IO流
IO流主要分为字符流和字节流,下面给出字符流和字节流的结构图:
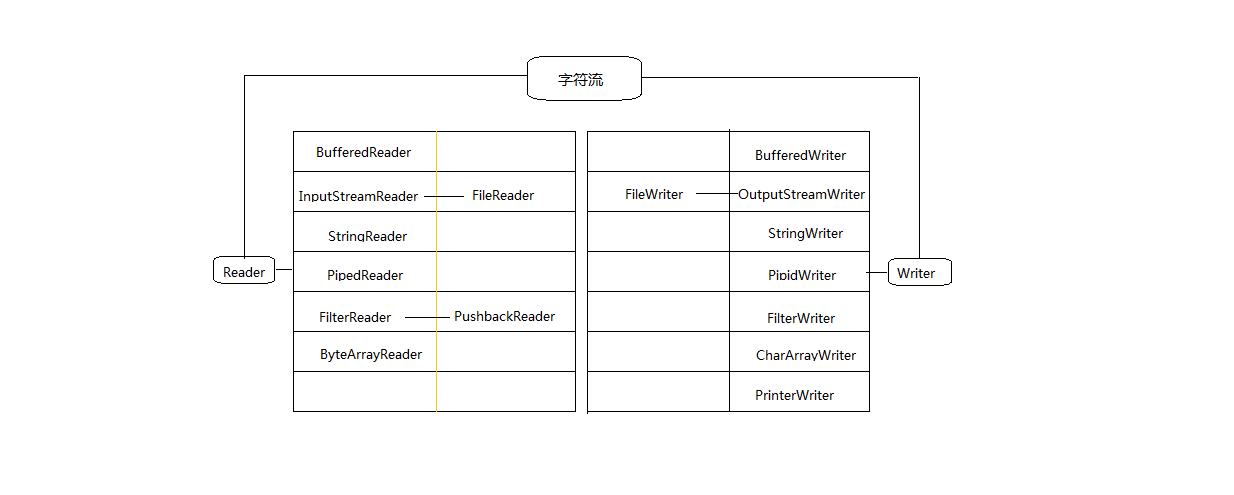

字符流
字符流主要对纯文本进行操作。Java提供了Reader和Writer两个专门操作字符流的类。
Reader和Writer是抽象类,要使用此类,需用子类
字符输出流Writer:
private static void demo1() throws IOException { File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt"); Writer out = new FileWriter(f); String str = "HelloWorld"; out.write(str); out.close(); }
文件没有可以自动创建,若向文件中添加内容,只需要向FileWriter 中添加 true,
即Writer out = new FileWriter(f,true);
字符输入流Reader:
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt"); Reader reader = new FileReader(f); char[] c = new char[1024]; int len = reader.read(c); reader.close(); System.out.println("内容为:" + new String(c, 0, len));
如果不知道要输入的数据的长度,使用循环方式进行内容读取:
private static void demo2() throws Exception { File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt"); Reader reader = new FileReader(f); int len = 0; char[] c = new char[1024]; int temp = 0; while ((temp = reader.read()) != -1) { c[len] = (char) temp; len++; } reader.close(); System.out.println("内容为:" + new String(c, 0, len)); }
字节流
字节输入流InputStream:
// 有大量空格,浪费空间 private static void demo1() throws Exception { File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt");// 路径不存在会抛出异常 InputStream input = new FileInputStream(f); byte[] b = new byte[1024];// 内容不能超过1024 input.read(b); input.close(); System.out.println("内容为:" + new String(b));// 把byte[]变为字符串输出,后有大量空格 }
修改代码,用len接收input.read(b);即int len = input.read(b);
打印new String(b,0,len);但是这样去除了空格,空间还是浪费,修改代码
byte[] b = new byte[(int) f.length()]; 这样数组大小由文件决定,解决了空间浪费的问题,但是要知道输入的内容有多大。若输入内容大小未知,需要通过判断是否读到文件末尾的方式来读取文件。
private static void demo4() throws Exception { File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt"); InputStream input = new FileInputStream(f); int len = 0;// 用于记录读取的数据个数 byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int temp = 0;// 接收读取的内容 while ((temp = input.read()) != -1) { b[len] = (byte) temp; len++; } input.close(); System.out.println("内容为:" + new String(b, 0, len)); }
字节输出流:OutputStream
若文件不存在,可以自动创建。
private static void demo5() throws Exception { File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt"); OutputStream out =new FileOutputStream(f); String str = "Hello World"; byte[] b =str.getBytes(); out.write(b); out.close(); }
追加新内容,只需修改代码OutputStream out =new FileOutputStream(f,true);即可。
字符流与字节流的区别:字节流不会用到缓冲区,是对文本进行直接操作,而字符流操作时需要用到缓冲区,通过缓冲区操作文件。
注意,程序最后要关闭流,字节流不关闭,内容可以输出,但字符流不关闭的话,最后一段内容存在于缓冲区中,无法读取出来,造成内容失真。如果想在不关闭流的情况下,将字符流的内容全部输出,可以用Writer中的flush()强制清空缓冲区。
转换流OutputStreamWriter与InputStreamReader
结构图:
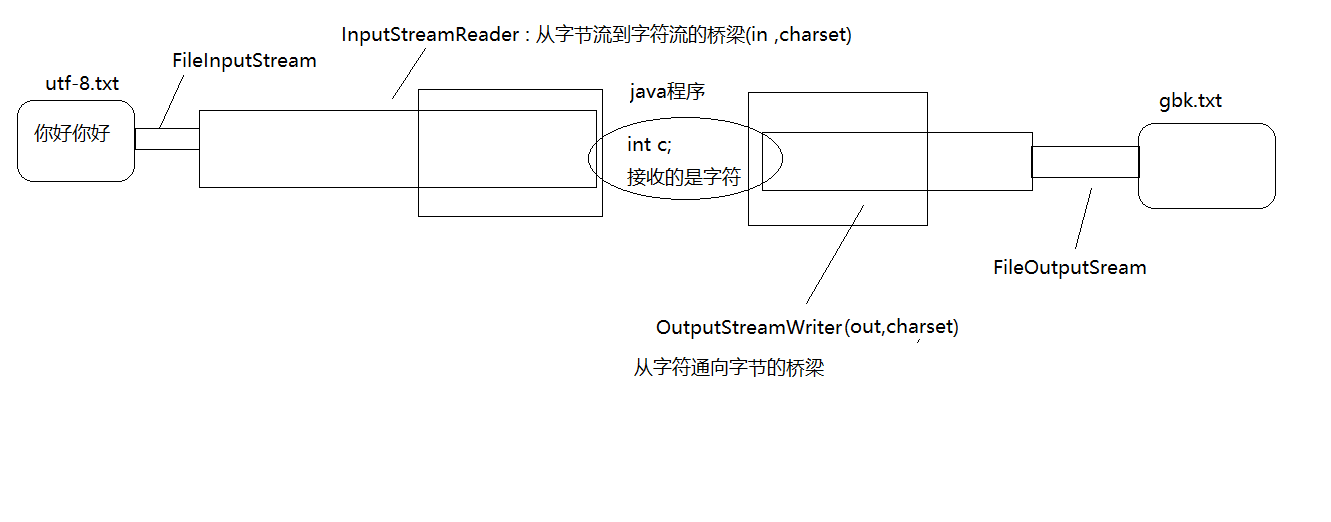
字节输出流变字符输出流:
private static void demo6() throws Exception { File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt"); Writer out =new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(f)); out.write("hello world"); out.close(); }
字节输入流变为字符输入流:
private static void demo7() throws Exception { File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt"); Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(f)); char[] c = new char[1024]; int len = reader.read(c); reader.close(); System.out.println(new String(c,0,len)); }
内存操作流
内存操作流一般在生成一些临时信息才会用到,如果将这些临时信息保存在文件中,则代码执行后肯定还要删除这个临时文件会比较麻烦,这个时候用内存操作流最合适。

private static void demo8() throws IOException { String str = "HELLOWORLD"; ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes()); ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); int temp = 0; while ((temp = bis.read()) != -1) { char c = (char) temp; bos.write(Character.toLowerCase(c)); } String newStr = bos.toString(); bis.close(); bos.close(); System.out.println(newStr); }
管道流
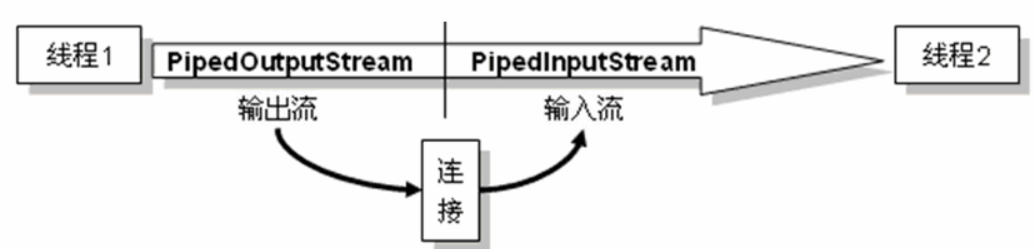
package guandaoliu; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PipedInputStream; import java.io.PipedOutputStream; public class PipidDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Send s = new Send(); Receive r = new Receive(); try { s.getPos().connect(r.getPis()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new Thread(s).start(); new Thread(r).start(); } } class Send implements Runnable { private PipedOutputStream pos = null; public Send() { this.pos = new PipedOutputStream(); } @Override public void run() { String str = "hello world"; try { this.pos.write(str.getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { this.pos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public PipedOutputStream getPos() { return pos; } } class Receive implements Runnable { private PipedInputStream pis = null; public Receive() { this.pis = new PipedInputStream(); } @Override public void run() { byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; try { len = pis.read(b); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { this.pis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("接收的内容为:" + new String(b, 0, len)); } public PipedInputStream getPis() { return pis; } }
BufferedReader类
BufferedReader类用于从缓冲区读取内容,所有的输入字节数据都放在缓冲区中。BufferedReader定义的构造方法只能接收字符输入流的实例,所以必须使用字符输入流和字节输入流的转换类InputStreamReader将字节输入流System.in变为字符流。
BufferedReader buf =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
常用方法:
public BufferedReader(Reader in) 构造 接收一个Reader的实例
public String readLine()throws IOException 普通 一次性从缓冲区将内容读出来。