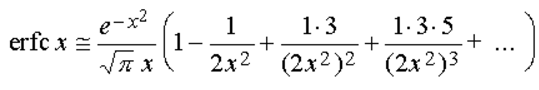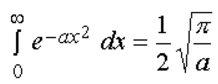首先正态分布的概率密度函数为:
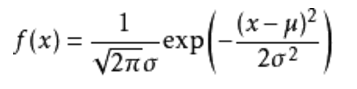
P{|X-μ|<σ}=2Φ(1)-1=0.6826, P{|X-μ|<2σ}=2Φ(2)-1=0.9544, P{|X-μ|<3σ}=2Φ(3)-1=0.9974
由于“小概率事件”和假设检验的基本思想 “小概率事件”通常指发生的概率小于5%的事件,认为在一次试验中该事件是几乎不可能发生的。由此可见X落在(μ-3σ,μ+3σ)以外的概率小于千分之三,在实际问题中常认为相应的事件是不会发生的,基本上可以把区间(μ-3σ,μ+3σ)看作是随机变量X实际可能的取值区间,这称之为正态分布的“3σ”原则。
f(x)关于μ对称,并在μ处取最大值,在正(负)无穷远处取值为0,在μ±σ处有拐点,形状呈现中间高两边低,正态分布的概率密度函数曲线呈钟形,因此人们又经常称之为钟形曲线。
我们有:
The Error function
the error function equals twice the integral of a normalized gaussian function between 0 and x/sÖ2:

The relation between the normalized gaussion distribution and the error function equals:
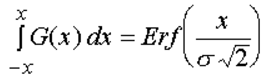
A series approximation for small value of x of this function is given by:
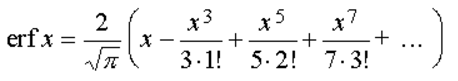
while an approximate expression for large values of x can be obtained from:
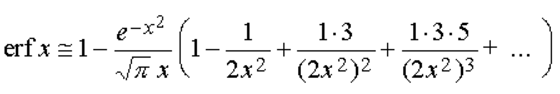
The Complementary Error function
The complementary error function equals one minus the error function yielding:
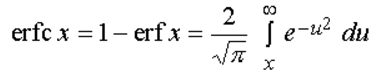
which, combined with the series expansion of the error function listed above, provides approximate expressions for small and large values of x: