于这一周阅读了ccs2020最新论文Enhancing State-of-the-art Classifiers with API Semantics to Detect Evolved Android Malware,做了一些笔记。
Enhancing State-of-the-art Classifiers with API Semantics to Detect Evolved Android Malware (用 API 语义加强现有的分类器以检测不断改进的安卓恶意软件)
1.现有的恶意软件检测分类器的问题:
performance degrades 当 malware evolution
使用 online learning, retraining, active learning 等技术需要大量新的恶意软件标记并消耗大量人力资源
2.本文的创新点:
提出 APIGraph (a framwork)
使用 API 语义的相似性,即为 (similarity information among evolved Android Malware)来减缓 performance degrades
similarity information: 语义上等价或类似的API使用
3. 核心
找到不同实现上的语义的相似性 (semantic similarity despite the different implementation)
建立一个 relation graph:
- node: entity
- edge: relation between two entities
随后从图中提取出 API 语义 (将每个 API entity 转变为一个 embedding),并将类似语义的进行分组为 API clusters (APIGraph 的 result)
使用指标 AUT (area under time) (在 TESSERACT 中提出:TESSERACT 使用 active learning 选择一小部分具有代表性的改进的安卓恶意软件)
作用: 1. 减少了人工标记所需要的劳动量
2.减缓了模型老化,即 performance degrades
将 APIGraph 应用于四个安卓恶意软件检测器上并进行测试,分别为 MAMADROID, DROIDEVOLVER (通过 online learning 持续引入新的恶意软件样本), BREBIN, DREBIN-DL
4.图的结构
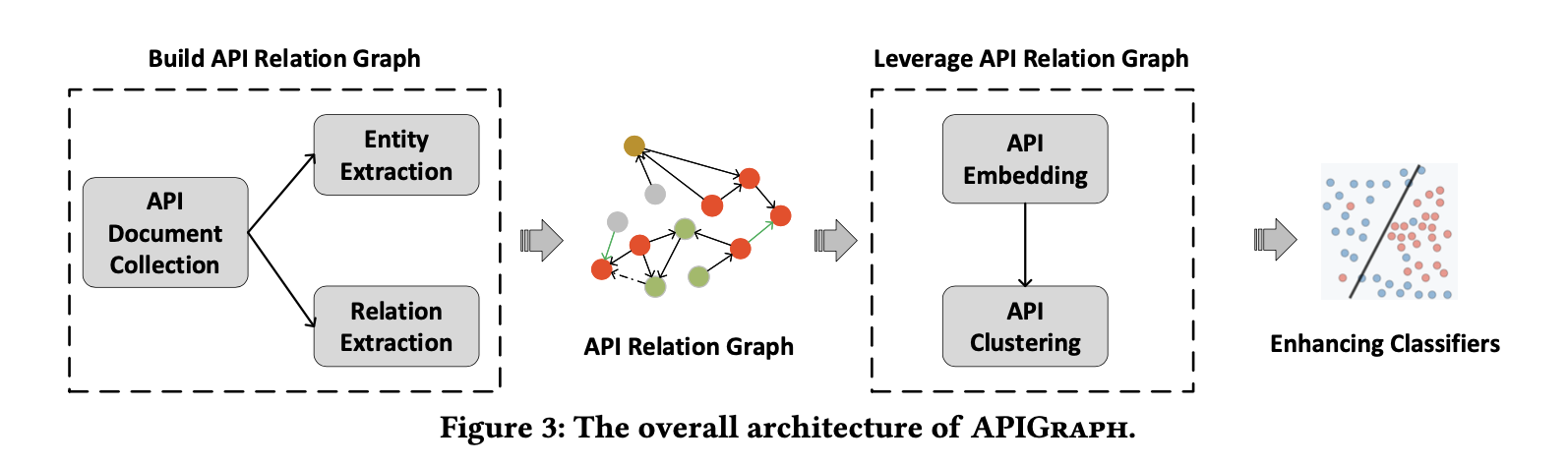
分为两部分:
- 建立 API Relation Graph: collecting Android API Documents related to a certain API level 并提取 entities 和 relations
- 使用 API Relation Graph 去加强现有的恶意软件检测技术
- 将所有 entities 转换为 vector (使用 graph embedding algorithm),
- 两个 entities 之间的 vector difference in the embedding space 即为两个 entities 之间的语义
- 使用优化使两个有相同关系的 entities 的 vector 变为类似的 (similar)
- 聚类语义类似的 APIs 生成 clusters
5.图的建立与使用
(1)API Relation Graph (异构图,有向图)
G = < E, R> (entities, relations)
entity types: method, class, package, permission
relation types: ten types
使用 API reference document (有明显的分层结构)
(2)提取 entity
从 API 文件中提取 entity,API 文件以 class 为分类 (organized in class)
1.从每个 per-class document file 提取 class entity
2.从完整 class name 中拆分出 package name (i.e. package entity)
3.phase per-class document files 为 Document Object Model (DOM) 并从中抽取属于某一个 class 的 method entity
4.phase the manifest file 中的所有 permissions 并从中抽取 permission entity
(3)提取 relation
-
从 structured texts 中提取 relation (6种)
直接进行文件解析
-
从 unstructured texts 中提取 relation (4种)
使用 NLP 的一种基于模型关系配对的方法
-
手动生成配对模型 (template set)
手动检测1%的 API 文件研究描述 relation 的 pattern
-
迭代扩展 template set
用半自动策略迭代生成 template set
-
使用 NLP 进行加强的模型匹配
将段落拆分为句子,然后使用 NLP 对每个句子进行预处理:
- 提取主干:将所有单词化为基本远行
- 基于 declaration 的指代消解 (co-reference resolution):指代消解指在文本中确定代词指向哪个名词短语
- entity 名称规范化:用 exact value 替代所有的多态名称
将预处理后的句子与模型进行匹配
-
(4)使用 API Relation Graph
将图中的 API 转换为 embedding representation (即 vector), 并将这些 embeddings 分类为 clusters
使用 TransE 进行转换
-
首先提取出 permission entity, 并且添加基于 permission 的新的 relation
-
将图中分实体 e 和关联 r 分别用向量 Le和 Lr表示
-
使用 TransE 算法对每个三元组 (h,r,t)最小化 ({||Lh + Lr - Lt||}^2_{2}) (h,t 为 entities, r 为 relation)
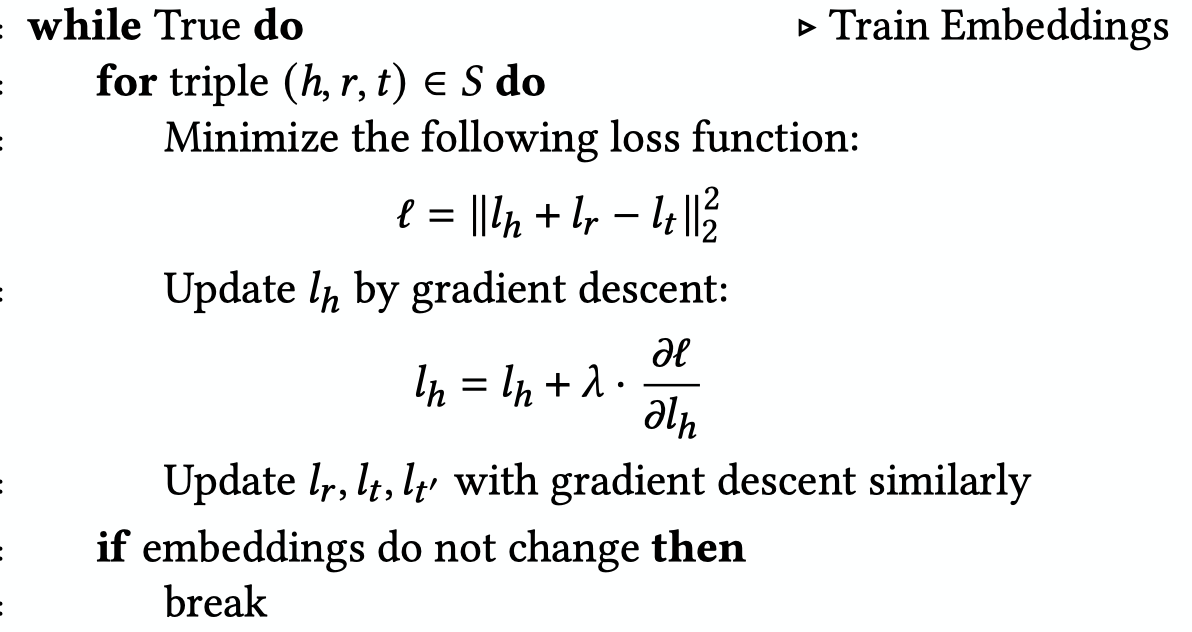
- 使用 K-Means 算法将 embeddings 分组,使用每个 cluster 中心的 embedding 来表示这个 cluster,并用 Elbow 算法决定 cluster 的数目
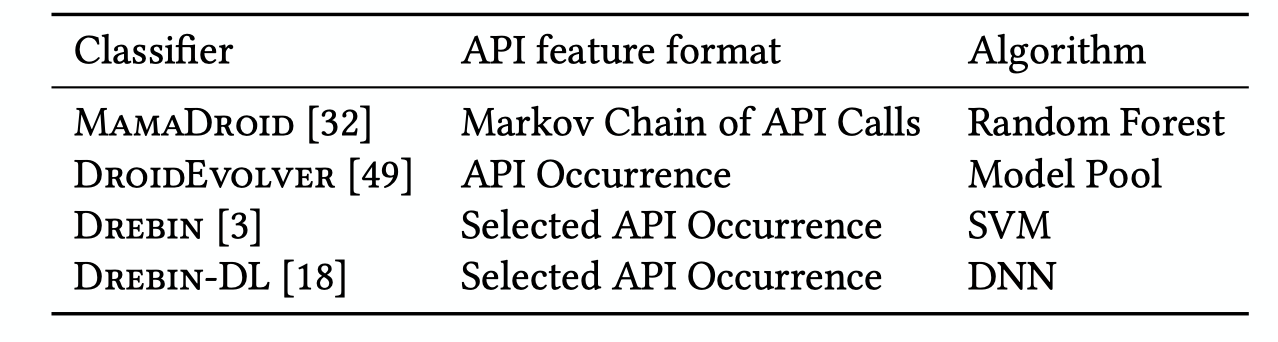
对于这四种 classifier, 将其中的 API feature format 替换为 cluster 进行改进
6.测试与讨论
- 模型可维护性分析
- 模型可持续性分析
- 特征空间稳定性分析
- 同一聚类中的相似程度分析