
如果是Enabled的状态,说明获取权限成功,后面只需要通过AuthzRegisterSecurityEventSource和AuthzReportSecurityEvent这两个api与LSA进行交互,从而写入安全日志。
最后的结果: