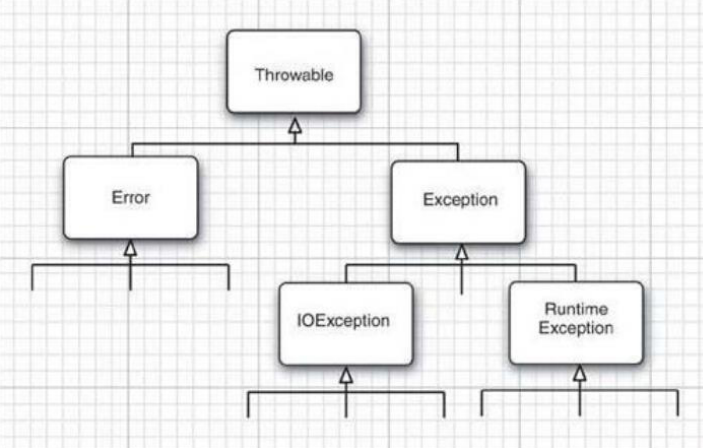
一:异常分类
Throwable:所有错误的祖先。
Error:系统内部错误或者资源耗尽。不用我们管
Exception: 程序有关的异常。重点关注
–RuntimeException: 程序自身的错误
• 5/0,空指针,数组越界…
–非RuntimeException:外界相关的错误
• 打开一个不存在文件
• 加载一个不存在的类...
(一)checked exception(IDE会直接显示出错)
非RuntimeException的Exception的子类: (编译器会辅助检查的)异常,checked exception。
注意: 编译器会检查程序是否为checked exception 配置了处理。如果没有处理,会报错。
Checked Exception(非RuntimeException的Exception的子类),程序员必须处理,以发生后处理为主。编译器会辅助检查
未编译运行:IDE直接指出
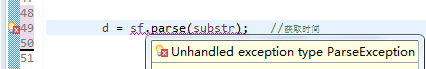
必须需要我们处理
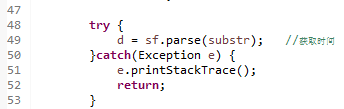
(二)Unchecked Exception(IDE不会指出,编译通过,若是运行到此处,才会报错)
Unchecked Exception : (编译器不会辅助检查的,需要程序员自己管的)异常,包括Error子类和RuntimeException子类
Unchecked Exception中的RuntimeException子类,程序必须处理,以预防为主。编译器不关心此类异常,也不会辅助检查。
Error的子类,可以不用处理
IDE不会报错,编译通过
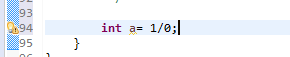
运行报错
总结:
异常是程序发生不正常的行为或出现不正常的状态
Java异常分成Exception(程序相关)和Error(系统相关)
Java程序相关的异常又分成unchecked 异常和checked异常,掌握其不同的处理原则
编译器会辅助检查checked异常
二:异常处理:try-catch-finally
try…catch(catch可以有多个,下同)
try…catch…finally
try…finally
try: 正常业务逻辑代码。
catch: 当try发生异常,将执行catch代码。若无异常,绕之。
finally: 当try或catch执行结束后,必须要执行finally
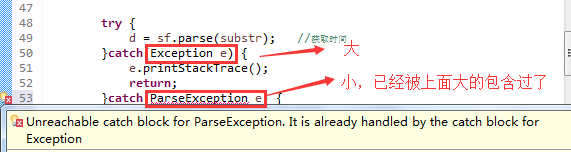
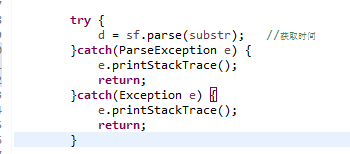
catch块的异常匹配是从上而下进行匹配的。
所以一般是将小的异常写在前面,而一些大(宽泛)的异常则写在末尾
三:异常声明和抛出throws,throw
方法存在可能异常的语句,但不处理,那么可以使用throws来声明异常。
调用带有throws异常(checked exception)的方法,要么处理这些异常,或者再次向外throws,直到main函数为为止
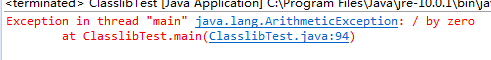
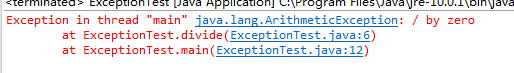
public class ExceptionTest {
//ArithmeticException is a RuntimeException, not checked exception
public int divide(int x, int y) throws ArithmeticException //编译器不会检查,可能会报错,需要我们最好在main函数或者调用函数中进行处理异常
{
int result = x/y;
return x/y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionTest et=new ExceptionTest();
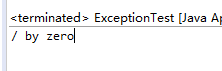
et.divide(1, 0); //不处理会报错
}
}
try {
et.divide(1, 0); //进行异常捕获
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
四:类方法中异常抛出
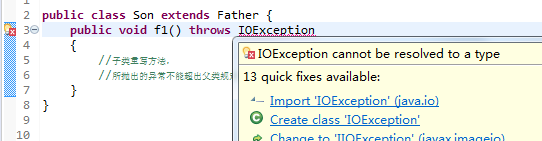
一个方法被覆盖,覆盖它的方法必须抛出相同的异常,或者异常的子类。 //可以不被覆盖,不会报错
如果父类的方法抛出多个异常,那么重写的子类方法必须抛出那些异常的子集,也就是不能抛出新的异常。
public class Father {
public void f1() throws ArithmeticException
{
}
}
(一)不允许抛出更大类

(二)不允许抛出新的类
(三)可以抛出相同异常或者子类

(四)可以不抛出异常《重点》
子类也可以选择不进行抛出任何异常,即使他们是父类所定义的异常。

五:自定义异常
Exception类是所有异常的父类。
Exception继承自java.lang.Throwable,同时它有一个兄弟Error。
Error是更严重的问题,一般是系统层面的,无需程序处理。
程序只需要处理Exception
(一)自定义规则《重点》
自定义异常,需要继承Exception类或其子类。
–继承自Exception,就变成Checked Exception
–继承自RuntimeException, 就变成Unchecked Exception
自定义重点在构造函数
–调用父类Exception的message构造函数
–可以自定义自己的成员变量
在程序中采用throw主动抛出异常
(二)自定义异常类
public class MyException extends Exception {
private String returnCode ; //异常对应的返回码
private String returnMsg; //异常对应的描述信息
public MyException() {
super();
}
public MyException(String returnMsg) {
super(returnMsg);
this.returnMsg = returnMsg;
}
public MyException(String returnCode, String returnMsg) {
super();
this.returnCode = returnCode;
this.returnMsg = returnMsg;
}
public String getReturnCode() {
return returnCode;
}
public String getreturnMsg() {
return returnMsg;
}
}
(二)自定义异常类抛出
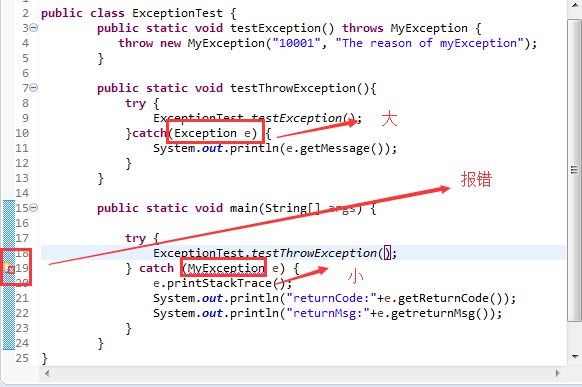
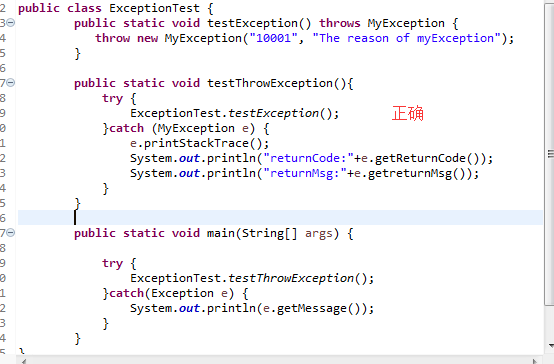
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void testException() throws MyException {
throw new MyException("10001", "The reason of myException");
}
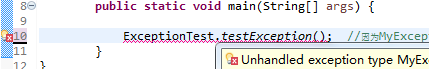
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionTest.testException(); //不会通过编译,因为没有处理checked异常
}
}
在方法声明使用throws,在函数中抛出异常使用throw
因为MyException是继承自Exception,checked异常,IDE会进行判断,不会通过,必须处理该异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
try { //编译通过
ExceptionTest.testException();
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("returnCode:"+e.getReturnCode());
System.out.println("returnMsg:"+e.getreturnMsg());
}
}
(三)对于checked异常,要么方法继续向外throws,要么就进行try...catch处理
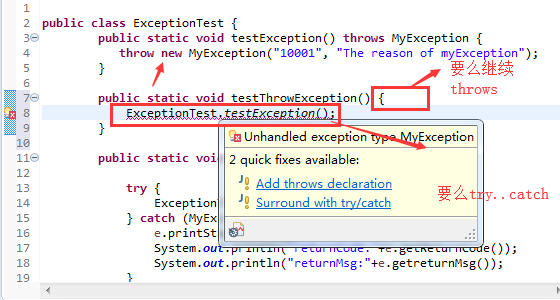
1.throws异常

2.进行捕获try...catch,但是注意大范围在后面
六:练习
(一)throws相关
import java.io.*;
class Master{
String doFileStuff() throws FileNotFoundException{
return "a";
}
}
class slave extends Master{
public static void main(String[] args){
String s = null;
try{
s = new slave().doFileStuff();
}catch(Exception x){
s = "b";
}
System.out.println(s);
}
// insert code here
}
Which, inserted independently at // insert code here, will compile, and produce the output b? (Choose all that apply.)
A.String doFileStuff() { return "b"; }
B.String doFileStuff() throws IOException { return "b"; } //新
C.String doFileStuff(int x) throws IOException { return "b"; } //新,且不是重写
D.String doFileStuff() throws Exception { return "b"; } //大
(二)throw相关
class Plane {
static String s = "-";
public static void main(String[] args){
new Plane().s1();
System.out.println(s);
}
void s1() {
try{
s2();
}catch (Exception e){
s += "c";
}
}
void s2() throws Exception {
s3();
s += "2";
s3();
s += "2b";
}
void s3() throws Exception{
throw new Exception();
}
}
void s2() throws Exception {
s3(); //会直接抛出异常,下面的代码不会执行
s += "2";
s3();
s += "2b";
}
(三)main参数args默认为null,0个
class MultiCatch
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
int a=args.length;
int b=42/a;
int c[]={1};
c[42]=99; //10行
System.out.println(“b=”+b);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println(“除0异常:”+e); //15行
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(“数组超越边界异常:”+e); //19行
}
}
}
A.程序将输出第15行的异常信息
B.程序第10行出错
C.程序将输出“b=42”
D.程序将输出第19行的异常信息

















