超参数
- 超参数:在算法运行之前需要决定的参数
- 模型参数:算法过程中学习到的参数
KNN算法作为最简单的机器学习算法,它没有模型参数,下面讨论它的超参数
加载数据集:
from sklearn import datasets, neighbors, model_selection
data = datasets.load_digits()
x = data.data
y = data.target
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.2)
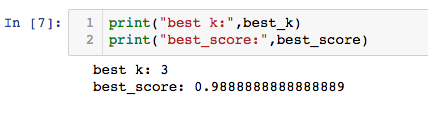
寻找最好的k:
best_score = 0.0
best_k = -2
for k in range(1,15):
knn_clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)
knn_clf.fit(x_train,y_train)
score = knn_clf.score(x_test,y_test)
if score > best_score:
best_k = k
best_score = score
考虑距离权重(weight)?
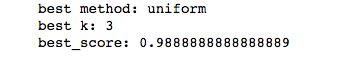
best_method = ""
best_score = 0.0
best_k = -2
for method in ["uniform","distance"]:
for k in range(1,15):
knn_clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k,weights=method)
knn_clf.fit(x_train,y_train)
score = knn_clf.score(x_test,y_test)
if score > best_score:
best_k = k
best_score = score
best_method = method
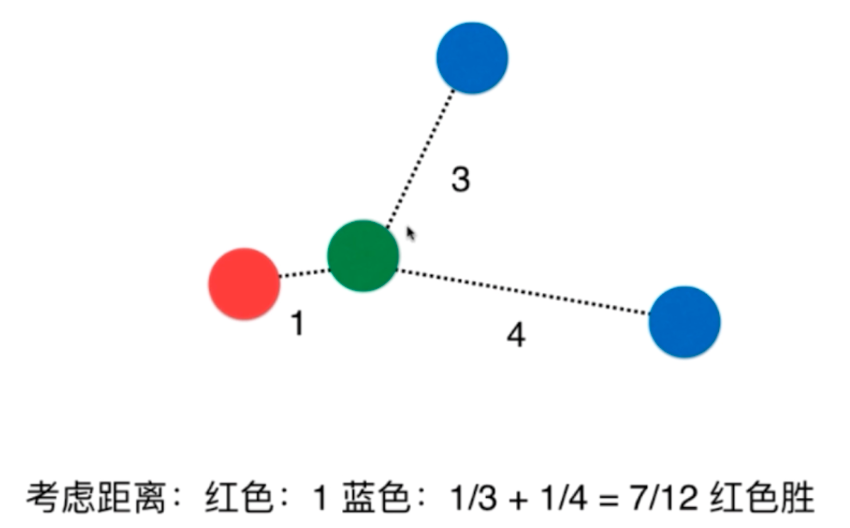
欧拉距离,曼哈顿距离,明可夫斯基距离

图中绿色最短的为欧拉距离,红黄蓝为曼哈顿距离
将距离一般化:明可夫斯基距离

得到了一个关于距离的超参数P,求最优的P
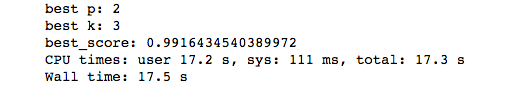
%%time
best_p = -1
best_score = 0.0
best_k = -2
for k in range(1,11):
for p in range(1,6):
knn_clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k,weights="distance",p=p)
knn_clf.fit(x_train,y_train)
score = knn_clf.score(x_test,y_test)
if score > best_score:
best_k = k
best_score = score
best_p = p
网格搜索最好的超参数(Grid Search)
param_grid = [
{
'weights':["uniform"],
'n_neighbors':[i for i in range(1,11)]
},
{
'weights':['distance'],
'n_neighbors':[i for i in range(1,11)],
'p':[i for i in range(1,6)]
}
]
knn_clf = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier()
# n_jobs 代表需要用几个核,传入-1,代表用所有核(我的是双核)verbose 搜索中输出信息
grid_search = model_selection.GridSearchCV(knn_clf, param_grid,n_jobs=-1,verbose=2)

返回最佳的分类器,用这个分类器预测:
knn_clf = grid_search.best_estimator_
查看用最好的超参数训练的算法的准确率和参数值:
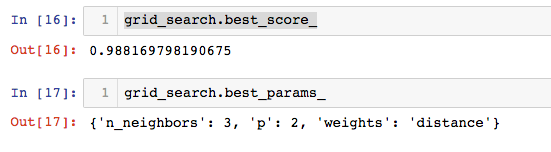
grid_search.best_score_
grid_search.best_params_