分页
在MySQL中提供了对数据库分页的支持:
select id,name from customer limit 0,5;
前面的数字表示从第几个位置,后面的数字表示获取的数据多少。
表示在customer表中获取从第0个位置开始的五条数据。
理解:将一个页面分成两个或两个以上的页面,以便实现数据的合理化显示。
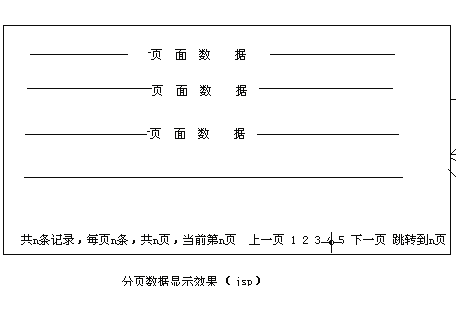
效果显示:
分页的页面显示数据流程图:
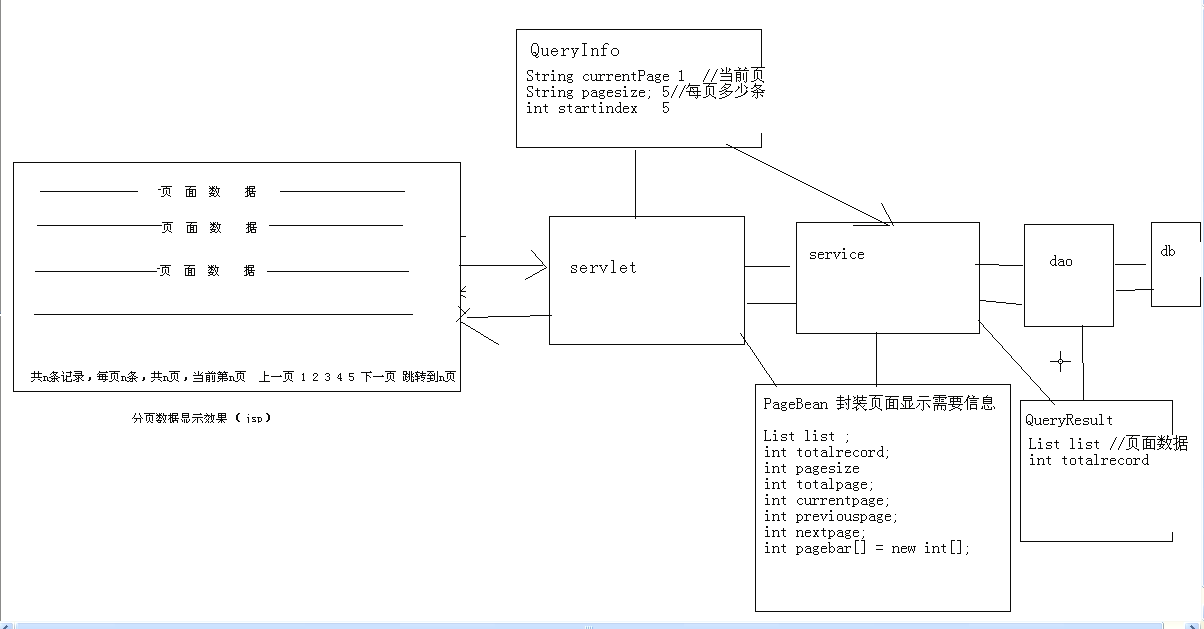
用户将自己想看的页面数据请求发送给servlet,servlet将请求(查询信息)封装到一个对象(QueryInfo)中交给service来处理,service拿到用户的请求(QueryInfo),去调用dao层,让dao层来查询数据库中的信息,从数据库中拿到查询后的数据封装到一个QueryResult中,这样service就拿到了数据库中用户想看的数据信息。这时生成一个PageBean对象,其中封装着需要在jsp页面中的所有需要的一切。最后由service将PageBean中封装的数据带给servlet,servlet再交给jsp页面显示。
查看演示效果:
过程步骤,先写好所要封装数据JavaBean(queryinfo,queryresult,pagebean),然后来改造dao,后改造service,再改造servlet。
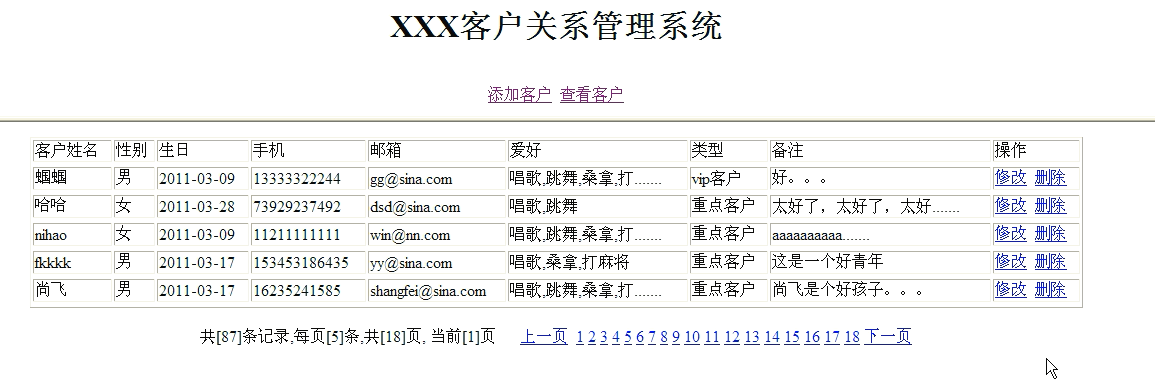
分页细节处理:
1.当分的页码过多时处理方案:
实现页码的固定,将固定多的页码显示在页面上,并且在动态显示页码条的大小:
解决代码如下:
1 //显示固定长度的页码条
2 public int[] getPagebar() {
3 int startpage;
4 int endpage;
5 int pagebar[]=null;
6 if(this.totalpage<=10){
7 pagebar=new int[this.totalpage];
8 startpage=1;
9 endpage=this.totalpage;
10 }else{
11 pagebar=new int[10];
12 startpage=this.currentpage-4;
13 endpage=this.currentpage+5;
14 if(startpage<1){
15 startpage=1;
16 endpage=10;
17 }
18 if(endpage>this.totalpage){
19 startpage=this.totalpage-9;
20 endpage=this.totalpage;
21 }
22 }
23 int index=0;
24 for(int i=startpage;i<=endpage;i++){
25 pagebar[index++]=i;
26 }
27 this.pagebar=pagebar;
28 return this.pagebar;
29 //显示所有的页码条
30 // int pagebar[]=new int[this.totalpage];
31 // for(int i=1;i<+this.totalpage;i++){
32 // pagebar[i-1]=i;//?
33 // }
34 // this.pagebar=pagebar;
35 // return pagebar;
36 }
实现的效果:

2.实现当点击页码时所点击的页码变色。
1 </c:if>
2 <!-- 迭代页码条 -->
3 <c:forEach var="pagenum" items="${pagebean.pagebar}" >
4 <!-- 利用if条件判断让当前所在的页码变色 -->
5 <c:if test="${pagenum==pagebean.currentpage}">
6 <font color="red"> ${pagenum}</font>
7
3.当修改每页数据显示大小时,可以改变数据在页面的显示大小。
代码参考listcustomer.jsp中的gotopage方法。
4.实现功能GO直接跳转到想去的页面。
代码参考listcustomer.jsp中的gotopage方法。
JDBC技术深入:
1.使用JDBC大数据:

使用JDBC处理大文本(字符):
对于MYSQL中的Text类型,可以调用如下的方法设置:
PreparedStatement.setCharacterStream(index,reder,length);
注意length长度需设置,并且设置为int型。
对于MYSQL中的Text类型,可调用如下方法获取:
reder=resultSet.getCharacterSteam(i);
reder=resultSet.getClob(i).getCharcaterStream();
string s=resultSet.getString(i);
练习代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast.demo;
2
3 import java.io.File;
4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
5 import java.io.FileReader;
6 import java.sql.Connection;
7 import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
8 import java.sql.ResultSet;
9 import java.sql.SQLException;
10
11 import org.junit.Test;
12
13 import cn.itcast.utils.JdbcUtils;
14
15 public class Demo1 {
16 /*
17 * 读写大文本
18 *
19 create table testclob
20 (
21 id varchar(40) primary key,
22 resume text
23 );
24 *
25 *
26 */
27
28 @Test
29 public void insert() throws SQLException, FileNotFoundException{
30 Connection conn=null;
31 PreparedStatement st= null;
32 ResultSet rs=null;
33 try{
34 conn= JdbcUtils.getconnection();
35 String sql="insert into testclob(id,resume) values(?,?)";
36 st=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
37 st.setString(1, "1");
38
39 File file=new File("src/1.txt");
40 FileReader reader=new FileReader(file);
41 st.setCharacterStream(2, reader, (int)file.length());
42 int num= st.executeUpdate();
43 if(num>0){
44 System.out.println("插入成功!!");
45
46 }
47 }finally{
48 JdbcUtils.relesase(conn, st, rs);
49
50
51 }
52
53 }
54
55 }
使用JDBC来处理二进制的数据(字节):
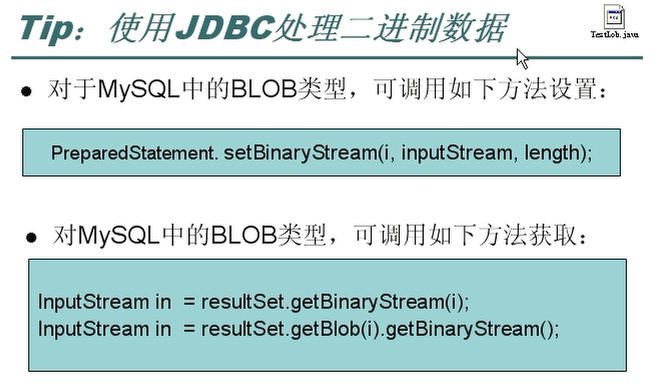
代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast.demo;
2
3 import java.io.File;
4 import java.io.FileInputStream;
5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
6 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
7 import java.io.IOException;
8 import java.io.InputStream;
9 import java.io.OutputStream;
10 import java.sql.Connection;
11 import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
12 import java.sql.ResultSet;
13 import java.sql.SQLException;
14
15 import org.junit.Test;
16
17 import cn.itcast.utils.JdbcUtils;
18
19 public class Demo2 {
20
21 /*
22 create table testblob
23 (
24 id varchar(40) primary key,
25 image blob
26 );
27 *
28 * */
29 @Test//大字节数据写入数据库中
30 public void insert() throws SQLException, FileNotFoundException{
31 Connection conn=null;
32 PreparedStatement st= null;
33 ResultSet rs=null;
34 try{
35 conn= JdbcUtils.getconnection();
36 String sql="insert into testblob(id,image) values(?,?) ";
37 st= conn.prepareStatement(sql);
38 st.setString(1, "1");
39 File file =new File("src/1.jpg");
40 FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
41
42 st.setBinaryStream(2, in, file.length());
43 st.executeUpdate();
44 }finally{
45 JdbcUtils.relesase(conn, st, rs);
46
47
48 }
49 }
50 @Test//将写入数据库的数据写到磁盘中加以显示
51 public void read() throws SQLException, IOException{
52 Connection conn=null;
53 PreparedStatement st= null;
54 ResultSet rs=null;
55 try{
56 conn= JdbcUtils.getconnection();
57 String sql="select id ,image from testblob where id='1'";
58 rs= conn.prepareStatement(sql).executeQuery();
59 if(rs.next()){
60 InputStream in=rs.getBinaryStream("image");
61 OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("d:\1.jpg");
62
63 try {
64 int len = 0;
65 byte buffer[] = new byte[1024];
66 while ((len = in.read(buffer)) > 0) {
67 out.write(buffer, 0, len);
68 }
69 } finally {
70 if (in != null)
71 in.close();
72 if (out != null)
73 out.close();
74 }
75 }
76
77 }finally{
78 JdbcUtils.relesase(conn, st, rs);
79
80
81 }
82 }
83
84 }
使用JDBC进行批处理:
第一种方式:

第二种方式:
采用PreparedStatement,addBatch()进行批处理

两种方式代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast.demo;
2
3 import java.sql.Connection;
4 import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
5 import java.sql.ResultSet;
6 import java.sql.SQLException;
7 import java.sql.Statement;
8
9 import org.junit.Test;
10
11 import cn.itcast.utils.JdbcUtils;
12
13 public class Demo3 {
14 /*
15 create table testbatch
16 (
17 id varchar(40) primary key,
18 name varchar(40)
19 );
20 *
21 */
22 @Test//实现批处理的第一种方式。可以插入多种不同的sql语句。
23 public void test() throws SQLException{
24 Connection conn=null;
25 Statement st= null;
26 ResultSet rs=null;
27 try{
28 conn= JdbcUtils.getconnection();
29 String sql1="insert into testbatch(id,name) values('1','aaa')";
30 String sql2="update testbatch set name='bbb' where id='1'";
31 st= conn.createStatement();
32 st.addBatch(sql1);
33 st.addBatch(sql2);
34 //int[]返回的是一个列表,其中存储着sql语句。
35 st.executeBatch();
36 st.clearBatch();
37
38 }finally{
39 JdbcUtils.relesase(conn, st, rs);
40
41
42 }
43 }
44
45 @Test//实现批处理的第二种方式。//适合做批量插入或批量更新。
46 public void test2() throws SQLException{
47
48 Connection conn=null;
49 PreparedStatement st= null;
50 ResultSet rs=null;
51 try{
52 conn= JdbcUtils.getconnection();
53 String sql= "insert into testbatch(id,name) values(?,?)";
54 st= conn.prepareStatement(sql);
55 for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
56 st.setString(1, i+"");
57 st.setString(2, "aa"+i);
58 st.addBatch();
59 //当存入的数据过多时采用分组处理将1000条作为一此处理。
60 // if(i%1000==0){
61 // st.executeBatch();
62 // st.clearBatch();
63 // }
64
65 }
66 st.executeBatch();
67 }finally{
68 JdbcUtils.relesase(conn, st, rs);
69
70
71 }
72 }
73
74
75
76 }
获取数据库自动生成的主键:

JDBC调用存储过程:
相当于一个Java方法,只不过是属于数据库中方法。
数据处理的两种方法:一是直接在Java中调取数据库中的存储过程,来获取并处理数据。
二是在Java中通过JDBC来写方法来处理数据库中的数据。
存储过程的优点:不必向外界暴露过多的信息。确保信息的安全性。
可以直接被Java程序调用简化了代码。

1 delimiter $$ //分隔符
//创建一个存储过程
2 CREATE PROCEDURE demoSp(IN inputParam VARCHAR(255), INOUT inOutParam varchar(255) )
3 BEGIN
4 SELECT CONCAT('zyxw---',inputParam) into inOutParam;
5 END $$
6 delimiter ;
存储过程代码如下:
package cn.itcast.demo;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Types;
import cn.itcast.utils.JdbcUtils;
public class Demo5 {
//调用存储过程
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//获取JDBC驱动
Connection conn=null;
CallableStatement st= null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try{
conn= JdbcUtils.getconnection();
//获取调用过程的名称
st= conn.prepareCall("{call demoSp(?,?)}");
st.setString(1,"aaaaaa");
//将获取的数据类型设置为字符型
st.registerOutParameter(2, Types.VARCHAR);
st.execute();
System.out.println( st.getString(2));
}finally{
JdbcUtils.relesase(conn, st, rs);
}
}
}
补充:结果集ResultSet:
实现对结果集的滚动。
