思维题--code forces round# 551 div.2-D
题目
D. Serval and Rooted Tree
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Now Serval is a junior high school student in Japari Middle School, and he is still thrilled on math as before.
As a talented boy in mathematics, he likes to play with numbers. This time, he wants to play with numbers on a rooted tree.
A tree is a connected graph without cycles. A rooted tree has a special vertex called the root. A parent of a node vv is the last different from vv vertex on the path from the root to the vertex vv. Children of vertex vv are all nodes for which vv is the parent. A vertex is a leaf if it has no children.
The rooted tree Serval owns has nn nodes, node 11 is the root. Serval will write some numbers into all nodes of the tree. However, there are some restrictions. Each of the nodes except leaves has an operation maxmax or minmin written in it, indicating that the number in this node should be equal to the maximum or minimum of all the numbers in its sons, respectively.
Assume that there are kk leaves in the tree. Serval wants to put integers 1,2,…,k1,2,…,k to the kk leaves (each number should be used exactly once). He loves large numbers, so he wants to maximize the number in the root. As his best friend, can you help him?
Input
The first line contains an integer nn (2≤n≤3⋅1052≤n≤3⋅105), the size of the tree.
The second line contains nn integers, the ii-th of them represents the operation in the node ii. 00 represents minmin and 11represents maxmax. If the node is a leaf, there is still a number of 00 or 11, but you can ignore it.
The third line contains n−1n−1 integers f2,f3,…,fnf2,f3,…,fn (1≤fi≤i−11≤fi≤i−1), where fifi represents the parent of the node ii.
Output
Output one integer — the maximum possible number in the root of the tree.
Examples
input
Copy
6
1 0 1 1 0 1
1 2 2 2 2
output
Copy
1
input
Copy
5
1 0 1 0 1
1 1 1 1
output
Copy
4
input
Copy
8
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
1 1 2 2 3 3 3
output
Copy
4
input
Copy
9
1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1
1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
output
Copy
5
Note
Pictures below explain the examples. The numbers written in the middle of the nodes are their indices, and the numbers written on the top are the numbers written in the nodes.
In the first example, no matter how you arrange the numbers, the answer is 11.
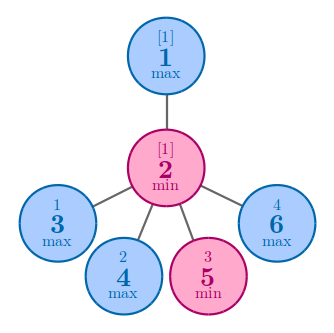
In the second example, no matter how you arrange the numbers, the answer is 44.
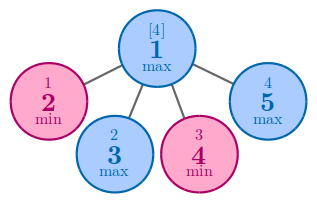
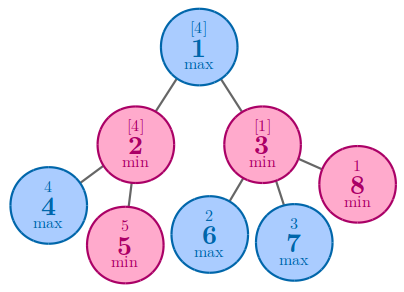
In the third example, one of the best solution to achieve 44 is to arrange 44 and 55 to nodes 44 and 55.
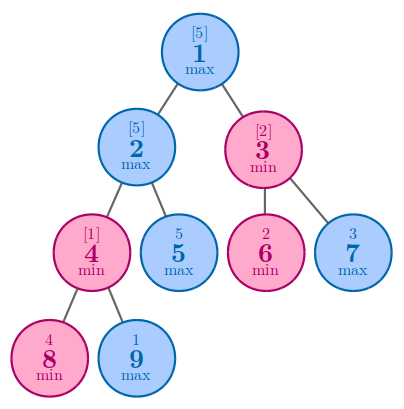
In the fourth example, the best solution is to arrange 55 to node 55.
题意易懂
思路
让所有叶子的值都为1
算的是必要的叶子个数,那么答案就是叶子个数 - 必要的叶子个数 + 1
如果是取max,那么该节点要取最大,那必要的叶子个数取决于该节点的所有子节点中,最小的必要叶子个数
如果是取min,那么该节点要取最大,必要的叶子个数为该节点的所有子节点中,所有的必要叶子个数的和
因为题目输入格式,可以知道父节点的输入一定在子节点前面,所以能遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 300000+50;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 9;
#define lson l, m, rt << 1
#define rson m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define F(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i <= (r);++i)
#define RF(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i >= (r);--i)
vector<int> v[N];
int a[N], c[N];
int n;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
F(i, 1, n) cin >> a[i];
F(i, 2, n)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
v[t].push_back(i);
}
int cnt = 0, ans = 0;
RF(i, n, 1)
{
if(v[i].size() == 0)
{
c[i] = 1;
cnt++;
}
else if(a[i])
{
c[i] = INF;
F(j, 0, v[i].size() - 1)
c[i] = min(c[i], c[v[i][j]]);
}
else
{
F(j, 0, v[i].size() - 1)
c[i] += c[v[i][j]];
}
}
cout << cnt + 1 - c[1] << endl;
return 0;
}
dfs写法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 300000+50;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 9;
#define lson l, m, rt << 1
#define rson m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define F(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i <= (r);++i)
#define RF(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i >= (r);--i)
vector<int> v[N];
int a[N], c[N];
int n, ant = 0, cnt;
void dfs(int now)
{
if(v[now].size() == 0)
{
c[now] = 1;
cnt++;
}
else if(a[now])
{
c[now] = INF;
F(j, 0, v[now].size() - 1)
{
dfs(v[now][j]);
c[now] = min(c[now], c[v[now][j]]);
}
}
else
{
F(j, 0, v[now].size() - 1)
{
dfs(v[now][j]);
c[now] += c[v[now][j]];
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
F(i, 1, n) cin >> a[i];
F(i, 2, n)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
v[t].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1);
cout << cnt + 1 - c[1] << endl;
return 0;
}