1.2.1
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Point2D; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class Point2DClient { public static void main(String[] args) { int pointnumber; Point2D[] points; double closestdistance = 0; int closestpair1; int closestpair2; //usage if(args.length < 1) { StdOut.println("Usage: Point2DClient N"); StdOut.println("Generate N random points"); return; } pointnumber = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); points = new Point2D[pointnumber]; //generate pointnumber random points StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.01); for(int i = 0; i < pointnumber; i++) { double x = StdRandom.random(); double y = StdRandom.random(); StdOut.printf("Point2D %d (%f %f) ",i, x,y); points[i] = new Point2D(x, y); points[i].draw(); } //find the closet pair of points closestdistance = points[0].distanceTo(points[1]); closestpair1 = 0; closestpair2 = 1; for(int i = 0; i< pointnumber; i++) { for(int j = i + 1; j < pointnumber; j++) { double distance = points[i].distanceTo(points[j]); StdOut.printf("distance from %d to %d is %f ", i,j,distance); if(distance < closestdistance) { closestdistance = distance; closestpair1 = i; closestpair2 = j; } } } StdOut.printf("closest distance is %f from %d to %d ", closestdistance, closestpair1, closestpair2); points[closestpair1].drawTo(points[closestpair2]); } }
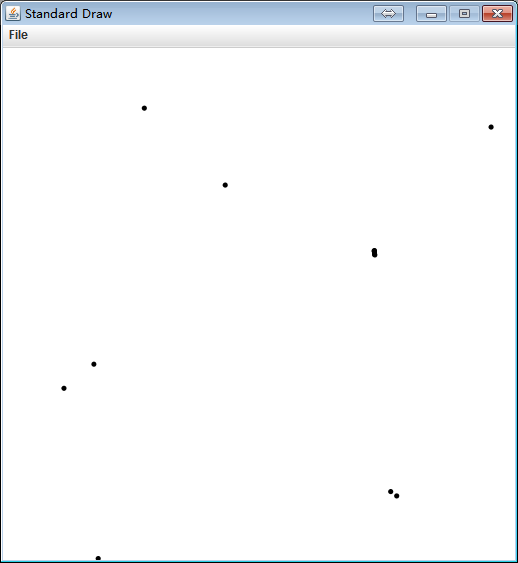
Point2D 0 (0.757256 0.133583) Point2D 1 (0.276017 0.882527) Point2D 2 (0.724763 0.603589) Point2D 3 (0.186021 0.002862) Point2D 4 (0.768848 0.125174) Point2D 5 (0.434056 0.732299) Point2D 6 (0.119133 0.335418) Point2D 7 (0.177490 0.382443) Point2D 8 (0.726221 0.595894) Point2D 9 (0.953359 0.845522) distance from 0 to 1 is 0.890230 distance from 0 to 2 is 0.471128 distance from 0 to 3 is 0.586001 distance from 0 to 4 is 0.014321 distance from 0 to 5 is 0.680382 distance from 0 to 6 is 0.669282 distance from 0 to 7 is 0.630920 distance from 0 to 8 is 0.463352 distance from 0 to 9 is 0.738453 distance from 1 to 2 is 0.528375 distance from 1 to 3 is 0.884257 distance from 1 to 4 is 0.903585 distance from 1 to 5 is 0.218048 distance from 1 to 6 is 0.569158 distance from 1 to 7 is 0.509697 distance from 1 to 8 is 0.533706 distance from 1 to 9 is 0.678352 distance from 2 to 3 is 0.806918 distance from 2 to 4 is 0.480442 distance from 2 to 5 is 0.317926 distance from 2 to 6 is 0.662347 distance from 2 to 7 is 0.590265 distance from 2 to 8 is 0.007831 distance from 2 to 9 is 0.332847 distance from 3 to 4 is 0.595523 distance from 3 to 5 is 0.770454 distance from 3 to 6 is 0.339217 distance from 3 to 7 is 0.379678 distance from 3 to 8 is 0.802187 distance from 3 to 9 is 1.139685 distance from 4 to 5 is 0.693316 distance from 4 to 6 is 0.682885 distance from 4 to 7 is 0.644896 distance from 4 to 8 is 0.472647 distance from 4 to 9 is 0.743603 distance from 5 to 6 is 0.506647 distance from 5 to 7 is 0.433849 distance from 5 to 8 is 0.322439 distance from 5 to 9 is 0.531503 distance from 6 to 7 is 0.074946 distance from 6 to 8 is 0.660609 distance from 6 to 9 is 0.977823 distance from 7 to 8 is 0.588784 distance from 7 to 9 is 0.903556 distance from 8 to 9 is 0.337499 closest distance is 0.007831 from 2 to 8
1.2.2和1.2.3解法跟1.2.1类似,略
1.2.4
输出结果为:
world
hello
因为最后string1是“world”的引用
string2是“hello”的引用
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Exercise124 { public static void main(String[] args) { String string1 = "hell0"; String string2 = string1; string1 = "world"; StdOut.println(string1); StdOut.println(string2); } }
结果:

1.2.5
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Exercise125 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "Hello World"; s.toUpperCase(); s.substring(6, 11); StdOut.println(s); } }
程序从头到尾s指向的对象都没有改变过,所以最后输出“Hello World”

1.2.6
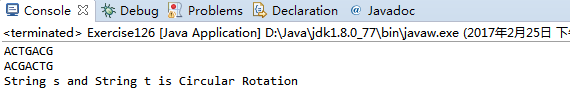
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Exercise126 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "ACTGACG"; String t = "ACGACTG"; StdOut.println(s); StdOut.println(t); if(isCircularRotation(s,t)) StdOut.println("String s and String t is Circular Rotation"); else StdOut.println("String s and String t isn't Circular Rotation"); } public static boolean isCircularRotation(String s, String t) { if(s.length() == t.length() && s.concat(s).indexOf(t) >= 0) return true; return false; } }
1.2.7
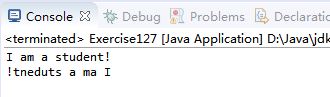
起到反转String的作用,以下是程序测试。
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Exercise127 { public static void main(String[] args) { String test = "I am a student!"; StdOut.println(test); StdOut.println(mystery(test)); } public static String mystery(String s) { int N = s.length(); if(N <= 1) return s; String a = s.substring(0, N/2); String b = s.substring(N/2, N); return mystery(b) + mystery(a); } }
1.2.8
书中有答案
1.2.9
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.Arrays; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Counter; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Exercise129 { public static int rank(int key, int[] a, Counter counter) { counter.increment(); //array must be sorted int lo = 0; int hi = a.length - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; if(key < a[mid]) hi = mid -1; else if(key > a[mid]) lo = mid + 1; else return mid; } return -1; } public static void main(String[] args) { Counter counter = new Counter("rank"); int[] whitelist = In.readInts(args[0]); Arrays.sort(whitelist); StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(whitelist)); while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) { int key = StdIn.readInt(); if(rank(key, whitelist, counter) < 0) StdOut.println(key); } StdOut.println(counter); } }
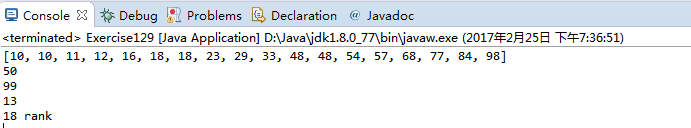
1.2.10
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class VisualCounter { private int maxx; private int maxabsy; private int count = 0; private int times = 0; public VisualCounter(int N, int max) { StdDraw.setXscale(0, N); StdDraw.setYscale(-max, max); StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.005); StdDraw.line(0, 0, N, 0); maxx = N; maxabsy = max; } public void increment() { times++; count++; StdDraw.point(times, count); } public void decrement() { times++; count--; StdDraw.point(times, count); } public static void main(String[] args) { VisualCounter counter = new VisualCounter(100, 100); for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { if(StdRandom.bernoulli()) { counter.increment(); } else { counter.decrement(); } } } }
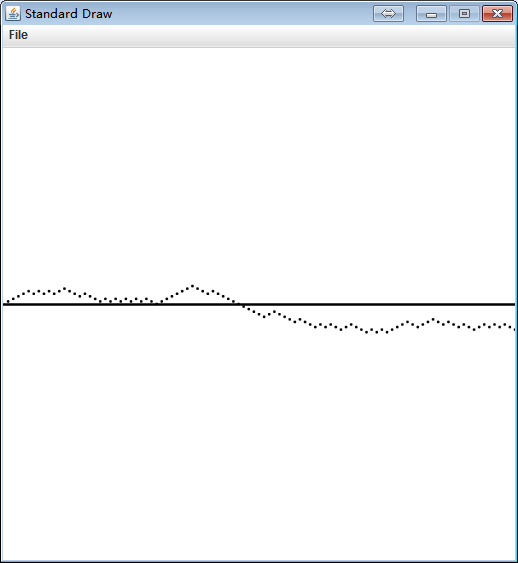
1.2.11
package com.qiusongde; public class SmartDate { private final int month; private final int day; private final int year; private final int[] MAXDAY = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; public SmartDate(int m, int d, int y) { if(!isValid(m, d, y)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Date:" + m + "/" + d + "/" + y); month = m; day = d; year = y; } private boolean isValid(int m, int d, int y) { if(m < 1 || m > 12) return false; if(d < 1 || d > MAXDAY[m-1]) return false; if(m == 2 && d == 29 && !isLeapYear(y)) return false; return true; } private boolean isLeapYear(int y) { if(y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0 || y % 400 == 0) return true; return false; } public int month() { return month; } public int day() { return day; } public int year() { return year; } public String toString() { return month() +"/" + day() + "/" + year(); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(13, 31, 2009); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(6, 32, 2009); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2017); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2016); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2000); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2100); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date7 = new SmartDate(6, 31, 2009); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date8 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2009); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:13/31/2009 at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13) at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:54) java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:6/32/2009 at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13) at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:60) java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:2/29/2017 at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13) at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:66) java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:2/29/2100 at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13) at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:84) java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid Date:6/31/2009 at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.<init>(SmartDate.java:13) at com.qiusongde.SmartDate.main(SmartDate.java:90)
1.2.12
public String dayOfTheWeek() { //assume that the date is in the 21st century //in 1/1/2000 is Saturday int offsetday = 0;//the offset of day from 1/1/2000 final String[] WEEKDAY = {"Saturday", "Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday"}; //year offsetday += 365 * (year - 2000);//ignore leap year first //month for(int i = 0; i < month - 1; i++) { offsetday += MAXDAY[i];//add according to the max day } if(month > 2) { if(!isLeapYear(year)) offsetday--; } //day offsetday += day - 1; //add leapyear day in February offsetday += Leapyears(year); return WEEKDAY[offsetday % 7]; } //return the number of leap year since 2000 private int Leapyears(int year) { if(year == 2000) return 0; int number = 0; int offset = year - 2001; number += offset/4;//how many 4 years since 2001 number -= offset/100 ;//how many 100 years since 2001 number += offset/400;//how many 400 years since 2001 number++;//2000 year is leap year return number; }
SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2017); StdOut.println(date1.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2000); StdOut.println(date2.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2100); StdOut.println(date3.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2101); StdOut.println(date4.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2400); StdOut.println(date5.dayOfTheWeek()); SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2401); StdOut.println(date6.dayOfTheWeek());
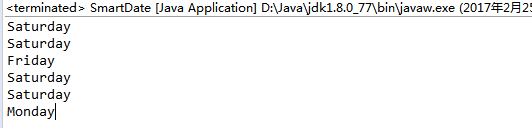
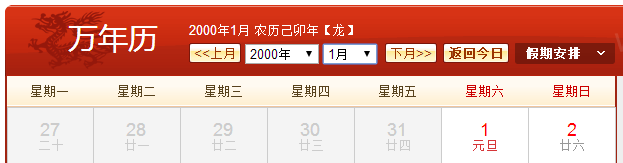

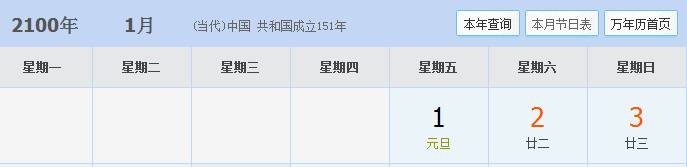
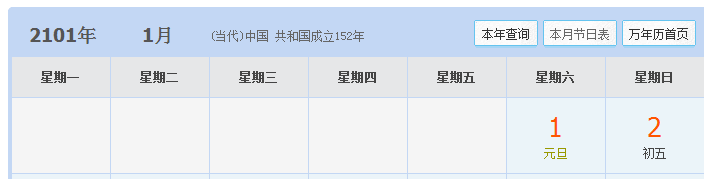
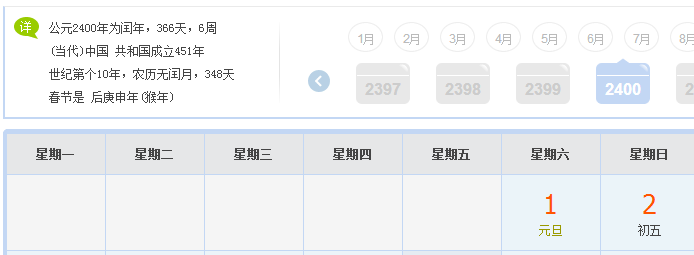
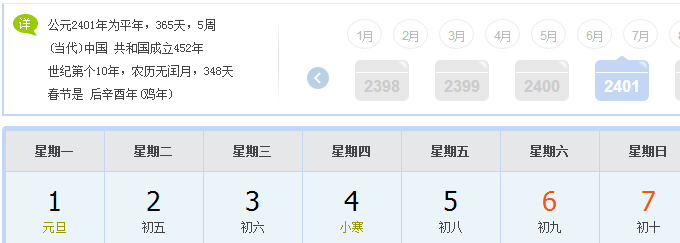
1.2.13
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Date; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Transaction { private String name; private Date date; private double amount; public Transaction(String who, Date when, double amount) { //should check the argument name = who; date = when; this.amount = amount; } public String who() { return name; } public Date when() { return date; } public double amount() { return amount; } public String toString() { return date + " " + name + " " + amount; } public static void main(String[] args) { Date date = new Date(2, 26, 2017); Transaction transaction = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500); StdOut.println(transaction); } }

1.2.14
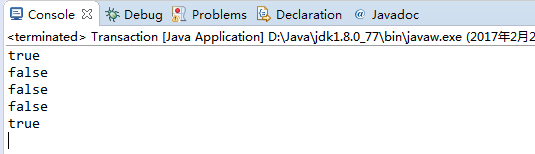
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Date; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Transaction { private String name; private Date date; private double amount; public Transaction(String who, Date when, double amount) { //should check the argument name = who; date = when; this.amount = amount; } public String who() { return name; } public Date when() { return date; } public double amount() { return amount; } public String toString() { return date + " " + name + " " + amount; } public boolean equals(Object x) { if(this == x) return true; if(x == null) return false; if(this.getClass() != x.getClass()) return false; Transaction that = (Transaction) x; if(!name.equals(that.name)) return false; if(!date.equals(that.date)) return false; if(amount != that.amount) return false; return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { Date date = new Date(2, 26, 2017); Transaction transaction = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500); Date date1 = new Date(2, 27, 2017); Transaction transaction1 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date1, 500); Transaction transaction2 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500); StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction)); StdOut.println(transaction.equals(null)); StdOut.println(transaction.equals(date)); StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction1)); StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction2)); } }
1.2.15
书中已经由答案
public static int[] readInts(String name) { In in = new In(name); String input = in.readAll(); String[] words = input.split("\s+"); int[] ints = new int[words.length]; for(int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) { ints[i] = Integer.parseInt(words[i]); } return ints; }
其中"\s+" \s表示空格、回车、换行符等空白符,+表示多个的意思。
1.2.16
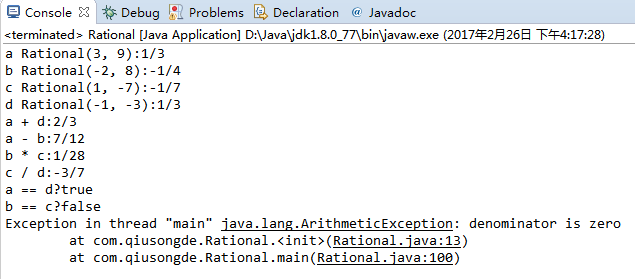
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Rational { private final long numerator; private final long denominator; public Rational(long numerator, long denominator) { if(denominator == 0) throw new ArithmeticException("denominator is zero"); //find the greatest common divisor //to reduce the result to the simplest fraction long gcd = gcd(numerator, denominator); //assure denominator is positive if(denominator < 0) { this.numerator = -numerator/gcd; this.denominator = -denominator/gcd; } else { this.numerator = numerator/gcd; this.denominator = denominator/gcd; } } //the greatest commom divisor of |p| and |q| private long gcd(long p, long q) { if(p < 0) p = -p; if(q < 0) q = -q; if(q == 0) return p; long r = p % q; return gcd(q, r); } public Rational plus(Rational b) { return new Rational((this.numerator * b.denominator + this.denominator * b.numerator), this.denominator * b.denominator); } public Rational minus(Rational b) { return this.plus(new Rational(-b.numerator, b.denominator)); } public Rational times(Rational b) { return new Rational(this.numerator * b.numerator, this.denominator * b.denominator); } public Rational divides(Rational b) { return new Rational(this.numerator * b.denominator, this.denominator * b.numerator); } public boolean equals(Object that) { if(this == that) return true; if(that == null) return false; if(this.getClass() != that.getClass()) return false; Rational other = (Rational) that; return (this.numerator == other.numerator) && (this.denominator == other.denominator); } public String toString() { return numerator + "/" + denominator; } public static void main(String[] args) { Rational a = new Rational(3, 9); Rational b = new Rational(-2, 8); Rational c = new Rational(1, -7); Rational d = new Rational(-1, -3); StdOut.println("a Rational(3, 9):" + a.toString()); StdOut.println("b Rational(-2, 8):" + b.toString()); StdOut.println("c Rational(1, -7):" + c.toString()); StdOut.println("d Rational(-1, -3):" + d.toString()); StdOut.println("a + d:" + a.plus(d).toString()); StdOut.println("a - b:" + a.minus(b).toString()); StdOut.println("b * c:" + b.times(c).toString()); StdOut.println("c / d:" + c.divides(d).toString()); StdOut.println("a == d?" + a.equals(d)); StdOut.println("b == c?" + b.equals(c)); new Rational(1, 0); } }
1.2.17
//1.2.16 //1.2.17 package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Rational { private final long numerator; private final long denominator; private final long MAX = Long.MAX_VALUE; private final long MIN = Long.MIN_VALUE; public Rational(long numerator, long denominator) { if(denominator == 0) throw new ArithmeticException("denominator is zero"); //find the greatest common divisor //to reduce the result to the simplest fraction long gcd = gcd(numerator, denominator); //assure denominator is positive if(denominator < 0) { this.numerator = -numerator/gcd; this.denominator = -denominator/gcd; } else { this.numerator = numerator/gcd; this.denominator = denominator/gcd; } } //the greatest commom divisor of |p| and |q| private long gcd(long p, long q) { if(p < 0) p = -p; if(q < 0) q = -q; if(q == 0) return p; long r = p % q; return gcd(q, r); } //true --> will overflow //false --> will not overflow private boolean is_overflow_plus(long a, long b) { return a >= 0 ? MAX - a < b : MIN - a > b; } //true --> will overflow //false --> will not overflow private boolean is_overflow_times(long a, long b) { if(a == 0 || b == 0) { return false; } if( a >= 0 && b >=0 ) { return MAX / a < b; } else if( a < 0 && b < 0 ) { return MAX / a > b; } else { return a < 0 ? MIN / a < b: MIN / a > b ; } } public Rational plus(Rational b) { assert is_overflow_times(this.numerator, b.denominator) : "plus overflows"; assert is_overflow_times(this.denominator, b.numerator) : "plus overflows"; assert is_overflow_plus(this.numerator * b.denominator, this.denominator * b.numerator) : "plus overflows"; return new Rational((this.numerator * b.denominator + this.denominator * b.numerator), this.denominator * b.denominator); } public Rational minus(Rational b) { return this.plus(new Rational(-b.numerator, b.denominator)); } public Rational times(Rational b) { assert is_overflow_times(this.numerator, b.numerator) : "times overflows"; assert is_overflow_times(this.denominator, b.denominator) : "times overflows"; return new Rational(this.numerator * b.numerator, this.denominator * b.denominator); } public Rational divides(Rational b) { return this.times(new Rational(b.denominator, b.numerator)); } public boolean equals(Object that) { if(this == that) return true; if(that == null) return false; if(this.getClass() != that.getClass()) return false; Rational other = (Rational) that; return (this.numerator == other.numerator) && (this.denominator == other.denominator); } public String toString() { return numerator + "/" + denominator; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Rational a = new Rational(3, 9); // Rational b = new Rational(-2, 8); // Rational c = new Rational(1, -7); // Rational d = new Rational(-1, -3); // // StdOut.println("a Rational(3, 9):" + a.toString()); // StdOut.println("b Rational(-2, 8):" + b.toString()); // StdOut.println("c Rational(1, -7):" + c.toString()); // StdOut.println("d Rational(-1, -3):" + d.toString()); // // StdOut.println("a + d:" + a.plus(d).toString()); // StdOut.println("a - b:" + a.minus(b).toString()); // StdOut.println("b * c:" + b.times(c).toString()); // StdOut.println("c / d:" + c.divides(d).toString()); // StdOut.println("a == d?" + a.equals(d)); // StdOut.println("b == c?" + b.equals(c)); // // new Rational(1, 0); Rational a = new Rational(Long.MAX_VALUE, 2); Rational b = new Rational(2, Long.MAX_VALUE); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MAX_VALUE - 1, 1)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MAX_VALUE - 1, 2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MIN_VALUE + 2, -2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_plus(Long.MIN_VALUE + 2, -3)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(Long.MAX_VALUE/2, 3)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(Long.MAX_VALUE/2, 2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MAX_VALUE/2), -3)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MAX_VALUE/2), -2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MIN_VALUE/2), -3)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times(-(Long.MIN_VALUE/2), -2)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times((Long.MIN_VALUE/2), 3)); StdOut.println(a.is_overflow_times((Long.MIN_VALUE/2), 2)); StdOut.println(a.plus(b)); StdOut.println(a.times(b)); } }
开启assert之前的运行结果:

开始之后的运行结果:

1.2.18
https://www.johndcook.com/blog/standard_deviation/
Accurately computing running variance
1.2.19
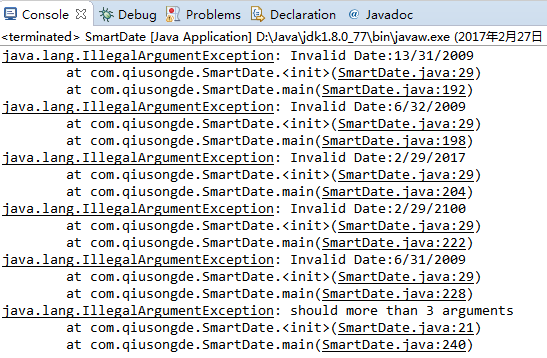
//1.2.11 //1.2.12 //1.2.19 package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class SmartDate { private final int month; private final int day; private final int year; private final int[] MAXDAY = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; public SmartDate(String date) { String[] fields = date.split("/"); if(fields.length < 3) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("should more than 3 arguments"); } int m = Integer.parseInt(fields[0]); int d = Integer.parseInt(fields[1]); int y = Integer.parseInt(fields[2]); if(!isValid(m, d, y)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Date:" + m + "/" + d + "/" + y); month = m; day = d; year = y; } public SmartDate(int m, int d, int y) { if(!isValid(m, d, y)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Date:" + m + "/" + d + "/" + y); month = m; day = d; year = y; } private boolean isValid(int m, int d, int y) { if(m < 1 || m > 12) return false; if(d < 1 || d > MAXDAY[m-1]) return false; if(m == 2 && d == 29 && !isLeapYear(y)) return false; return true; } private boolean isLeapYear(int y) { if(y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0 || y % 400 == 0) return true; return false; } public int month() { return month; } public int day() { return day; } public int year() { return year; } public String dayOfTheWeek() { //assume that the date is in the 21st century //in 1/1/2000 is Saturday int offsetday = 0;//the offset of day from 1/1/2000 final String[] WEEKDAY = {"Saturday", "Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday"}; //year offsetday += 365 * (year - 2000);//ignore leap year first //month for(int i = 0; i < month - 1; i++) { offsetday += MAXDAY[i];//add according to the max day } if(month > 2) { if(!isLeapYear(year)) offsetday--; } //day offsetday += day - 1; //add leapyear day in February offsetday += Leapyears(year); return WEEKDAY[offsetday % 7]; } //return the number of leap year since 2000 private int Leapyears(int year) { if(year == 2000) return 0; int number = 0; int offset = year - 2001; number += offset/4;//how many 4 years since 2001 number -= offset/100 ;//how many 100 years since 2001 number += offset/400;//how many 400 years since 2001 number++;//2000 year is leap year return number; } public String toString() { return month +"/" + day + "/" + year; } public static void main(String[] args) { // try { // SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(13, 31, 2009); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // try { // SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(6, 32, 2009); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // try { // SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2017); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // try { // SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2016); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // try { // SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2000); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // try { // SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(2, 29, 2100); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // try { // SmartDate date7 = new SmartDate(6, 31, 2009); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // try { // SmartDate date8 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2009); // } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate(2, 25, 2017); // StdOut.println(date1.dayOfTheWeek()); // // SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2000); // StdOut.println(date2.dayOfTheWeek()); // // SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2100); // StdOut.println(date3.dayOfTheWeek()); // // SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2101); // StdOut.println(date4.dayOfTheWeek()); // // // SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2400); // StdOut.println(date5.dayOfTheWeek()); // // SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate(1, 1, 2401); // StdOut.println(date6.dayOfTheWeek()); try { SmartDate date1 = new SmartDate("13/31/2009"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date2 = new SmartDate("6/32/2009"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date3 = new SmartDate("2/29/2017"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date4 = new SmartDate("2/29/2016"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date5 = new SmartDate("2/29/2000"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date6 = new SmartDate("2/29/2100"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date7 = new SmartDate("6/31/2009"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date8 = new SmartDate("2/25/2009"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { SmartDate date9 = new SmartDate("2/25"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
//1.2.13 //1.2.14
//1.2.19
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Date; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Transaction { private final String name; private final Date date; private final double amount; public Transaction(String transaction) { String[] fields = transaction.split("\s+"); if(fields.length < 3) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("should more than 3 arguments"); } name = fields[0]; date = new Date(fields[1]); amount = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]); } public Transaction(String who, Date when, double amount) { //should check the argument name = who; date = when; this.amount = amount; } public String who() { return name; } public Date when() { return date; } public double amount() { return amount; } public String toString() { return date + " " + name + " " + amount; } public boolean equals(Object x) { if(this == x) return true; if(x == null) return false; if(this.getClass() != x.getClass()) return false; Transaction that = (Transaction) x; return (this.amount == that.amount) && (this.name.equals(that.name)) && (this.date.equals(that.date)); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Date date = new Date(2, 26, 2017); // Transaction transaction = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500); // // Date date1 = new Date(2, 27, 2017); // Transaction transaction1 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date1, 500); // // Transaction transaction2 = new Transaction("Songde Qiu", date, 500); // // StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction)); // StdOut.println(transaction.equals(null)); // StdOut.println(transaction.equals(date)); // StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction1)); // StdOut.println(transaction.equals(transaction2)); Transaction transaction1 = new Transaction("Songde 2/26/2017 500"); StdOut.println(transaction1); Transaction transaction2 = new Transaction("Songde 2/27/2017 500"); StdOut.println(transaction2); try { Transaction transaction3 = new Transaction("Songde 2/27/2017"); StdOut.println(transaction3); } catch(IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
