6.1 什么是MyBatis
Mybatis(前身是iBatis)是一个支持普通SQL查询、存储过程以及高级映射的持久层框架。MyBatis框架也被称为ORM(Object/Relational Mapping,即对象关系映射)框架,所谓的ORM就是一种为了 解决面向对象与关系型数据库中数据类型不匹配的技术,它通过描述Java对象与数据库表之间的映射关系,自动将Java应用程序中的对象持久化到关系型数据库的表中。原理:

使用ORM框架后,应用程序不直接访问数据库,以面向对象的方式操作持久化对象(Persisent Object,PO),而ORM框架则会通过映射关系将这些面向对象的操作转换成底层的SQL操作。
Hibernate与MyBatis的区别:

6.3 MyBatis的工作原理
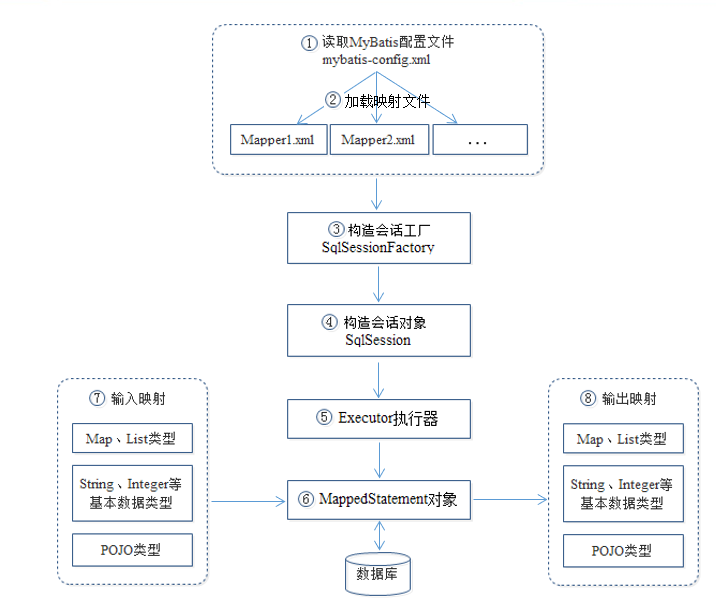
1.读取配置文件mybatis-config.xml,主要是获取数据库连接
2.加载映射文件Mapper.xml即SQL映射文件,该文件配置了操作数据库的SQL语句,需要在mybatis-config.xml中加载才能执行,每个配置文件对应数据库的一张表。
3.构建会话工厂。
4.创建Sqlsession对象,该对象包含了执行SQL的所有方法。
5.底层定义一个Executor接口操作数据库
6.在Executor接口的执行方法中,包含一个MappedStatement类型的参数,该参数是对映射信息的封装,用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等。Mapper.xml文件中一个SQL对应一个MappedStatement对象,SQL的id即是MappedStatement的id
7.输入参数映射
8.输出参数映射
6.4 MyBatis入门程序
6.41 查询客户:
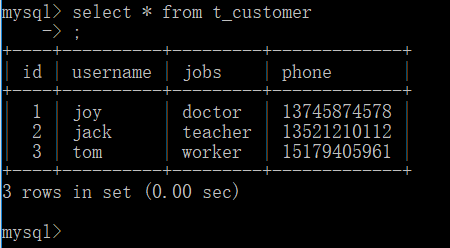
1.在建一个数据库mybatis,在库中建表t_customer,插入一些信息,如下
2.由于MyBatis默认使用log4j输出日志信息,所以如果要查看控制台的输出SQL语句,那么就需要在classpath路径下配置其日志文件。在项目的src目录下创建log4j.properties文件。
# Global logging configuration全局日志配置 log4j.rootLogger=ERROR, stdout # MyBatis logging configuration...MyBatis日志配置 log4j.logger.com.itheima=DEBUG # Console output...控制台输出 log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
3.创建持久化类Customer,并在类中声明id、username、jobs和phone属性,看起来和普通的类没有区别,只是其属性性字段与数据库中的表字段相对应。实际上,Costomer就是一个POJO(普通Java对象),MyBatis就是采用POJO作为持久化类来完成对数据库操作的。
package com.itheima.po; /** * 客户持久化类 */ public class Customer { private Integer id; // 主键id private String username; // 客户名称 private String jobs; // 职业 private String phone; // 电话 public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getJobs() { return jobs; } public void setJobs(String jobs) { this.jobs = jobs; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } @Override public String toString() { return "Customer [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", jobs=" + jobs + ", phone=" + phone + "]"; } }
4.创建映射文件CustomerMapper.xml:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <!-- MyBatis的约束配置 --> 3 <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" 4 "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> 5 <!-- namespace表示命名空间 --> 6 <mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper"> 7 <!--根据客户编号获取客户信息 --> 8 <select id="findCustomerById" parameterType="Integer" 9 resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> 10 select * from t_customer where id = #{id} 11 </select> 12 </mapper>
套路1:<mapper>是配置文件的根元素,有一个属性名namespace属性,该属性为<mapper>指定了唯一的命名空间,通常设“包+SQL文件名”,即路径。
套路2:<select>中的信息是用于执行查询操作的配置,其id属性是<select>元素在映射文件中的唯一标识;parameterType属性用于指定传入参数类型,这里表示传递给SQL的是一个Integer类型的参数;resultType属性用于指定返回结果的类型,这里表示返回的是Customer类型。
套路3:#{} 用于表示一个占位符,相当于“?”,而“#{id}”表示该占位符待接收参数的名称为id
5.创建核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!--1.配置环境 ,默认的环境id为mysql--> <environments default="mysql"> <!--1.2.配置id为mysql的数据库环境 --> <environment id="mysql"> <!-- 使用JDBC的事务管理 --> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!--数据库连接池 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="***" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--2.配置Mapper的位置,映射文件CustomerMapper.xml --> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/CustomerMapper.xml" /> </mappers> </configuration>
6.创建测试类MybatisTest,并在类中编写测试类方法findCustomerByIdTest(),通过客户编号查询
/** * 入门程序测试类 */ public class MybatisTest { /** * 根据客户编号查询客户信息 */ @Test public void findCustomerByIdTest() throws Exception { // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回映射结果 Customer customer = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.findCustomerById", 1); // 打印输出结果 System.out.println(customer.toString()); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); }
套路1:通过输入流读核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml
套路2:造会话工厂sqlSessionFactory
套路3:通过工厂造会话对象sqlSession
套路4:使用会话对象 执行映射文件 并存到对象里,用toString()输出
套路5:关闭会话对象。
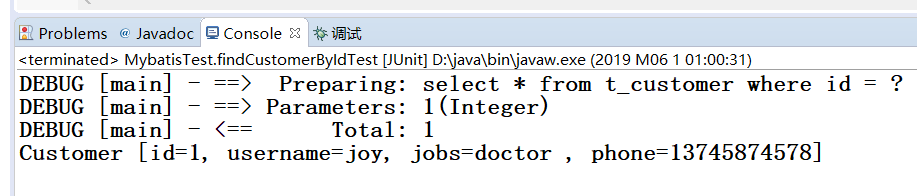
结果:
7.根据客户名模糊查询客户信息
需要在映射文件中加点东西:
<!--根据客户名模糊查询客户信息列表--> <select id="findCustomerByName" parameterType="String" resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> <!-- select * from t_customer where username like '%${value}%' --> select * from t_customer where username like concat('%',#{value},'%') </select>
SQL语句中的“ ${} ”用来表示拼接SQL的字符串,即不加解释的原样输出。 " ${value} "表示要拼接的是简单类型参数
写测试类:
/** * 根据用户名称来模糊查询用户信息列表 */ @Test public void findCustomerByNameTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回映射结果 List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.findCustomerByName", "j"); for (Customer customer : customers) { //循环打印输出结果集 System.out.println(customer); } // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); }
两种查询方法在第四步有点不同,由于可能查出多条数据,调用SqlSession的selectList()方法来查询返回结果的集合对象,并用for循环输出。
结果:

8.添加客户,映射文件需要加点东西:
<!-- 添加客户信息 --> <insert id="addCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> insert into t_customer(username,jobs,phone) values(#{username},#{jobs},#{phone}) </insert>
测试方法:
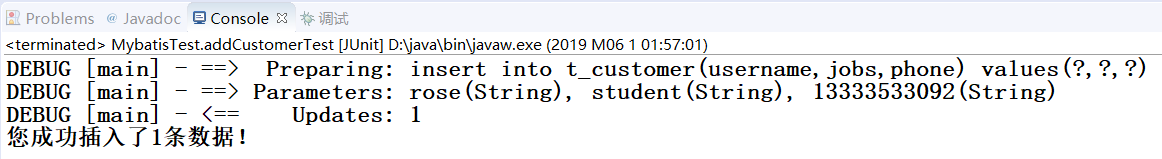
/** * 添加客户 */ @Test public void addCustomerTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行添加操作 // 4.1创建Customer对象,并向对象中添加数据 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setUsername("rose"); customer.setJobs("student"); customer.setPhone("13333533092"); // 4.2执行SqlSession的插入方法,返回的是SQL语句影响的行数 int rows = sqlSession.insert("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.addCustomer", customer); // 4.3通过返回结果判断插入操作是否执行成功 if(rows > 0){ System.out.println("您成功插入了"+rows+"条数据!"); }else{ System.out.println("执行插入操作失败!!!"); } // 4.4提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); }
和之前的不同点:非查询的修改类方法比如插入删除都需要用会话对象提交事务,再关闭会话对象。
结果:
9.更新客户,在映射文件中加点东西:
<!-- 更新客户信息 --> <update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> update t_customer set username=#{username},jobs=#{jobs},phone=#{phone} where id=#{id} </update>
测试方法:
/** * 更新客户 */ @Test public void updateCustomerTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行更新操作 // 4.1创建Customer对象,对对象中的数据进行模拟更新 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setId(4); customer.setUsername("rose"); customer.setJobs("programmer"); customer.setPhone("13311111111"); // 4.2执行SqlSession的更新方法,返回的是SQL语句影响的行数 int rows = sqlSession.update("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.updateCustomer", customer); // 4.3通过返回结果判断更新操作是否执行成功 if(rows > 0){ System.out.println("您成功修改了"+rows+"条数据!"); }else{ System.out.println("执行修改操作失败!!!"); } // 4.4提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); }
10.删除客户,老规矩在配置文件加点东西:
<!-- 删除客户信息 --> <delete id="deleteCustomer" parameterType="Integer"> delete from t_customer where id=#{id} </delete>
测试方法:
/** * 删除客户 */ @Test public void deleteCustomerTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行删除操作 // 4.1执行SqlSession的删除方法,返回的是SQL语句影响的行数 int rows = sqlSession.delete("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.deleteCustomer", 4); // 4.2通过返回结果判断删除操作是否执行成功 if(rows > 0){ System.out.println("您成功删除了"+rows+"条数据!"); }else{ System.out.println("执行删除操作失败!!!"); } // 4.3提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); }
全套代码:
映射文件:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- MyBatis的约束配置 --> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- namespace表示命名空间 --> <mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper"> <!--根据客户编号获取客户信息 --> <select id="findCustomerById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> select * from t_customer where id = #{id} </select> <!--根据客户名模糊查询客户信息列表--> <select id="findCustomerByName" parameterType="String" resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> <!-- select * from t_customer where username like '%${value}%' --> select * from t_customer where username like concat('%',#{value},'%') </select> <!-- 添加客户信息 --> <insert id="addCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> insert into t_customer(username,jobs,phone) values(#{username},#{jobs},#{phone}) </insert> <!-- 更新客户信息 --> <update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"> update t_customer set username=#{username},jobs=#{jobs},phone=#{phone} where id=#{id} </update> <!-- 删除客户信息 --> <delete id="deleteCustomer" parameterType="Integer"> delete from t_customer where id=#{id} </delete> </mapper>
持久化对象类:

package com.itheima.po; /** * 客户持久化类 */ public class Customer { private Integer id; // 主键id private String username; // 客户名称 private String jobs; // 职业 private String phone; // 电话 public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getJobs() { return jobs; } public void setJobs(String jobs) { this.jobs = jobs; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } @Override public String toString() { return "Customer [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", jobs=" + jobs + ", phone=" + phone + "]"; } }
核心配置文件:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!--1.配置环境 ,默认的环境id为mysql--> <environments default="mysql"> <!--1.2.配置id为mysql的数据库环境 --> <environment id="mysql"> <!-- 使用JDBC的事务管理 --> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!--数据库连接池 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="17251104238" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--2.配置Mapper的位置,映射文件CustomerMapper.xml --> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/CustomerMapper.xml" /> </mappers> </configuration>
测试类:

package com.itheima.test; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.Test; import com.itheima.po.Customer; /** * 入门程序测试类 */ public class MybatisTest { /** * 根据客户编号查询客户信息 */ @Test public void findCustomerByIdTest() throws Exception { // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回映射结果 Customer customer = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.findCustomerById", 1); // 打印输出结果 System.out.println(customer.toString()); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); } /** * 根据用户名称来模糊查询用户信息列表 */ @Test public void findCustomerByNameTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,并返回映射结果 List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.findCustomerByName", "j"); for (Customer customer : customers) { //循环打印输出结果集 System.out.println(customer); } // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); } /** * 添加客户 */ @Test public void addCustomerTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行添加操作 // 4.1创建Customer对象,并向对象中添加数据 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setUsername("rose"); customer.setJobs("student"); customer.setPhone("13333533092"); // 4.2执行SqlSession的插入方法,返回的是SQL语句影响的行数 int rows = sqlSession.insert("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.addCustomer", customer); // 4.3通过返回结果判断插入操作是否执行成功 if(rows > 0){ System.out.println("您成功插入了"+rows+"条数据!"); }else{ System.out.println("执行插入操作失败!!!"); } // 4.4提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); } /** * 更新客户 */ @Test public void updateCustomerTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行更新操作 // 4.1创建Customer对象,对对象中的数据进行模拟更新 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setId(4); customer.setUsername("rose"); customer.setJobs("programmer"); customer.setPhone("13311111111"); // 4.2执行SqlSession的更新方法,返回的是SQL语句影响的行数 int rows = sqlSession.update("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.updateCustomer", customer); // 4.3通过返回结果判断更新操作是否执行成功 if(rows > 0){ System.out.println("您成功修改了"+rows+"条数据!"); }else{ System.out.println("执行修改操作失败!!!"); } // 4.4提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); } /** * 删除客户 */ @Test public void deleteCustomerTest() throws Exception{ // 1、读取配置文件 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 2、根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、SqlSession执行删除操作 // 4.1执行SqlSession的删除方法,返回的是SQL语句影响的行数 int rows = sqlSession.delete("com.itheima.mapper" + ".CustomerMapper.deleteCustomer", 5); // 4.2通过返回结果判断删除操作是否执行成功 if(rows > 0){ System.out.println("您成功删除了"+rows+"条数据!"); }else{ System.out.println("执行删除操作失败!!!"); } // 4.3提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 5、关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); } }
