简介
TensorFlow是一个实现机器学习算法的接口,也是执行机器学习算法的框架。使用数据流式图规划计算流程,可以将计算映射到不同的硬件和操作系统平台。
主要概念
TensorFlow的计算可以表示为有向图(directed graph),或者计算图(computation graph),计算图描述了数据的就算流程,其中每个运算操作(operation)作为一个节点(node),节点与节点之间连接称为边(edge)。在计算图变中流动(flow)的数据被称为张量(tensor),故称TensorFlow。

计算图实例[ref1]
具体说,在一次运算中[ref2]:
1. 使用图 (graph) 来表示计算任务:基本操作示例 ;
2. 在被称之为 会话 (Session) 的上下文 (context) 中执行图:基本操作示例;
3. 通过 变量 (Variable) 维护状态:基本操作示例。
代码实例
完整示例:
#!/usr/bin/pyton
'''
A simple example(linear regression) to show the complete struct that how to run a tensorflow
create_data -> create_tensorflow_struct->start session
create date: 2017/10/20
'''
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
#create data
x_data = np.random.rand(100).astype(np.float32)
y_data = x_data*0.1 + 0.3
###create tensorflow structure begin##
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1], -1.0, 1.0))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
y = Weights*x_data + biases
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_data))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
#when define variables, initialize must be called
#init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
### create tensorflow structure end ###
sess = tf.Session()
#note: initialize_local_variables no more support in new version
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
for step in range(201):
sess.run(train)
if step % 20 == 0:
#session controls all opertions and varilables
print(step, sess.run(Weights), sess.run(biases))
sess.close()
计算结果:
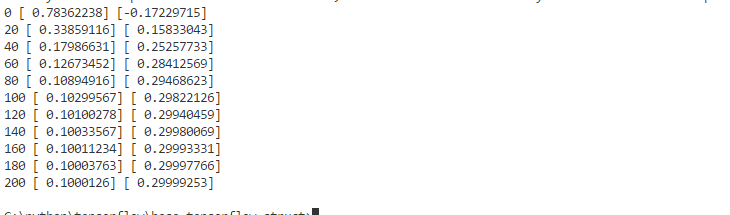
基本操作示例
Session操作:
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
A example to show how to call session
create date: 2017/10/20
'''
import tensorflow as tf
#1. 定义一个操作
m1 = tf.constant([[2, 2]])
m2 = tf.constant([[3],
[3]])
dot_opeartion = tf.matmul(m1, m2)
#2. 调用session实现
# 图画好以后,需要通过session来控制执行,让图来运行
# 另外每一个图中的操作都需要通过session来控制
# print result
#method1 use session
sess = tf.Session()
result = sess.run(dot_opeartion)
print(result)
sess.close()
#method2 use session
with tf.Session() as sess:
result_ = sess.run(dot_opeartion)
print(result_)
##output
[[12]]
[[12]]
Placeholder操作
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
A example to show how to call placehoder(类似于占位符)
create date: 2017/10/20
'''
import tensorflow as tf
#1. 声明placehoder:待传入值
x1 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=None)
y1 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=None)
z1 = x1 + y1
x2 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=None)
y2 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=None)
z2 = tf.matmul(x2, y2)
#2. 调用session,传入值
with tf.Session() as sess:
#when only one operation to run
#feed_dict: input the values into placeholder
z1_value = sess.run(z1, feed_dict={x1: 1, y1:2})
# when run multiple operaions
#run the two opeartions together
z1_value, z2_value = sess.run(
[z1, z2],
feed_dict={
x1:1, y1:2,
x2:[[2],[2]], y2:[[3,3]]
}
)
print(z1_value)
print(z2_value)
Variable操作
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
A example to show how to call variables
create date: 2017/10/20
'''
import tensorflow as tf
# 1.stuct
#our first variable in the "global_variable" set
var = tf.Variable(0)
add_operation = tf.add(var,1)
#把add_operation值给var
update_operation = tf.assign(var, add_operation)
# once define variables, you have to initialize them by doing this
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 2. call session
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for count in range(3):
sess.run(update_operation)
print(sess.run(var))
--------------------------------------
说明:本列为前期学习时记录,为基本概念和操作,不涉及深入部分。文字部分参考在文中注明,代码参考莫凡