
上图为Hashmap的数据结构图,具体实线是采用数组结合链表实现,链表是为了解决在hash过程中因hash值一样导致的碰撞问题。
所以在使用自定义对象做key的时候,一定要去实现hashcode方法,不然hashmap就成了纯粹的链表,查找性能非常的慢,添加节点元素也非常的慢。如
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class User {
private String username;
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
User user=(User)obj;
return username.equals(user.username);}
//手动将hashCode 返回一样的值
public int hashCode() {
return 1;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Map<User,String>map=new HashMap<User,String>();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
User one=new User();
one.setUsername(i+" user");
map.put(one, i+"");
}
}
}
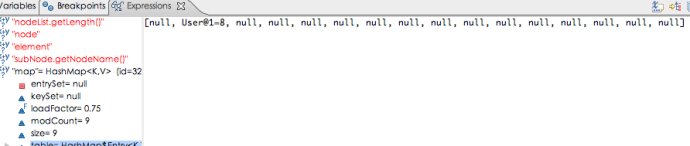
debug发现,添加9个user对象后数组table的entry通过hash后的到数组index为1,即数组第二个位置,每次都是一样的值,导致hash碰撞,所有的元素都通过链表形式加入到entry当中,并没有均匀分布到16个位置当中(默认使用的map构造方法),所以如果在查找的时候就是纯粹的线性查找(链表)。性能相当相当的低。
具体HashMap分析如下:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;//初始容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;//最大容量 2的30次方
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;//默认加载因子
transient Entry[] table;//条目(entry),大小跟容量大小一致(capacity)
transient int size; //map所包含键-值对的数量 每增加一个k-v,根据k来判断是否自增长
int threshold; //容量与加载因子的乘积,当map的size(entry个数)大于等于这个值时,会重新构造map-table的大小(为原来size的2倍大小,而此时threshold=size*loadFactor)
final float loadFactor;//加载因子(人为指定,即在构造对象的时候指定合适的加载因子)
transient int modCount;//当条目增加或者删除的时候modCount会自增长,这个主要用来在防止在非线程安全下迭代访问map的时候发生变化会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
//Map容量大小必须为2的幂次方,这里通过算法找出合适的容量大小,如您给定initialCapacity为17,它 //的二进制数为10001
//当capacity16的时候(10000)已经左移了4次,16<17,所以会将capacity再左移1位,即 //32(100000),所以在创建对象使用
//Map map=new HashMap(17,0.75),此时真正capacity=32,而不是你开始给的17.
//想要创建17个容量大小的时候,实际上为您创建了32个容量大小的map
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);//32*0.75=24, 当条目达到24的时候会重新构造map结构
table = new Entry[capacity];//创建条目,大小为32
init();
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);//12(默认值)
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];//16个(默认值)
init();
}
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
putAllForCreate(m);
}
void init() {
}
static int hash(int h) {
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
//h&(length-1)等价于h%length,取模运算
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
//根据KEY找出V,如果key==null,会返回table[0](如果table[0]不为null,并且table[0]对应的key==null)
//如果table[0]不为null,则检查table[0]的下一个节点(线性链表)是否满足上述情况,满足则返回value,否
//则没有该key对应的value。
//key不为null,则计算出key的hash,并根据hash得出在table中的位置,该位置不一定是真正Value对应的
//位置,还要根据table位置的entry的key的hash以及key值进行比较,不相等则要该位置entry的下一个节点
//是否满足,满足返回,否则返回null
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
......
......
//根据Key的hash值得出在table中的位置,该位置可能会被占用,如果占用entry的hash以及key值完全跟put的key相等,则对该entry进行update,如果不相等,则发生了碰撞,测试要判断当期entry是否有(next)下一个节点(entry),有则继续上一步判断,没有则新增一个entry节点到当前节点。
//这里可以hash不可能保证每次都不一样,所以我们使用的key的对象如果是自定义的对象,一定要重写hashcode方法保证每个对象的唯一性,这洋就能减少碰撞,如果hashcode一样,这洋在查找对象的时候等于是线性查找,算法复杂度近似O(n),并不能达到hashmap设计本来近似的O(1)
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
......
......
//重构map的大小,及重新hash所有元素
//newCapacity=table.length*2 (即原始table的大小乘以2),按照前面给定的值,这里是32*2=64
//重构后capacity=64,table的length=64,threshold=64*0.75=48,即当entry的size达到48的时候会再次重构
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
//entry-table的复制,复制过程中重新计算hash,算出在新table中的位置
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();
if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)
return;
if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {
int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);
if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int newCapacity = table.length;
while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)
newCapacity <<= 1;
if (newCapacity > table.length)
resize(newCapacity);
}
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
//移除Key对应的entry,如果table中存在因为碰撞问题导致的横向拉链(链表),要对链表进行操作,保证链表的连续性
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key);
return (e == null ? null : e.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev;
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
e.recordRemoval(this);
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
}
return e;
}
.....
......
public void clear() {
modCount++;
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; i++)
tab[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
.......
.......
public Object clone() {
HashMap<K,V> result = null;
try {
result = (HashMap<K,V>)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// assert false;
}
result.table = new Entry[table.length];
result.entrySet = null;
result.modCount = 0;
result.size = 0;
result.init();
result.putAllForCreate(this);
return result;
}
//entry数据结构,真正Key和Value保存的地方
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
final int hash;
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
(value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
......
....
}