一、java.util.ArrayList
1.1 ArrayList 继承结构
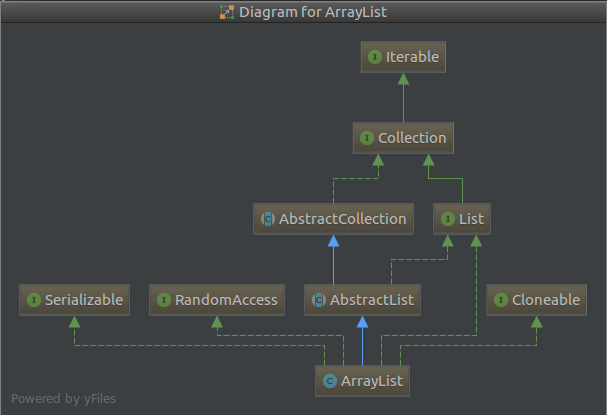
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess,可以随机访问(其实就是通过数组下标访问);实现了Cloneable,可以拷贝(通过System.arraycopy方法实现);实现了Serializable,可以进行序列化,能被序列化传输。
ArrayList非线程安全。
1.2 ArrayList 属性
1 private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; 2 // 初始化容量 3 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 4 // 共享空的数组 5 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 6 // 共享一个具有初始化容量的数组 7 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 8 9 // 核心数组 10 transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access 11 // 数组存放元素总数 12 private int size;
1.3 ArrayList 方法
1 // 确保Capacity能达到指定的minCapacity 2 public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { 3 int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) 4 // any size if not default element table 5 ? 0 6 // larger than default for default empty table. It's already 7 // supposed to be at default size. 8 : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; 9 10 if (minCapacity > minExpand) { 11 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); 12 } 13 } 14 15 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 16 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { 17 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); 18 } 19 20 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); 21 } 22 23 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { 24 modCount++; 25 26 // overflow-conscious code 27 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 28 grow(minCapacity); 29 } 30 31 // 数组可以分配的最大长度 32 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; 33 34 // 扩容 35 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 36 // overflow-conscious code 37 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 38 // 扩容为之前的1.5倍 39 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 40 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 41 newCapacity = minCapacity; 42 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 43 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 44 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 45 // 将原数组内容拷贝到扩容后数组 46 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 47 } 48 49 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 50 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 51 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 52 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? 53 Integer.MAX_VALUE : 54 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 55 }
上面是ensureCapacity方法,确保Capacity能大于等于minCapacity。ArrayList每次扩容为之前的1.5倍。
1 public Object clone() { 2 try { 3 ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone(); 4 v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); 5 v.modCount = 0; 6 return v; 7 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { 8 // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable 9 throw new InternalError(e); 10 } 11 }
拷贝ArrayList方法,这也不是一种深度拷贝,只是将源数组的内容拷贝到新数组,元素并未重建(拷贝)。
1 public void add(int index, E element) { 2 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 3 // 确保容量足够 4 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount !! 5 // 将index及其后元素统统向后移动一位 6 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, 7 size - index); 8 elementData[index] = element; 9 size++; 10 } 11 12 public E remove(int index) { 13 rangeCheck(index); 14 15 modCount++; 16 E oldValue = elementData(index); 17 18 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 19 if (numMoved > 0) 20 // 删除的不是最后的一个元素,需要将后面的元素向前移动一个位置 21 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 22 numMoved); 23 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 24 25 return oldValue; 26 }
ArrayList其根本是个数组,因此在数组末尾增删元素是很高效的。但是要在中间增删元素,就必须移动后面的所有元素,效率肯定会有影响。
如果需要频繁向中间增删元素还是LinkedList比较合适。
1 public boolean remove(Object o) { 2 if (o == null) { 3 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 4 if (elementData[index] == null) { 5 fastRemove(index); 6 return true; 7 } 8 } else { 9 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 10 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { 11 fastRemove(index); 12 return true; 13 } 14 } 15 return false; 16 }
remove某个value,找到第一个value之后,就删除并return。
// 将ArrayList写入到ObjectOutputStream private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException{ // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff int expectedModCount = modCount; // 将非静态和非transient字段写入流 s.defaultWriteObject(); // 将size写入流 s.writeInt(size); // 将所有的元素写入流中 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { s.writeObject(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // 从流中读入非静态和非transient字段 // Read in size, and any hidden stuff s.defaultReadObject(); // 读入size s.readInt(); // ignored if (size > 0) { // be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity ensureCapacityInternal(size); Object[] a = elementData; // Read in all elements in the proper order. // 读取元素 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { a[i] = s.readObject(); } } }
这两个方法将ArrayList写入流或者从流中读入。但是我有个疑问,都是private方法,这个写出来谁能调用?
二、java.util.Vector
2.1 Vector 继承结构
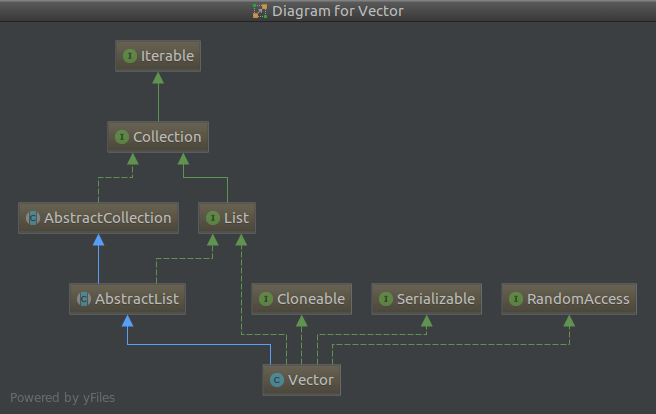
Vector继承结构和ArrayList相同。ArrayList是非线程安全的,与之对应的Vector是线程安全的。
2.2 Vector 属性
1 // 存储对象的数组 2 protected Object[] elementData; 3 // 可以理解为Vector的capacity,也可以理解为数组的length 4 protected int elementCount; 5 // 可以自定义capacity扩容量 6 protected int capacityIncrement; 7 private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L;
2.3 Vector 方法
扩容方法
1 public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { 2 if (minCapacity > 0) { 3 // 注意这里会导致modCount++ !! 4 modCount++; 5 ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity); 6 } 7 } 8 9 private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) { 10 // overflow-conscious code 11 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 12 // 需要扩容处理 13 grow(minCapacity); 14 } 15 16 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; 17 18 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 19 // overflow-conscious code 20 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 21 // 如果没有自定义扩容增量capacityIncrement,则直接扩容为之前的容量的两倍 22 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? 23 capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); 24 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 25 // 扩容为之前容量的两倍如果还不够,则直接扩容为minCapacity 26 newCapacity = minCapacity; 27 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 28 // 防止扩容超出设定的范围 29 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 30 // 将元素拷贝到新数组 31 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 32 } 33 34 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 35 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 36 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 37 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? 38 Integer.MAX_VALUE : 39 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 40 }
ensureCapacity方法加了synchronized同步锁。在扩容策略上跟ArrayList稍有不同,ArrayList默认扩容为之前容量的1.5倍,而Vector则默认扩容为之前容量的2倍。除此之外Vector还允许自定义扩容增量。
1 public synchronized List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 2 return Collections.synchronizedList(super.subList(fromIndex, toIndex), 3 this); 4 }
在subList方法中,为了返回一个线程安全的List,加上了Collections.synchronizedList封装。
If you need synchronization, a Vector will be slightly faster than an ArrayList synchronized with Collections.synchronizedList.
Collections.synchronizedList封装是对List对象添加同步锁,各方法本质上还是调用的List的方法。
Vector类其他方法和ArrayList差不多,无非加上了一个synchronized同步处理,这里就不再赘述了。
三、java.util.LinkedList
3.1 LinkedList继承结构
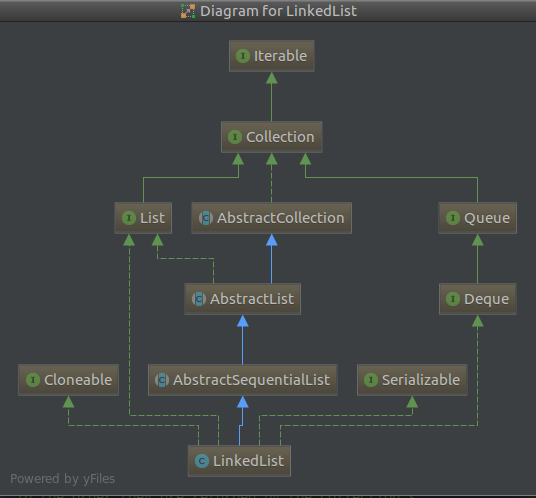
LinkedList没有实现RandomAccess interface,可见其并不具备随机访问特性,毕竟是链表。
LinkedList同样是非线程安全的。
LinkedList比较适合从中间删除、添加元素的场景;ArrayList则更适合只在末尾增删元素,遍历的场景。
3.2 LinkedList 属性
1 transient int size = 0; 2 // 指向第一个节点 3 transient Node<E> first; 4 // 指向最后一个节点 5 transient Node<E> last;
其中Node类为:
1 private static class Node<E> { 2 E item; 3 Node<E> next; 4 Node<E> prev; 5 6 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { 7 this.item = element; 8 this.next = next; 9 this.prev = prev; 10 } 11 }
Node节点包含next和prev两个指针,分别指向前面和后面的一个节点。
3.3 LinkedList 方法
1 public E set(int index, E element) { 2 // 检查index是否在范围内 3 checkElementIndex(index); 4 // 找出这个node节点 5 Node<E> x = node(index); 6 // 保存旧的值 7 E oldVal = x.item; 8 // 更新值 9 x.item = element; 10 return oldVal; 11 } 12 13 Node<E> node(int index) { 14 // assert isElementIndex(index); 15 // 如果index指向链表前半部分,则从前向后遍历 16 if (index < (size >> 1)) { 17 Node<E> x = first; 18 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) 19 x = x.next; 20 return x; 21 } else { 22 // index指向链表的后半部分,从后往前遍历 23 Node<E> x = last; 24 for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) 25 x = x.prev; 26 return x; 27 } 28 } 29 30 private void checkElementIndex(int index) { 31 if (!isElementIndex(index)) 32 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 33 } 34 35 private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { 36 return index >= 0 && index < size; 37 }
在这个set方法中,有个参数是index,修改指定index上的元素内容,但链表本身是不具备index属性的,为此通过node()方法遍历(从first向last方向开始计数)找到第index个Node,即为需要修改的节点。
node方法为了提高效率,根据index所指向的位置,从前向后或从后向前遍历,因此最多遍历size/2个节点就可以找到index节点了。
1 // 获取第一个节点内容,但是不删除 2 public E peek() { 3 final Node<E> f = first; 4 return (f == null) ? null : f.item; 5 } 6 7 // 获取第一个节点内容并且删除之 8 public E poll() { 9 final Node<E> f = first; 10 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); 11 } 12 13 // 删除第一个节点并返回其内容,跟poll一样 14 public E pop() { 15 return removeFirst(); 16 } 17 18 // 添加一个元素到结尾 19 public boolean offer(E e) { 20 return add(e); 21 } 22 23 // 添加一个元素到开头 24 public void push(E e) { 25 addFirst(e); 26 }
上面是几个比较容易混淆的方法,其实看下代码就明白了。
1 private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> { 2 private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size()); 3 public boolean hasNext() { 4 return itr.hasPrevious(); 5 } 6 public E next() { 7 return itr.previous(); 8 } 9 public void remove() { 10 itr.remove(); 11 } 12 }
LinkedList提供了一个反向迭代器,因为LinkedList本身就是一个双向链表,反向遍历也是很方便的。
1 private LinkedList<E> superClone() { 2 try { 3 return (LinkedList<E>) super.clone(); 4 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { 5 throw new InternalError(e); 6 } 7 } 8 9 public Object clone() { 10 LinkedList<E> clone = superClone(); 11 12 // Put clone into "virgin" state 13 clone.first = clone.last = null; 14 clone.size = 0; 15 clone.modCount = 0; 16 17 // Initialize clone with our elements 18 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 19 clone.add(x.item); 20 21 return clone; 22 }
拷贝方法,同样是浅拷贝,每个节点的元素内容并没有被拷贝。拷贝出来的结果是两个链表都引用的同一个元素内容。