$Treap$ $and$ $Splay$
我隐约记得之前说NOIP之前不再学超纲算法。但是我又开始学了。所以说我NOIP会不会凉。这真是个好问题。中考前在家无聊地报了NOI的网上同步赛,后来发现要全网公示成绩......所以赶紧学点东西骗骗分。
记得以前初赛曾经考过一个东西叫做二叉排序树,这个东西非常好啊,平均时间复杂度是$O(logN)$的(如果插入节点的顺序随机)。但是构造数据就会被卡,树就成了一条链,退化到了O(N)。随机一下就可以不被卡啦,但是有时候要求强制在线,就用到了神奇的平衡树。
$Treap$依靠的是随机,给每个节点随机的权值,要求根节点的权值大于两棵子树,依赖这样的随机化保证均摊复杂度比较低,树高不超过$logN$。$Treap$=$Tree$+$Heap$;
这是我第一次用指针,其实指针还是挺有意思的,就是一定要注意不要访问空指针,否则程序就炸掉啦!
$Splay$依靠的是信仰,复杂度似乎也是有保证的,但是比较难证。
普通平衡树:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3224
插入x数;
删除x数(若有多个相同的数,只删除一个);
查询x数的排名(若有多个相同的数,输出最小的排名);
查询排名为x的数;
求x的前驱(前驱定义为小于x,且最大的数);
求x的后继(后继定义为大于x,且最小的数);
这里讲一下旋转的问题:程序中的$rotate(n,d)$是指将$n$点的$d$儿子旋转上来作为新的$n$.以$d=1$为例子:
初始状态:
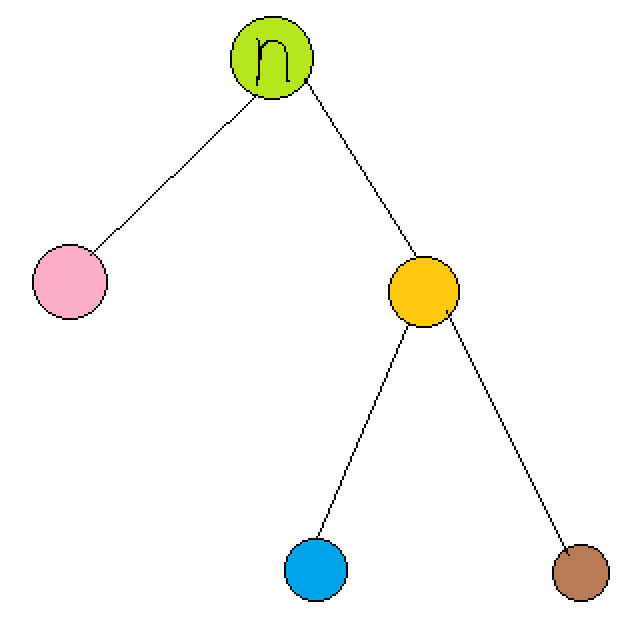
1 node *k=n->ch[d];
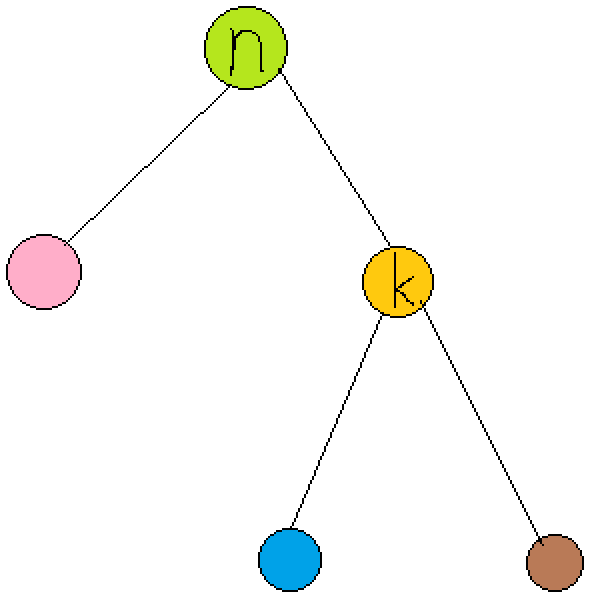
1 n->ch[d]=k->ch[d^1];


1 k->ch[d^1]=n;
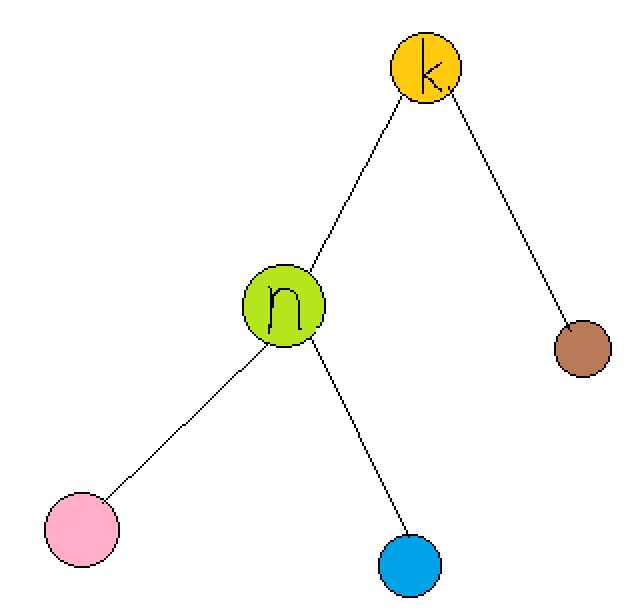
显然这个样子转是不会破坏平衡性的~

1 # include <cstdio> 2 # include <iostream> 3 # include <cstring> 4 # include <string> 5 # include <algorithm> 6 # include <cmath> 7 # include <cstdlib> 8 # define R register int 9 # define ll long long 10 # define inf 100000008 11 12 using namespace std; 13 14 const int maxn=100005; 15 int n,opt,x; 16 struct node 17 { 18 int n,r,s,v; 19 node *ch[2]; 20 void in (int x) 21 { 22 n=s=1; 23 v=x; 24 r=rand(); 25 ch[0]=ch[1]=NULL; 26 } 27 void update () 28 { 29 s=n; 30 if(ch[0]) s+=ch[0]->s; 31 if(ch[1]) s+=ch[1]->s; 32 } 33 int cmp (int x) 34 { 35 if(x==v) return -1; 36 return x>v; 37 } 38 }*roo,pool[maxn]; 39 40 node *newnode () 41 { 42 static int cnt=0; 43 return &pool[++cnt]; 44 } 45 46 void rotate (node *&n,int d) 47 { 48 node *k=n->ch[d]; 49 n->ch[d]=k->ch[d^1]; 50 k->ch[d^1]=n; 51 n->update(); 52 k->update(); 53 n=k; 54 } 55 56 void ins (node *&n,int x) 57 { 58 if(!n) n=newnode(),n->in(x); 59 else 60 { 61 int d=n->cmp(x); 62 if(d==-1) n->n++; 63 else 64 { 65 ins(n->ch[d],x); 66 if(n->ch[d]->r > n->r) rotate(n,d); 67 } 68 n->update(); 69 } 70 } 71 72 void del (node *&n,int x) 73 { 74 if(!n) return; 75 int d=n->cmp(x); 76 if(d==-1) 77 { 78 if(n->n > 1) --n->n; 79 else if(!n->ch[1]) n=n->ch[0]; 80 else if(!n->ch[0]) n=n->ch[1]; 81 else 82 { 83 int f=(n->ch[0]->r > n->ch[1]->r)?0:1; 84 rotate(n,f); 85 del(n->ch[f^1],x); 86 } 87 88 }else del(n->ch[d],x); 89 if(n) n->update(); 90 } 91 92 int ask_key (node *&n,int x) 93 { 94 if(!n) return 1; 95 if(n->v==x) return (n->ch[0]?n->ch[0]->s:0)+1; 96 if(n->v<x) return (n->ch[0]?n->ch[0]->s:0)+n->n+ask_key(n->ch[1],x); 97 return ask_key(n->ch[0],x); 98 } 99 100 int ask_value (node *&n,int x) 101 { 102 if(!n||n->s<x||x<=0) return 0; 103 int s=n->ch[0]?n->ch[0]->s:0; 104 if(s<x&&x<=s+n->n) return n->v; 105 if(s>=x) return ask_value(n->ch[0],x); 106 return ask_value(n->ch[1],x-s-n->n); 107 } 108 109 int lef (node *&n,int x) 110 { 111 if(!n) return -inf; 112 if(n->v >= x) return lef(n->ch[0],x); 113 return max(n->v,lef(n->ch[1],x)); 114 } 115 116 int rig (node *&n,int x) 117 { 118 if(!n) return inf; 119 if (n->v <= x) return rig(n->ch[1], x); 120 return min(n->v,rig(n->ch[0], x)); 121 } 122 123 int main() 124 { 125 scanf("%d",&n); 126 for (R i=1;i<=n;++i) 127 { 128 scanf("%d%d",&opt,&x); 129 if(opt==1) ins(roo,x); 130 else if(opt==2) del(roo,x); 131 else if(opt==3) printf("%d ",ask_key(roo,x)); 132 else if(opt==4) printf("%d ",ask_value(roo,x)); 133 else if(opt==5) printf("%d ",lef(roo,x)); 134 else printf("%d ",rig(roo,x)); 135 } 136 return 0; 137 }
文艺平衡树:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3223
区间翻转。这种题大概只能用$Splay$来做了吧,反正我不知道$Treap$怎么做这东西.
首先$Splay$也是一种平衡树,人气很高,常数据传比较大.它的复杂度不依赖于随机,但是也有一点玄学.它的核心操作就叫$Splay$,是一种很精巧的旋转,它的作用是将任意节点旋转到某一节点底下作为它的儿子,这样的特性就决定了她对于许多序列操作的不可替代性.关于$Splay$有几点要注意的问题:
·旋转不分左旋右旋($Treap$的关键在于将父亲往下转,因为有两个儿子所以要分开看;而$Splay$的核心是往父亲上面转,显然父亲只有一个);
·维护序列时可以打$delta$标记,但是一定要记得下放;
说了这么多下面就来讲讲旋转:
$Splay$的旋转很有意思,它基于一个相对简单的$rotate$操作(把自己转到父亲的位置),但是不是一味的瞎转,这样有可能虽然达成了目的却使链的长度越来越长;首先我们要找到这个节点的父亲,再找到他的爷爷,如果爷爷就是目标节点,转一下自己,退出.如果爷爷父亲自己三点共线,那么先转一下父亲,再转一下自己,否则自己转两次即可.
如果我们要操作区间$[l,r]$,那么首先找到$l$的前驱,把它转到根的位置,再将$r$的后继转到根的右儿子,此时根的右儿子的左儿子就是我们所需要的区间了,可以用来维护一些带插入的,线段树做不了的操作.

1 # include <cstdio> 2 # include <iostream> 3 # include <queue> 4 # include <cstring> 5 # include <string> 6 # define R register int 7 # define ll long long 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int maxn=100005; 12 int n,m,x,y,roo; 13 struct node 14 { 15 int delta,ch[2],f,siz; 16 }t[maxn]; 17 18 int read(); 19 20 inline void update (int id) 21 { 22 t[id].siz=t[ t[id].ch[0] ].siz+t[ t[id].ch[1] ].siz+1; 23 } 24 25 inline void lin (int x,int f,int d) 26 { 27 t[x].f=f; 28 t[f].ch[d]=x; 29 } 30 31 int build (int l,int r) 32 { 33 if(l>r) return 0; 34 int mid=(l+r)>>1; 35 lin(build(l,mid-1),mid,0); 36 lin(build(mid+1,r),mid,1); 37 t[mid].delta=0; 38 update(mid); 39 return mid; 40 } 41 42 inline void pushdown (int n) 43 { 44 t[n].delta=0; 45 t[ t[n].ch[0] ].delta^=1; 46 t[ t[n].ch[1] ].delta^=1; 47 swap(t[n].ch[0],t[n].ch[1]); 48 } 49 50 void write (int x) 51 { 52 if(!x) return; 53 if(t[x].delta) pushdown(x); 54 write(t[x].ch[0]); 55 if(x!=1&&x!=n+2) printf("%d ",x-1); 56 write(t[x].ch[1]); 57 } 58 59 inline int D (int x) 60 { 61 return x==t[ t[x].f ].ch[1]; 62 } 63 64 void rotate (int x) 65 { 66 int f=t[x].f; 67 if(f==roo) roo=x; 68 int g=t[f].f; 69 int mf=D(x),gf=D(f); 70 int k=t[x].ch[mf^1]; 71 lin(k,f,mf),lin(f,x,mf^1),lin(x,g,gf); 72 update(f),update(x); 73 } 74 75 void splay (int x,int g) 76 { 77 while(t[x].f!=g) 78 { 79 if(t[ t[x].f ].f==g) rotate(x); 80 else if(D(x)==D(t[x].f)) rotate(t[x].f),rotate(x); 81 else rotate(x),rotate(x); 82 } 83 update(x); 84 } 85 86 inline int find (int x) 87 { 88 int no=roo; 89 x--; 90 if(t[no].delta) pushdown(no); 91 while (t[ t[no].ch[0] ].siz!=x) 92 { 93 if(t[ t[no].ch[0] ].siz<x) 94 x-=t[ t[no].ch[0] ].siz+1,no=t[no].ch[1]; 95 else no=t[no].ch[0]; 96 if(t[no].delta) pushdown(no); 97 } 98 return no; 99 } 100 101 int main() 102 { 103 n=read(),m=read(); 104 roo=build(1,n+2); 105 while(m--) 106 { 107 x=read(),y=read(); 108 x=find(x); 109 splay(x,0); 110 y=find(y+2); 111 splay(y,roo); 112 t[ t[y].ch[0] ].delta^=1; 113 } 114 write(roo); 115 return 0; 116 } 117 118 inline int read() 119 { 120 int x=0; 121 char c=getchar(); 122 while (!isdigit(c)) c=getchar(); 123 while (isdigit(c)) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar(); 124 return x; 125 }
营业额统计:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1588
题意概述:每次插入一个数,并找到以前插入过的数中和它最接近的一个作差取绝对值加起来,输出总的差;
Treap板子题,就当练练手。最接近的一个必然是前驱或者后继...没了。

1 # include <cstdio> 2 # include <iostream> 3 # include <cstdlib> 4 # include <algorithm> 5 # define inf 1000009 6 # define R register int 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 const int maxn=32770; 11 int n,x,l,r,ans; 12 struct node 13 { 14 int n,v,s,r; 15 node *ch[2]; 16 void in (int x) 17 { 18 v=x; 19 n=s=1; 20 r=rand(); 21 ch[0]=ch[1]=NULL; 22 } 23 void update() 24 { 25 s=n; 26 if(ch[0]) s+=ch[0]->s; 27 if(ch[1]) s+=ch[1]->s; 28 } 29 int cmp (int x) 30 { 31 if(x==v) return -1; 32 return x>v; 33 } 34 }*roo,pool[maxn]; 35 36 node *newnode() 37 { 38 static int cnt=0; 39 return &pool[++cnt]; 40 } 41 42 inline int read() 43 { 44 int x=0,f=1; 45 char c=getchar(); 46 while (!isdigit(c)) { if(c=='-') f=-f; c=getchar(); } 47 while (isdigit(c)) { x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48); c=getchar(); } 48 return x*f; 49 } 50 51 void rotate (node *&n,int d) 52 { 53 node *k=n->ch[d^1]; 54 n->ch[d^1]=k->ch[d]; 55 k->ch[d]=n; 56 n->update(); 57 k->update(); 58 n=k; 59 } 60 61 void ins (node *&n,int x) 62 { 63 if(!n) n=newnode(),n->in(x); 64 else 65 { 66 int d=n->cmp(x); 67 if(d==-1) n->n++; 68 else 69 { 70 ins(n->ch[d],x); 71 if(n->r < n->ch[d]->r) rotate(n,d^1); 72 } 73 n->update(); 74 } 75 } 76 77 int lef (node *&n,int x) 78 { 79 if(!n) return -inf; 80 if(n->v > x) return lef(n->ch[0],x); 81 return max(n->v,lef(n->ch[1],x)); 82 } 83 84 int rig (node *&n,int x) 85 { 86 if(!n) return inf; 87 if(n->v < x) return rig(n->ch[1],x); 88 return min(n->v,rig(n->ch[0],x)); 89 } 90 91 int main() 92 { 93 scanf("%d",&n); 94 x=read(); 95 ans=x; 96 ins(roo,x); 97 for (int i=2;i<=n;++i) 98 { 99 x=read(); 100 l=lef(roo,x); 101 r=rig(roo,x); 102 if(l==-inf) ans+=r-x; 103 else if(r==inf) ans+=x-l; 104 else ans+=min(x-l,r-x); 105 ins(roo,x); 106 } 107 printf("%d",ans); 108 return 0; 109 }
宠物收养所:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1208
题意概述:一个宠物收养所,当有人来且有宠物时,他就带走一个与自己的特征值最接近的宠物,如果没有宠物就在里面等,宠物同样。
可以看出,无论什么时候,收养所里面不可能又有宠物又有人,所以可以用一棵Treap维护,顺便维护一下现在里面有几个人或是宠物就好了。其实本质上人和宠物是没有区别的,可以认为当人都在里面等的时候就是宠物领养人了(雾。不过嘛...还真是,到底是你在养宠物还是宠物在养你?每次猫猫挠我的时候,睡觉不理我的时候,我都很好奇。

1 # include <cstdio> 2 # include <iostream> 3 # include <cstdlib> 4 # define inf 21474836480LL 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const int maxn=80008; 9 int n,cw,ly; 10 long long l,r; 11 int a; 12 long long ans,b; 13 14 struct node 15 { 16 int n,s,r; 17 long long v; 18 node *ch[2]; 19 void in (long long x) 20 { 21 v=x; 22 n=s=1; 23 r=rand(); 24 ch[0]=ch[1]=NULL; 25 } 26 void update() 27 { 28 s=n; 29 if(ch[0]) s+=ch[0]->s; 30 if(ch[1]) s+=ch[1]->s; 31 } 32 int cmp (long long x) 33 { 34 if(x==v) return -1; 35 return x>v; 36 } 37 }*roo,pool[maxn]; 38 39 node *newnode() 40 { 41 static int cnt=0; 42 return &pool[++cnt]; 43 } 44 45 void rotate (node *&n,int d) 46 { 47 node *k=n->ch[d^1]; 48 n->ch[d^1]=k->ch[d]; 49 k->ch[d]=n; 50 n->update(); 51 k->update(); 52 n=k; 53 } 54 55 long long lef (node *&n,long long x) 56 { 57 if(!n) return -inf; 58 if(n->v > x) return lef(n->ch[0],x); 59 return max(n->v,lef(n->ch[1],x)); 60 } 61 62 long long rig (node *&n,long long x) 63 { 64 if(!n) return inf; 65 if(n->v < x) return rig(n->ch[1],x); 66 return min(n->v,rig(n->ch[0],x)); 67 } 68 69 void ins (node *&n,long long x) 70 { 71 if(!n) n=newnode(),n->in(x); 72 else 73 { 74 int d=n->cmp(x); 75 if(d==-1) n->n++; 76 else 77 { 78 ins(n->ch[d],x); 79 if(n->r < n->ch[d]->r) rotate(n,d^1); 80 } 81 n->update(); 82 } 83 } 84 85 void del (node *&n,long long x) 86 { 87 if(!n) return ; 88 int d=n->cmp(x); 89 if(d==-1) 90 { 91 if(n->n > 1) --n->n; 92 else if(!n->ch[0]) n=n->ch[1]; 93 else if(!n->ch[1]) n=n->ch[0]; 94 else 95 { 96 int f=(n->ch[0]->r > n->ch[1]->r)?1:0; 97 rotate(n,f); 98 del(n->ch[f],x); 99 } 100 }else del(n->ch[d],x); 101 if(n) n->update(); 102 } 103 104 int main() 105 { 106 scanf("%d",&n); 107 for (int i=1;i<=n;++i) 108 { 109 scanf("%d%lld",&a,&b); 110 if(a==1&&cw==0) ins(roo,b),ly++; 111 else if(a==1&&cw) 112 { 113 l=lef(roo,b); 114 r=rig(roo,b); 115 if(l==-inf) { ans+=r-b; del(roo,r); } 116 else if(r==inf) { ans+=b-l; del(roo,l); } 117 else if(b-l<=r-b) { ans+=b-l; del(roo,l); } 118 else { ans+=r-b; del(roo,r); } 119 cw--; 120 } 121 else 122 if(a==0&&ly==0) ins(roo,b),cw++; 123 else if(a==0&&ly) 124 { 125 l=lef(roo,b); 126 r=rig(roo,b); 127 if(l==-inf) { ans+=r-b; del(roo,r); } 128 else if(r==inf) { ans+=b-l; del(roo,l); } 129 else if(b-l<=r-b) { ans+=b-l; del(roo,l); } 130 else { ans+=r-b; del(roo,r); } 131 ly--; 132 } 133 ans%=1000000; 134 } 135 printf("%lld",ans); 136 return 0; 137 }
永无乡:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2733
题意概述:有一些岛,每个岛有一个重要程度,每次询问某个岛所在的联通块内重要度第$k$小的岛的编号,或是在两岛之间修一条路.
首先找第$k$小就可以想到平衡树啦,联通块可以拿并查集来维护,但是合并两个联通块之后怎么办呢?可以想到一个暴力的做法,每当两块合并时直接将小一点的平衡树拆掉塞进大的里面,然后再考虑优化...等等...过了!
其实这个做法听起来暴力极了,其实还是挺科学的,这就是所谓启发式合并。因为每次都把小的往大的里边合并,所以每个点最多也只会被合并$log$次,复杂度是$O(N(logN)^2)$

1 // luogu-judger-enable-o2 2 # include <cstdio> 3 # include <iostream> 4 # include <cstring> 5 # include <string> 6 # include <algorithm> 7 # include <cmath> 8 # include <cstdlib> 9 # include <queue> 10 # include <ctime> 11 # define R register int 12 # define ll long long 13 14 using namespace std; 15 16 const int maxn=100005; 17 int n,m,v[maxn],h,f[maxn],x,y,k,Q,pos[maxn]; 18 char s[2]; 19 struct node 20 { 21 int n,v,s,r; 22 node *ch[2]; 23 void in (int x) 24 { 25 n=s=1; 26 v=x; 27 r=rand(); 28 ch[0]=ch[1]=NULL; 29 } 30 int cmp (int x) 31 { 32 if(x==v) return -1; 33 return x>v; 34 } 35 void update() 36 { 37 s=n; 38 if(ch[0]) s+=ch[0]->s; 39 if(ch[1]) s+=ch[1]->s; 40 } 41 }*roo[maxn],pool[maxn*50]; 42 node *q[maxn]; 43 44 inline int read(); 45 node *newnode(); 46 void ins (node *&node,int x); 47 inline void mer (int x,int y); 48 void rotate (node *&n,int d); 49 int father (int x); 50 int ask (node *&n,int k); 51 52 void write (int x) 53 { 54 if(x<0) putchar('-'),write(-x); 55 else 56 { 57 if(x>=10) write(x/10); 58 putchar(x%10+'0'); 59 } 60 } 61 62 int main() 63 { 64 srand(time(0)); 65 n=read(),m=read(); 66 for (R i=1;i<=n;++i) 67 x=read(),f[i]=i,ins(roo[i],x),pos[x]=i; 68 for (R i=1;i<=m;++i) 69 { 70 x=read(),y=read(); 71 if(x==0||y==0) continue; 72 mer(x,y); 73 } 74 Q=read(); 75 int ans=0; 76 while (Q--) 77 { 78 scanf("%s",s); 79 x=read(),y=read(); 80 if(s[0]=='Q') 81 { 82 83 x=father(x); 84 if(roo[x]->s<y) ans=-1; 85 else ans=pos[ ask(roo[x],y) ]; 86 write(ans); 87 putchar(' '); 88 } 89 else 90 { 91 mer(x,y); 92 if(x==0||y==0) continue; 93 } 94 } 95 return 0; 96 } 97 98 inline int read() 99 { 100 int x=0; 101 char c=getchar(); 102 while(!isdigit(c)) c=getchar(); 103 while(isdigit(c)) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar(); 104 return x; 105 } 106 107 int father (int x) { if(x!=f[x]) return f[x]=father(f[x]); return x; } 108 109 node *newnode() 110 { 111 static int cnt=0; 112 return &pool[++cnt]; 113 } 114 115 void ins (node *&n,int x) 116 { 117 if(!n) n=newnode(),n->in(x); 118 else 119 { 120 int d=n->cmp(x); 121 if(d==-1) ++n->n; 122 else 123 { 124 ins(n->ch[d],x); 125 if(n->ch[d]->r > n->r) rotate(n,d); 126 } 127 n->update(); 128 } 129 } 130 131 void rotate (node *&n,int d) // rotate n->ch[d] to n 132 { 133 node *k=n->ch[d]; 134 n->ch[d]=k->ch[d^1]; 135 k->ch[d^1]=n; 136 n->update(); 137 k->update(); 138 n=k; 139 } 140 141 inline void mer (int x,int y) 142 { 143 if(roo[x]->s<roo[y]->s) swap(x,y); 144 x=father(x); 145 y=father(y); 146 if(x==y) return; 147 f[y]=x; 148 int h=1,t=0; 149 q[++t]=roo[y]; 150 node *k; 151 while(h<=t) 152 { 153 k=q[h]; 154 ins(roo[x],k->v); 155 if(k->ch[0]) q[++t]=k->ch[0]; 156 if(k->ch[1]) q[++t]=k->ch[1]; 157 h++; 158 } 159 roo[y]=roo[x]; 160 } 161 162 int ask (node *&n,int k) 163 { 164 if(!n||k<0||n->s<k) return 0; 165 int s=n->ch[0]?n->ch[0]->s:0; 166 if(s<k&&k<=n->n+s) return n->v; 167 if(s<k) return ask(n->ch[1],k-n->n-s); 168 return ask(n->ch[0],k); 169 }
---shzr
