一:概念
在Mediator模式中,类之间的交互行为被统一放在Mediator的对象中,对象通过Mediator对象同其他对象交互。Mediator对象起到控制器的作用
二:动机
在软件构建的过程中,经常出现多个对象互相关联交互的情况,对象之间常常会维持一种复杂的引用关系,如果遇到了一些需求的更改,这种直接的引用关系将面临不断的变化。在这种情况下,我们可以使用“中介对象”来管理对象间的关联关系,避免相互交互的对象之间的紧耦合引用关系,从而更好地抵御变化。
在这种情况下,我们可使用一个“中介对象”来管理对象间的关联关系,避免相互交互的对象之间额紧耦合引用关系,从而更好地抵御变化。
三:模式定义
用一个中介对象来封装(封装变化)一系列的对象交互。中介者使各个对象不需要显示的相互引用(编译时依赖 -> 运行时依赖),从而使其耦合松散(管理变化),而且可以独立的改变他们之间的交互。
--《设计模式》Gof
四:结构
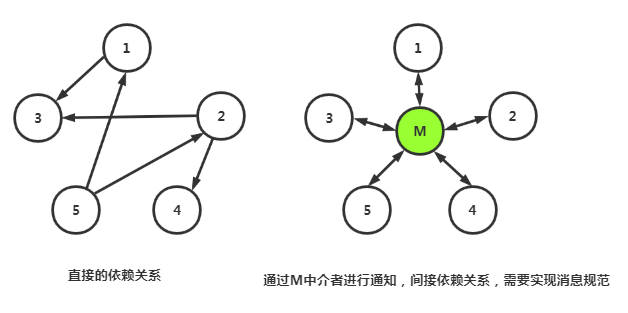
五:与Facade模式比较
Facade是系统外与系统内之间的隔离,而中介者Mediator解决的是系统内中各个对象之间的隔离。
多个对象,呈现复杂的引用关系时使用Mediator模式
六:类图
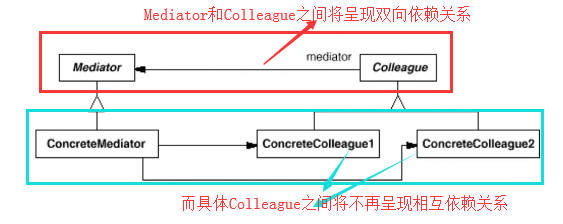
七:要点总结
(一)将多个对象间复杂的关联关系解耦,Mediator模式将多个对象间的控制逻辑进行集中管理(定义一套调用机制的协议),变“多个对象互相关联”为“多个对象和一个中介者关联”,简化了系统的维护,抵御了可能的变化。
(二)随着控制逻辑的复杂化,Mediator具体对象的实现可能相当复杂。这时候可以对Mediator对象进行分解处理。
(三)Facade模式是解耦系统间(单向)的对象关联关系;Mediator模式是解耦系统内各个对象之间(双向)的关联关系。
八:案例实现
(一)反例:类的紧密性抢,需要解耦合
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
protected:
string m_name;
int m_sex;
int m_condition;
public:
Person(string name, int sex, int condit)
{
m_name = name;
m_sex = sex;
m_condition = condit;
}
string getName()
{
return m_name;
}
int getSex()
{
return m_sex;
}
int getCondit()
{
return m_condition;
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p) = 0; //接口获取伴侣
};
class Man :public Person
{
public:
Man(string name, int sex, int condit) :Person(name, sex, condit)
{
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p)
{
if (this->getSex() == p->getSex())
{
cout << "no I`m don't same sex" << endl;
}
else
{
if (this->getCondit() == p->getCondit())
cout << this->getName() << " matching with " << p->getName() << endl;
else
cout << this->getName() << " not matching with " << p->getName() << endl;
}
}
};
class Woman :public Person
{
public:
Woman(string name, int sex, int condit) :Person(name, sex, condit)
{
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p)
{
if (this->getSex() == p->getSex())
{
cout << "no I`m don't same sex" << endl;
}
else
{
if (this->getCondit() == p->getCondit())
cout << this->getName() << " matching with " << p->getName() << endl;
else
cout << this->getName() << " not matching with " << p->getName() << endl;
}
}
};
void main()
{
Woman *w1 = new Woman("xioafang", 2, 4);
Man* m1 = new Man("zhangsan", 1, 3);
Man* m2 = new Man("lisi", 1, 4);
w1->getParter(m1);
w1->getParter(m2);
m1->getParter(m2);
delete w1;
delete m2;
delete m1;
system("pause");
return;
}
(二)使用中介者模式进行解耦合
1.实现系统内对象
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Mediator;
class Person
{
protected:
string m_name;
int m_sex;
int m_condition;
Mediator* m_m;
public:
Person(string name, int sex, int condit,Mediator* m)
{
m_name = name;
m_sex = sex;
m_condition = condit;
m_m = m;
}
string getName()
{
return m_name;
}
int getSex()
{
return m_sex;
}
int getCondit()
{
return m_condition;
}
Mediator* getMediator()
{
return m_m;
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p) = 0; //接口获取伴侣
};
class Man :public Person
{
public:
Man(string name, int sex, int condit,Mediator* m) :Person(name, sex, condit,m)
{
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p)
{
//使用中介者来实现判断
this->getMediator()->setMan(this);
this->getMediator()->setWoman(p);
this->getMediator()->getPartner();
}
};
class Woman :public Person
{
public:
Woman(string name, int sex, int condit, Mediator* m) :Person(name, sex, condit,m)
{
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p)
{
//使用中介者来实现判断
this->getMediator()->setWoman(this);
this->getMediator()->setMan(p);
this->getMediator()->getPartner();
}
};
2.实现中介者
class Mediator
{
private:
Person* pMan; //中介者Mediator解决的是系统内中各个对象之间的隔离
Person* pWoman; //所以我们要对所有要处理的类设置一个指针,实现双向关联(上面Person基类指向了中介者,代表Man和Woman都指向了,现在要中介者执行Man和Woman)
public:
Mediator()
{
pMan = NULL;
pWoman = NULL;
}
void setWoman(Person* p)
{
pWoman = p;
}
void setMan(Person* p)
{
pMan = p;
}
void getPartner()
{
if (pMan->getSex() == pWoman->getSex())
{
cout << "no I`m don't same sex" << endl;
}
else
{
if (pMan->getCondit() == pWoman->getCondit())
cout << pMan->getName() << " matching with " << pWoman->getName() << endl;
else
cout << pMan->getName() << " not matching with " << pWoman->getName() << endl;
}
}
};
3.中介者测试
void main()
{
Mediator* mediator = new Mediator();
Woman *w1 = new Woman("xioafang", 2, 4,mediator);
Man* m1 = new Man("zhangsan", 1, 3,mediator);
Man* m2 = new Man("lisi", 1, 4,mediator);
w1->getParter(m1);
w1->getParter(m2);
m1->getParter(m2);
delete w1;
delete m2;
delete m1;
delete mediator;
system("pause");
return;
}


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Mediator;
class Person
{
protected:
string m_name;
int m_sex;
int m_condition;
Mediator* m_m;
public:
Person(string name, int sex, int condit,Mediator* m)
{
m_name = name;
m_sex = sex;
m_condition = condit;
m_m = m;
}
string getName()
{
return m_name;
}
int getSex()
{
return m_sex;
}
int getCondit()
{
return m_condition;
}
Mediator* getMediator()
{
return m_m;
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p) = 0; //接口获取伴侣
};
class Mediator
{
private:
Person* pMan; //中介者Mediator解决的是系统内中各个对象之间的隔离
Person* pWoman; //所以我们要对所有要处理的类设置一个指针,实现双向关联(上面Person基类指向了中介者,代表Man和Woman都指向了,现在要中介者执行Man和Woman)
public:
Mediator()
{
pMan = NULL;
pWoman = NULL;
}
void setWoman(Person* p)
{
pWoman = p;
}
void setMan(Person* p)
{
pMan = p;
}
void getPartner()
{
if (pMan->getSex() == pWoman->getSex())
{
cout << "no I`m don't same sex" << endl;
}
else
{
if (pMan->getCondit() == pWoman->getCondit())
cout << pMan->getName() << " matching with " << pWoman->getName() << endl;
else
cout << pMan->getName() << " not matching with " << pWoman->getName() << endl;
}
}
};
class Man :public Person
{
public:
Man(string name, int sex, int condit,Mediator* m) :Person(name, sex, condit,m)
{
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p)
{
//使用中介者来实现判断
this->getMediator()->setMan(this);
this->getMediator()->setWoman(p);
this->getMediator()->getPartner();
}
};
class Woman :public Person
{
public:
Woman(string name, int sex, int condit, Mediator* m) :Person(name, sex, condit,m)
{
}
virtual void getParter(Person* p)
{
//使用中介者来实现判断
this->getMediator()->setWoman(this);
this->getMediator()->setMan(p);
this->getMediator()->getPartner();
}
};
void main()
{
Mediator* mediator = new Mediator();
Woman *w1 = new Woman("xioafang", 2, 4,mediator);
Man* m1 = new Man("zhangsan", 1, 3,mediator);
Man* m2 = new Man("lisi", 1, 4,mediator);
w1->getParter(m1);
w1->getParter(m2);
m1->getParter(m2);
delete w1;
delete m2;
delete m1;
delete mediator;
system("pause");
return;
}
全部代码





