一、实验目的
- 理解类的继承和派生机制
- 掌握派生类的定义和使用
- 掌握派生类成员的标识与访问中同名覆盖原则、二元作用域分辨符和虚基类的用法
- 掌握派生类构造函数和析构函数的定义及调用次序
- 理解运算符重载的目的,掌握运算符重载函数的编写方法
二、实验准备
- 类的继承和派生
请结合第 7 章课件和教材复习以下内容:- 引入继承和派生机制的目的
- 基本概念:继承、派生、基类、直接基类、间接基类、派生类
- 语法:
- 派生类定义的语法格式(单重继承、多重继承);
- 派生类构造函数极其初始化列表写法
- 派生类成员的标识与访问
- 同名覆盖指的是什么?
- 二元作用域分辨符在什么情况下使用?
- 什么是虚基类?引入虚基类的目的是什么?如何使用?
- 运算符重载
请结合第 8 章课件和教材学习以下内容:- 运算符重载的目的
- 运算符重载的规则和限制
- 运算符重载函数的语法格式
- 运算符重载时,究竟重载为类的成员函数,还是友元,还是普通函数,需要综合考虑哪些因素?
三、实验内容
-
某计算机硬件系统,为了实现特定的功能,在某个子模块设计了 ABC 三款芯片用于
数字计算。各个芯片的计算功能如下:
A 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的减法(m-n)
B 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的乘法(m*n)
C 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的除法(m/n)
为 ABC 三个芯片分别定义类,描述上述芯片的功能,并在 main 函数中测试这三个类。
(提示:利用类的继承和派生,抽象出共有属性和操作作为基类。) -
定义一个车(vehicle)基类,具有数据成员 maxspeed, weight(均为 int 型), 函数成员 run(), stop(),由此派生出自行车(bicycle)类、汽车(motorcar)类。其中, bicycle 类新增数据成员高度(height),motorcar 类新增数据成员座位数(seatnum)属性。再从 bicycle 和 motorcar 派生出摩托车(motorcycle)类,并在主程序中测试这个类。(每个类都要求定义构造函数和析构函数)
(提示: ① 注意把 vehicle 设置为虚基类; ② run(), stop()函数体,通过输出字符串run, stop 简单模拟。) -
基于「实验 4 类和对象-2」中设计并实现的类 Fraction,创建派生类 iFraction,用以
描述如下形式的分数:
(1frac 2 3)
要求:- 更新 Fraction 类
为 Fraction 类编写运算符+、-、、/重载函数,实现在 main 函数中直接用+、-、、/进行 Fraction 类运算。 - 设计并实现派生 iFraction 类
- 为派生类 iFraction 定义构造函数,实现 iFraction 对象的初始化
- 为派生类 iFraction 增加一个成员函数,用于在屏幕上显示 iFraction 对象
- 设计一个普通函数 convertF()用于对 iFraction 类对象进行规范化处理。(选做)
(提示:把 convertF()设计为 Fraction 类和 iFraction 类的友元函数)
例如:(更多情形请自行考虑)
(frac 5 3 o 1 frac 2 3)
- 更新 Fraction 类
-
以多文件结构方式编写(fraction.h, fraction.cpp, ifraction.h, ifraction.cpp, main.cpp)
(选做)
基于提供的程序文件,补足并扩充程序,实现一个多类型玩家角色扮演游戏。
在本次实验附件包 ex4 中有如下文件:
container.h, container.cpp, player.h, player.cpp, swordsman.h, swordsman.cpp, main.cpp- 阅读源码,理解并补足程序,让程序运行生效。
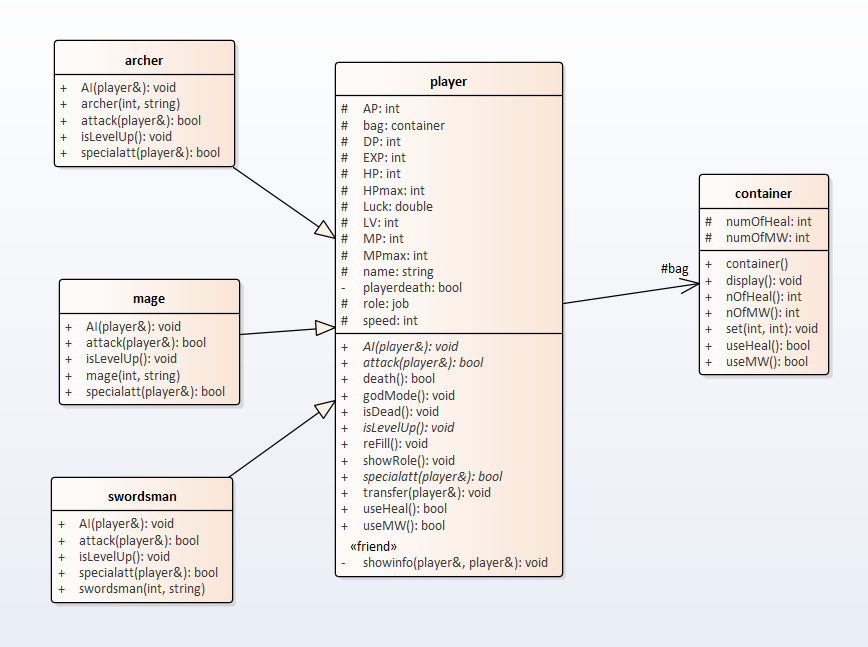
其中,程序中出现有????????之处,是需要补足的部分。 - 画出这个角色扮演游戏 UML 类图,尤其是类和类之间的关系
- 设计并实现 archer 类和 mage 类。在 UML 类图中也加进这两个新类。
- 修改 main 函数,随机生成不同角色的敌人,并保证程序正常运行。
- 为游戏增加其它元素,完善游戏的可玩性、趣味性,等。
(说明:这道涉及虚函数、运行时多态。你可以在第 8 章学完后尝试编写,或者,在尝试编写这道题的过程中,学习第 8 章虚函数和运行时多态的知识。)
- 阅读源码,理解并补足程序,让程序运行生效。
四、实验结论
- 实验内容 1
- LM51.h
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifndef _LM51_H
#define _LM51_H
class LM51{
protected:
int m,n;
public:
int plus();
LM51(int M=2016,int N=133);
~LM51();
};
#endif
- LM51.cpp
#include"LM51.h"
int LM51::plus() {
cout << "LM51.plus " << endl;
return m+n;
}
LM51::LM51(int M,int N) {
cout << "Constru
}ctor LM51 is called" << endl;
m=M;
n=N;
LM51::~LM51() {
cout << "Deconstructor LM51 is called" << endl;
}
- A.h
#include"LM51.h"
#ifndef _A_h
#define _A_h
class A:public LM51{
public :
A(int M=2016,int N=133);
int minus();
~A();
};
#endif
- A.cpp
#include"A.h"
A::A(int M,int N){
m=M;
n=N;
cout << "Constructor A is called" << endl;
}
int A::minus() {
cout << "A.minus " << endl;
return m-n;
}
A::~A() {
cout << "Deconstructor A is called" << endl;
}
- B.h
#include"LM51.h"
#ifndef _B_h
#define _B
class B:public LM51{
public :
B(int M=2016,int N=133);
int mulip();
~B();
};
#endif
- B.cpp
#include"B.h"
B::B(int M,int N){
m=M;
n=N;
cout << "Constructor B is called" << endl;
}
int B::mulip() {
cout << "B.mulip " << endl;
return m*n;
}
B::~B() {
cout << "Deconstructor B is called" << endl;
}
- C.h
#include"LM51.h"
#ifndef _C_h
#define _C
class C:public LM51{
public :
C(int M=2016,int N=133);
double divi();
~C();
};
#endif
- C.cpp
#include"C.h"
C::C(int M,int N){
m=M;
n=N;
cout << "Constructor C is called" << endl;
}
double C::divi() {
cout << "C.divi " << endl;
return m/n;
}
C::~C() {
cout << "Deconstructor C is called" << endl;
}
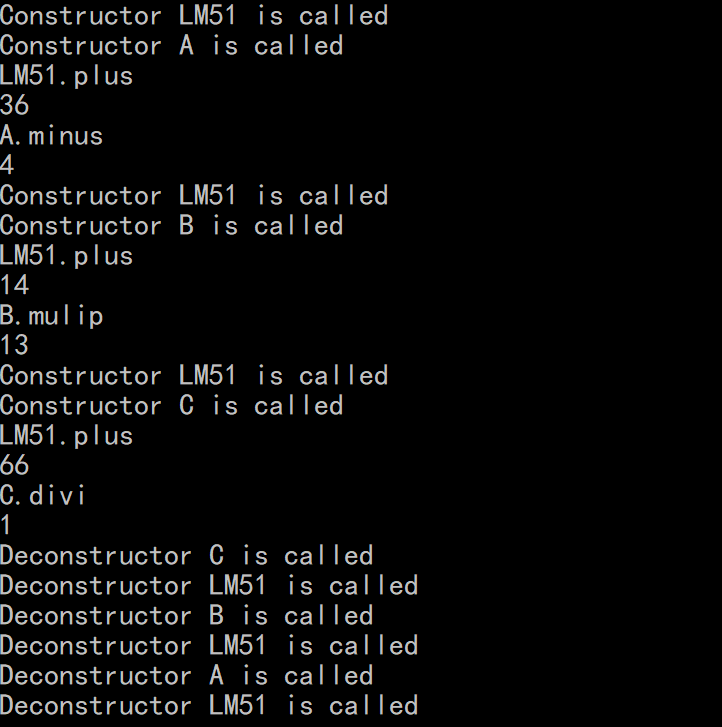
- Main.cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include "A.h"
#include "B.h"
#include "C.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
A a(20,16);
cout<<a.plus()<<endl;
cout<<a.minus()<<endl;
B b(13,1);
cout<<b.plus()<<endl;
cout<<b.mulip()<<endl;
C c(40,26);
cout<<c.plus()<<endl;
cout<<c.divi()<<endl;
return 0;
}
- Screenshot:
- 实验内容 2
- vehicle.h
#ifndef _VEHICLE
#define _VEHICLE
class vehicle{
protected:
int maxspeed,weight;
public:
void run();
void stop();
vehicle(int M=100,int W=1000);
~vehicle();
};
#endif
- vehicle.cpp
#include "vehicle.h"
void vehicle::run() {
cout<<"run"<<endl;
}
void vehicle::stop() {
cout<<"stop"<<endl;
}
vehicle::vehicle(int M,int W) {
maxspeed=M;
weight=W;
cout<<"Constructor vehicle is called"<<endl;
}
vehicle::~vehicle() {
cout<<"Deconstructor vehicle is called"<<endl;
}
- bicycle.h
#ifndef _BICYCLE
#define _BICYCLE
class bicycle:virtual public vehicle{
protected:
int height;
public:
bicycle(int M=100,int W=1000,int H=2):vehicle(M,W);
~bicycle();
};
#endif
- bicycle.cpp
#include"bicycle.h"
bicycle::bicycle(int M,int W,int H):vehicle(M,W) {
height=H;
cout<<"Constructor bicycle is called"<<endl;
}
bicycle::~bicycle() {
cout<<"Deconstructor bicycle is called"<<endl;
}
- motorcar.h
#ifndef _MOTORCAR
#define _MOTORCAR
class motorcar:virtual public vehicle{
protected:
int seatnum;
public:
motorcar(int M,int W,int H):vehicle(M,W);
~motorcar();
};
#endif
- motorcar.cpp
#include"motocar.h"
motocar::motorcar(int M,int W,int S):vehicle(M,W) {
seatnum=S;
cout<<"Constructor motorcar is called"<<endl;
}
motocar::~motorcar() {
cout<<"Deconstructor motorcar is called"<<endl;
}
- motorcycle.h
#ifndef _MOTORCYCLE
#define _MOTORCYCLE
class motorcycle:public bicycle,public motorca{
public:
motorcycle(int M=100,int W=1000,int S=4,int H=2):vehicle(M,W);
~motorcycle();
};
#endif
- motorcycle.cpp
#include"motorcycle.h"
motorcycle::motorcycle(int M,int W,int S,int H):vehicle(M,W) {
seatnum=S;
height=H;
cout<<"Constructor motorcycle is called"<<endl;
}
motorcycle::~motorcycle() {
cout<<"Deconstructor motorcycle is called"<<endl;
}
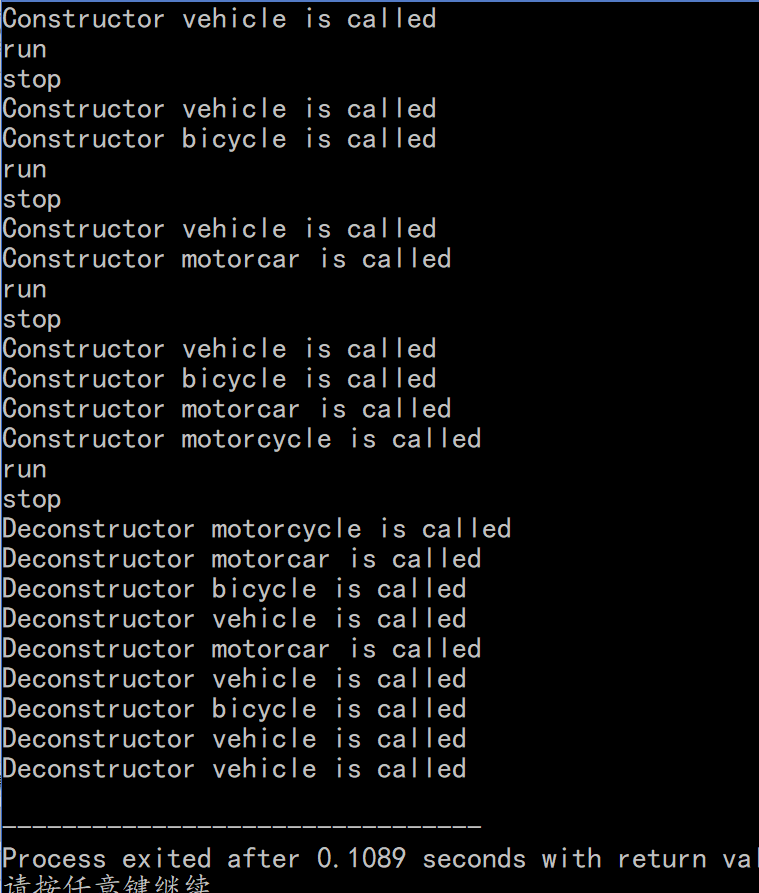
- Main.cpp
#include"vehicle.h"
#include"bicycle.h"
#include"motorcar.h"
#include"motorcycle.h"
int main(){
vehicle a;
a.run();
a.stop();
bicycle b;
b.run();
b.stop();
motorcar c;
c.run();
c.stop();
motorcycle d;
d.run();
d.stop();
return 0;
}
-Screenshot:
- 实验内容 3
- iFraction.h
#include "Fraction.h"
#ifndef _IFRACTION
#define _IFRACTION
class iFraction:public Fraction{
private:
int i;
public:
iFraction(int t=0,int b=1,int I=0):Fraction(t,b){i=I;}
iFraction(const iFraction &c0):Fraction(c0){i=c0.i;}
void print();
friend iFraction convertF(const iFraction &c0);
};
#endif
- iFraction.cpp
#include"iFraction.h"
void iFraction::print() {
if(top==0){cout<<i<<endl;
return ;
}
cout<<setw(4)<<setfill(' ')<<top<<endl;
cout<<setw(3)<<setfill(' ')<<i<<'-'<<endl;
cout<<setw(4)<<setfill(' ')<<bottom<<endl;
}
iFraction convertF(const iFraction &c0) {
iFraction tmp(c0);
tmp.simplify();
int tt=tmp.top/tmp.bottom;
tmp.i+=tt;
tmp.top%=tmp.bottom;
return tmp;
}
- Fraction.h
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#ifndef _FRACTION
#define _FRACTION
using namespace std;
class Fraction {
protected:
int top, bottom;
int gcd(int a, int b);
public:
Fraction(int t, int b);
Fraction(int t);
Fraction();
void simplify();
void add(Fraction c0);
void subtract(Fraction c0);
void multiple(Fraction c0);
void divde(Fraction c0);
bool compare(Fraction c0);
void readln();
void writeln();
double todecimal();
friend Fraction operator +(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1);
friend Fraction operator -(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1);
friend Fraction operator *(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1);
friend Fraction operator /(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1);
Fraction &operator +=(const Fraction &c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom + c0.top * bottom;
simplify();
return *this;
}
Fraction &operator -=(const Fraction &c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom - c0.top * bottom;
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
simplify();
return *this;
}
Fraction &operator *=(const Fraction &c0) {
top *= c0.top;
bottom *= c0.bottom;
simplify();
return *this;
}
Fraction &operator /=(const Fraction &c0) {
if(c0.top == 0) {
return *this;
}
top *= c0.bottom;
bottom *= c0.top;
simplify();
return *this;
}
};
#endif
- Fraction.cpp
#include"Fraction.h"
int Fraction:: gcd(int a, int b) {
return a % b == 0 ? b : gcd(b, a%b);
}
Fraction:: Fraction(int t, int b) {
top = t;
bottom = b;
}
Fraction:: Fraction(int t) {
top = t;
bottom = 1;
}
Fraction:: Fraction() {
top = 0;
bottom = 1;
}
void Fraction:: simplify() {
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
int g = gcd(abs(top),abs(bottom));
top /= g;
bottom /= g;
}
void Fraction:: add(Fraction c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom + c0.top * bottom;
simplify();
}
void Fraction:: subtract(Fraction c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom - c0.top * bottom;
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
simplify();
}
void Fraction:: multiple(Fraction c0) {
top *= c0.top;
bottom *= c0.bottom;
simplify();
}
void Fraction:: divde(Fraction c0) {
if(c0.top == 0) {
cout << "Error: Zero can't be divided.
";
return ;
}
top *= c0.bottom;
bottom *= c0.top;
simplify();
}
bool Fraction:: compare(Fraction c0) {
return top * gcd(bottom, c0.bottom) - c0.top
* gcd(bottom, c0.bottom) > 0 ? true : false;
}
void Fraction:: readln() {
cout << "Plz input the Numerator and Denominator" << endl;
cin >> top;
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
while (tmp == 0) {
cout << "Zero can't be the Denominator, plz try again!" << endl;
cin >> tmp;
}
bottom = tmp;
}
void Fraction:: writeln() {
if(bottom != 1) cout << top << "/" << bottom << endl;
else cout << top <<endl;
}
double Fraction:: todecimal() {
return (double)top / bottom;
}
Fraction operator +(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1) {
Fraction tmp;
tmp.bottom = c0.bottom * c1.bottom;
tmp.top = c1.top * c0.bottom + c0.top * c1.bottom;
tmp.simplify();
return tmp;
}
Fraction operator -(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1) {
Fraction tmp;
tmp.bottom = c0.bottom * c1.bottom;
tmp.top = c0.top * c1.bottom - c1.top * c0.bottom;
if(tmp.bottom < 0) {
tmp.top = - tmp.top;
tmp.bottom = - tmp.bottom;
}
tmp.simplify();
return tmp;
}
Fraction operator *(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1) {
Fraction tmp;
tmp.top = c0.top * c1.top;
tmp.bottom = c0.bottom * c1.bottom;
tmp.simplify();
return tmp;
}
Fraction operator /(const Fraction &c0,const Fraction &c1) {
Fraction tmp;
if(c0.top == 0 || c1.top == 0) {
return tmp;
}
tmp.top = c0.top * c1.bottom;
tmp.bottom = c0.bottom * c1.top;
tmp.simplify();
return tmp;
}
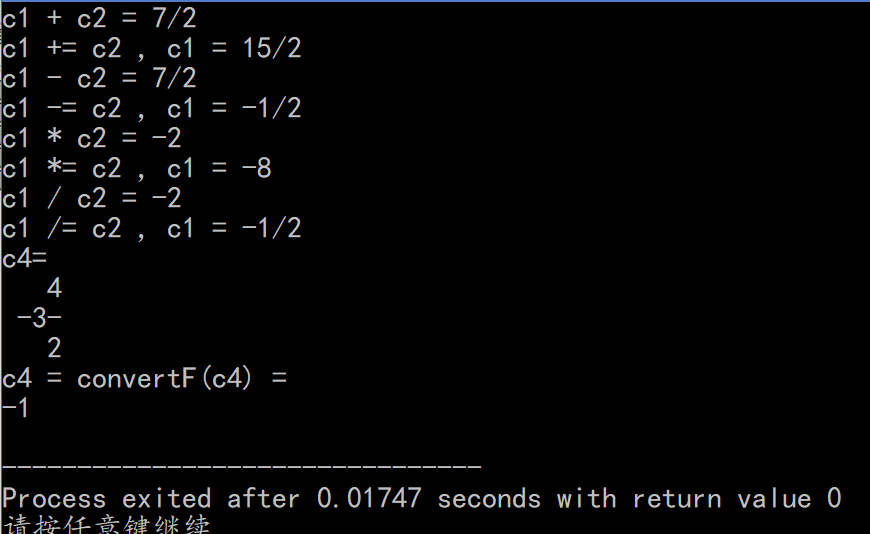
- Main.cpp
#include "Fraction.h"
#include "iFraction.h"
int main() {
Fraction c1 (11,-22);
Fraction c2 (4);
Fraction c3 ;
c1 = c1 + c2;
cout << "c1 + c2 = ";c1.writeln();
c1 += c2;
cout << "c1 += c2 , c1 = ";c1.writeln();
c1 = c1 - c2;
cout << "c1 - c2 = ";c1.writeln();
c1 -= c2;
cout << "c1 -= c2 , c1 = ";c1.writeln();
c1 = c1 * c2;
cout << "c1 * c2 = ";c1.writeln();
c1 *= c2;
cout << "c1 *= c2 , c1 = ";c1.writeln();
c1 = c1 / c2;
cout << "c1 / c2 = ";c1.writeln();
c1 /= c2;
cout << "c1 /= c2 , c1 = ";c1.writeln();
cout << "c4="<<endl;
iFraction c4(4,2,-3);
c4.print();
c4=convertF(c4);
cout<<"c4 = convertF(c4) = "<<endl;
c4.print();
return 0;
}
- Screenshot:
- 实验内容4:
Github Address : https://github.com/shylocks/ex_6_4.git
*Press Commits Buttom to see changes.
UML :
五、实验总结与体会
C++ 与 Java 之间关于“类的继承与多态”一些概念的重叠:
C++ Java
虚函数 普通函数
纯虚函数 抽象函数
抽象类 抽象类
虚基类 接口
(C++先辈万物之父说)