源码版本: .Net Core 3.1.14
上篇文章: 【.Net Core】.Net Core 源码分析与深入理解 - 入口 Program.cs (一)
注意:本篇文章主要研究的是 Startup.cs 中做了什么,Configure里面是怎么配置管道的,各种参数到底有何功能。
具体Configure的源码探究比较复杂,准备再仔细学习一下,等下一章 【.Net Core】.Net Core 源码分析与深入理解 - 管道核心 Configure(三)。
可以看到Startup.cs 的代码如下,接下来将会从执行顺序逐一分析。
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddControllers(); } public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllers(); }); }
IConfiguration:应用程序的各种配置信息。
IApplicationBuilder:获取应用程序中的环境变量,配置Http请求管道。
IHostingEnvironment:包含应用程序宿主环境相关信息的接口。
Startup Constructor 构造函数
首先是构造函数注入进来的Configuration对像,这个对象的加载进了不同类型的配置信息,通过统一的抽象接口进行管理。比如说可以在appsettings.json中配置数据库连接信息,在这里使用配置好的信息。
IConfiguration的源码如下,地址 ......extensions-3.1.14srcConfigurationConfig.AbstractionssrcIConfiguration
/// <summary> /// Represents a set of key/value application configuration properties. /// </summary> public interface IConfiguration { /// <summary> /// Gets or sets a configuration value. /// </summary> /// <param name="key">The configuration key.</param> /// <returns>The configuration value.</returns> string this[string key] { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets a configuration sub-section with the specified key. /// </summary> /// <param name="key">The key of the configuration section.</param> /// <returns>The <see cref="IConfigurationSection"/>.</returns> /// <remarks> /// This method will never return <c>null</c>. If no matching sub-section is found with the specified key, /// an empty <see cref="IConfigurationSection"/> will be returned. /// </remarks> IConfigurationSection GetSection(string key); /// <summary> /// Gets the immediate descendant configuration sub-sections. /// </summary> /// <returns>The configuration sub-sections.</returns> IEnumerable<IConfigurationSection> GetChildren(); /// <summary> /// Returns a <see cref="IChangeToken"/> that can be used to observe when this configuration is reloaded. /// </summary> /// <returns>A <see cref="IChangeToken"/>.</returns> IChangeToken GetReloadToken(); }
它有以下三个方法:
- GetChildren():获取直接子配置子节
- GetReloadToken():返回一个IChangeToken,可用于确定何时重新加载配置
- GetSection(String):获取指定键的子节点
ConfigureServices
接下来主要说一下方法里面配置的是什么,重点在于参数是什么,怎么来的,这个方法的参数是IServiceCollection,是一个非常重要的对象,这是一个原生的Ioc容器,所有需要用到的服务都可以注册到里面, 调用service.AddXXXX方法,比如数据库、MVC、跨域、swagger、过滤器等Middleware。
这个IServiceCollection 接口,在框架初始建立时,看起来只有 services.AddControllers(); 注册了控制器的服务,其实不然,基本上要用到的服务全都注册在里面。这里如果直接去看IServiceCollection的接口是看不出什么的,这个需要回到入口--Program。
当IHost对象建立后,第二步Build时,执行了以下方法(源码位置......extensions-3.1.14srcHostingHostingsrcHostBuilder ):
public IHost Build() { if (_hostBuilt) { throw new InvalidOperationException("Build can only be called once."); } _hostBuilt = true; BuildHostConfiguration(); // 创建ConfigurationBuilder,并调用_configureHostConfigActions列表进行配置的初始化 CreateHostingEnvironment(); // 构建HostingEnvironment对象,从配置中获取key为applicationName、environment的应用名称和环境名称 CreateHostBuilderContext(); // HostBuilderContext宿主上下文,保存HostingEnvironment、Configuration和宿主的一些自定义属性 BuildAppConfiguration(); // 合并之前的_hostConfiguration,调用_configureAppConfigActions列表初始化应用配置 CreateServiceProvider(); return _appServices.GetRequiredService<IHost>(); }
可以看到主要执行了5个方法,但是重要的是最后一个方法 CreateServiceProvider()。
private void CreateServiceProvider() { var services = new ServiceCollection(); #pragma warning disable CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete services.AddSingleton<IHostingEnvironment>(_hostingEnvironment); #pragma warning restore CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete services.AddSingleton<IHostEnvironment>(_hostingEnvironment); services.AddSingleton(_hostBuilderContext); // register configuration as factory to make it dispose with the service provider services.AddSingleton(_ => _appConfiguration); #pragma warning disable CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete services.AddSingleton<IApplicationLifetime>(s => (IApplicationLifetime)s.GetService<IHostApplicationLifetime>()); #pragma warning restore CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete services.AddSingleton<IHostApplicationLifetime, ApplicationLifetime>(); services.AddSingleton<IHostLifetime, ConsoleLifetime>(); services.AddSingleton<IHost, Internal.Host>(); services.AddOptions(); services.AddLogging(); foreach (var configureServicesAction in _configureServicesActions) { configureServicesAction(_hostBuilderContext, services); } var containerBuilder = _serviceProviderFactory.CreateBuilder(services); foreach (var containerAction in _configureContainerActions) { containerAction.ConfigureContainer(_hostBuilderContext, containerBuilder); } _appServices = _serviceProviderFactory.CreateServiceProvider(containerBuilder); if (_appServices == null) { throw new InvalidOperationException($"The IServiceProviderFactory returned a null IServiceProvider."); } // resolve configuration explicitly once to mark it as resolved within the // service provider, ensuring it will be properly disposed with the provider _ = _appServices.GetService<IConfiguration>(); }
从第一句,var services = new ServiceCollection();,可以看出来了,我们在Startup.cs中的 IServiceCollection 服务容器是这里创建并初始化的。
接下来都是注册前面4个方法BuildHostConfiguration() CreateHostingEnvironment()CreateHostBuilderContext()BuildAppConfiguration()所加工出来的各种信息。
services.AddSingleton<IHostingEnvironment>(_hostingEnvironment); services.AddSingleton<IHostEnvironment>(_hostingEnvironment); services.AddSingleton(_hostBuilderContext); services.AddSingleton(_ => _appConfiguration);
Host的IHostApplicationLifetime和IHostLifetime这两个接口可以用来进行应用程序的生命周期管理。
这里不细究,详情可参考 探索 ASP.Net Core 3.0系列五:引入IHostLifetime并弄清Generic Host启动交互
services.AddSingleton<IHostApplicationLifetime, ApplicationLifetime>();
services.AddSingleton<IHostLifetime, ConsoleLifetime>();
接下来几句话 分别是:
注册IHost进服务容器,IHost的默认实现是一个内部类Host
注册Options(一个类似Configuration功能的服务,这里不细讲)
注册默认日志容器
services.AddSingleton<IHost, Internal.Host>();
services.AddOptions();
services.AddLogging();
后面是调用_configureServicesActions列表把其他服务注册进来......这里打住,我们知道了在ConfigureServices中配置了很多东西就可以了。
Configure
configure方法用于指定应用程序如何响应HTTP请求。通过将中间件组件添加到IApplicationBuilder实例来配置请求管道。
可以配置跨域、静态文件访问、HTTP重定向、异常处理等,如下图所示
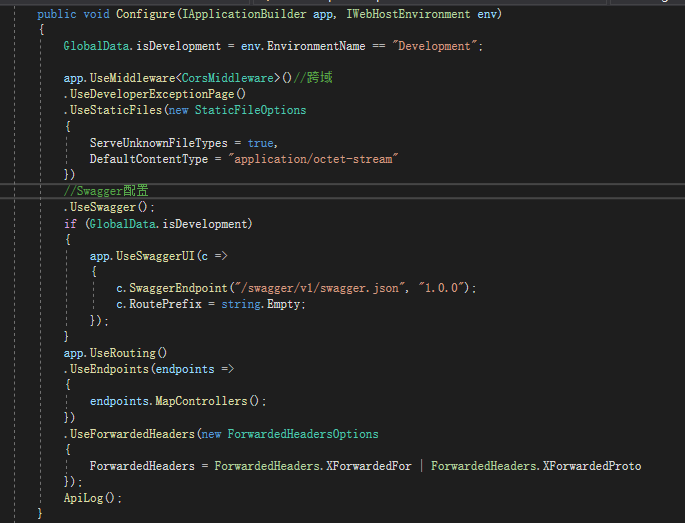
接下来请看.Net Core 3.1 ,Configure的的代码如下:主要参数是 IApplicationBuilder ,IWebHostEnvironment 。
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllers(); }); }
IWebHostEnvironment 包含各种配置中要使用到的环境变量。
IApplicationBuilder 是重点,Configure 方法 使用 IApplicationBuilder 来使用中间件,使用 app.Use______ 来注册中间件请求管道
IApplicationBuilder 的源码如下:......aspnetcore-3.1.14srcHttpHttp.AbstractionssrcIApplicationBuilder
public interface IApplicationBuilder { IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get; set; } IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; } IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures { get; }
RequestDelegate Build(); IApplicationBuilder New(); IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware); }
先说注入的三个参数
ApplicationServices :获取或设置提供对应用程序服务容器的访问的 IServiceProvider 提供程序,为其他对象提供自定义支持的对象,可以参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/watermoon2/p/5075002.html。
Properties:获取可用于在中间件之间共享数据的 键/值 集合,Properties 是类型为 IDictionary<string,object>。
ServerFeatures:获取应用程序服务器提供的HTTP特性集。
然后是三个方法
Build():可以看到这个方法是一个委托,使用此委托来处理HTTP请求
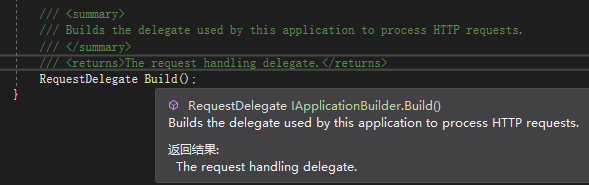
New():创建一个 IApplicationBuilder 共享 Properties 的 IApplicationBuilder

Use():将中间件委托添加到应用程序的请求管道中。
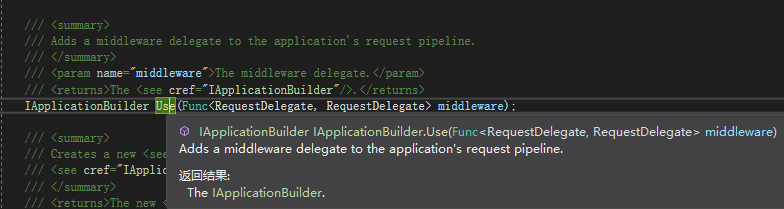
以上合起来就是Configure方法会调用ServiceProvider所解析的相应的参数,再可以使用IApplicationBuilder将中间件添加到应用程序管道中。最终RequestDelegate由IApplicationBuilder构建并返回的。
最后用一张图总结一下HTTP请求在中间件管道中的流程:
