@Data public class CreditCard extends BankCard { /** * 消费额度 */ private String creditLine; } @Data public class DebitCard extends BankCard { /** * 存款金额 */ private String deposit; }
resultmap是mybatis中最复杂的元素之一,它描述如何从结果集中加载对象,主要作用是定义映射规则、级联的更新、定制类型转化器。
resultmap构成元素

1.id和result元素
以User类为例:
class User{ private int userId; private String name; public User(long userId,String name){ this.userId = userId; this.name = name; } }
id、result是最简单的映射,id为主键映射;result其他基本数据库表字段到实体类属性的映射。resultmap的xml如下:
<resultMap type="User" id="userMap"> <id property="UserId" column="user_id" javaType="int" jdbcType="int"/> <result property="name" column="name" javaType="String" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/> </resultMap>
id、result语句属性配置细节:

2. CONSTRUCTOR 构造器
在resultMap中,通常使用id、result子元素把Java实体类的属性映射到数据库表的字段上。但是如果在遇到JavaBean没有无参构造函数时,我还需要使用构造器元素实现一个JavaBean的实例化和数据注入。
再以User为例,那么对应的resultmap就需要添加构造器:
<constructor> <idArg column="user_id" javaType="long"/> <arg column="name" javaType="String"/> </constructor>
定义java实体类的属性映射到数据库表的字段上。我们也可以使用实体类的构造方法来实现值的映射,这是通过构造方法参数的书写的顺序来进行赋值的。
这样MyBatis就知道需要用这个构造方法构造了。
3.结果集处理方法
1. 使用map储存结果集
一般情况下,所有select语句都可以使用map储存,但是使用map就意味着可读性的下井,所以这不是推荐的方式。
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="long" resultType="map"> select user_id ,name form user where user_id=#{userId} </select>
2. 使用POJO储存结果集(推荐)
一般我们都使用POJO储存查询结果。我们可以使用select自动映射,还可以使用select语句中的resultMap属性配置映射集合,不过需要提前定义resultMap。
那我们就可以将之前的select语句修改:
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="long" resultMap="userMap"> select user_id ,name form user where user_id=#{userId} </select>
4.级联
在数据库中包含着一对多、一对一的关系。比如说一个人和他的身份证就是一对一的关系,但是他和他的银行卡就是一对多的关系。我们的生活中存在着很多这样的场景。我们也希望在获取这个人的信息的同时也可以把他的身份证信息一同查出,这样的情况我们就要使用级联。在级联中存在3种对应关系。
- 一对一的关系
- 一对多的关系
- 多对多的关系(这种情况由于比较复杂,我们通常会使用双向一对多的关系来降低复杂度)
1.association 一对一级联
我们继续使用User类,同时为其增加一个Card类,人和他的身份证就行成了一对一的关系。我们再创建一个Card类。
@Data @Alias("card") public class Card { private Long id; private Long userId; private String name; private String address; }
这是需要在User中添加属性Card,这样就形成了一对一的级联。
@Data @Alias("user") public class User { private Long id; private String username; private String password; private String email; private Card card; }
这时需要CardMapper提供findCardByUserId(Long userId)方法,定义其映射器如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.changzhen.mybatis.mapper.CardMapper"> <resultMap id="cardMap" type="card"> <id property="id" column="id"></id> <result property="userId" column="user_id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <result property="address" column="address"/> </resultMap> <select id="findCardByUserId" parameterType="long" resultMap="cardMap"> SELECT id, user_id, name, address FROM card WHERE user_id = #{userId} </select> </mapper>
有了CardMapper,我们将可以在UserMaper中使用 findCardByUserId 进行级联
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.changzhen.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="getUser" resultMap="userMap" parameterType="long"> SELECT id,username,password,email FROM USER WHERE id=#{id} </select> <resultMap id="userMap" type="user"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result property="password" column="password"/> <result property="email" column="email"/> <association property="card" column="id" select="com.changzhen.mybatis.mapper.CardMapper.findCardByUserId"/> </resultMap>
通过关联处理,其中select元素指定的sql查询,而column则是指定传递给select的参数,是user对象id。当取出User的时候,MyBatis就知道下面的sql取出我们需要的级联信息。
<association property="card" column="id" select="com.changzhen.mybatis.mapper.CardMapper.findCardByUserId"/>
其中参数是User的值,通过column配置,如果是多个参数则使用逗号隔开。
可以看出执行了两条sql分别查询了User和Card。
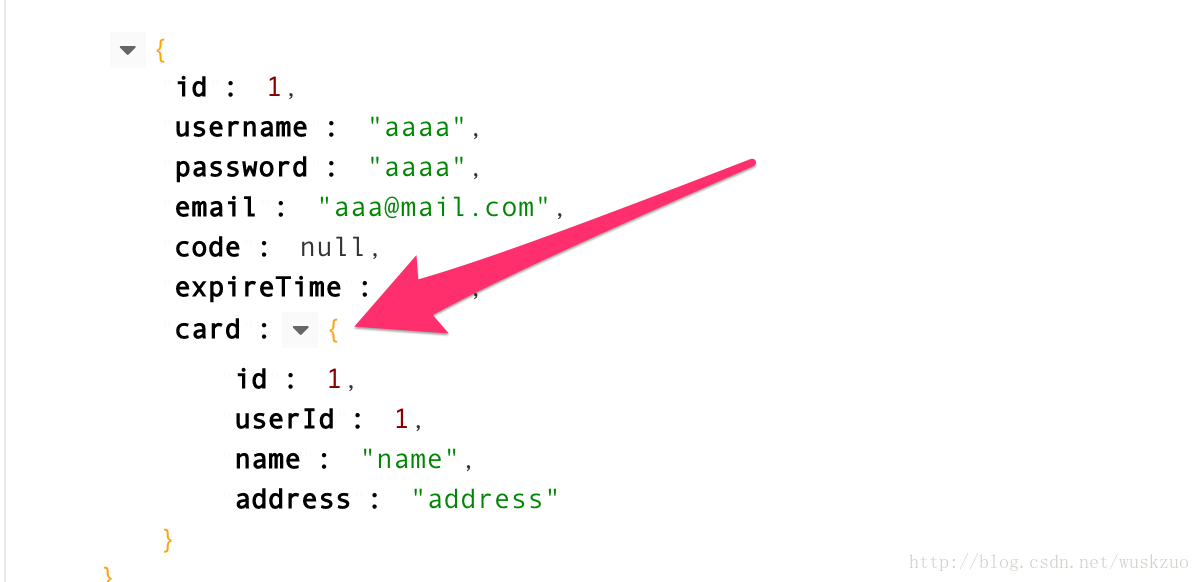
2.collection 一对多级联
这一对多的级联,一个身份证可以办理多张银行卡。每个用户对应一个身份证,每个身份证对应多个银行卡。所以这两个级联,分别使用association和collection完成。
- 首先,创建BankCard类,为Card增加bankCardList属性
@Alias("bankCard")
@Data
public class BankCard {
private Long id;
private Long userId;
private String bankName;
private int type;
}
@Data
@Alias("card")
public class Card {
private Long id;
private Long userId;
private String name;
private String address;
private List<BankCard> bankCards;
}
创建BankCardMapper
@Mapper public interface BankCardMapper { public List findCreditCardsByUserId(Long userId); }
xml最简单的映射器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.changzhen.mybatis.mapper.CreditCardMapper"> <select id="findCreditCardsByUserId" parameterType="long" resultType="creditCard"> SELECT id, user_id, bank_name, type FROM bank_card WHERE user_id = #{userId} </select> </mapper>
- 最后在Card映射器中添加collection,一对多级联。
-
<mapper namespace="com.changzhen.mybatis.mapper.CardMapper"> <resultMap id="cardMap" type="card"> <id property="id" column="id"></id> <result property="userId" column="user_id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <result property="address" column="address"/> <collection property="creditCards" column="id" select="com.changzhen.mybatis.mapper.BankCardMapper.findBankCardsByUserId"/> </resultMap> <select id="findCardByUserId" parameterType="long" resultMap="cardMap"> SELECT id, user_id, name, address FROM card WHERE user_id = #{userId} </select> </mapper>

3.discriminator 鉴别器级联
鉴别器级联是在不公情况下使用不同的POJO。例如,在本例中我们每个人都有好多银行卡,但是银行卡的种类却不同,比如有借记卡(DebitCard)和信用卡(CreditCard),我们需要按需来创建不同的POJO。这时我们就需要在BankCard中添加types属性进行判断,确定使用哪个POJO。
接下来需要创建DebitCard和CreditCard两个继承BankCard的子类
案例
<!--column不做限制,可以为任意表的字段,而property须为type 定义的pojo属性--> <resultMap id="唯一的标识" type="映射的pojo对象"> <id column="表的主键字段,或者可以为查询语句中的别名字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="映射pojo对象的主键属性" /> <result column="表的一个字段(可以为任意表的一个字段)" jdbcType="字段类型" property="映射到pojo对象的一个属性(须为type定义的pojo对象中的一个属性)"/>
<association property="pojo的一个对象属性" javaType="pojo关联的pojo对象"> <id column="关联pojo对象对应表的主键字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="关联pojo对象的主席属性"/> <result column="任意表的字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="关联pojo对象的属性"/> </association>
<!-- 集合中的property须为oftype定义的pojo对象的属性--> <collection property="pojo的集合属性" ofType="集合中的pojo对象"> <id column="集合中pojo对象对应的表的主键字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="集合中pojo对象的主键属性" /> <result column="可以为任意表的字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="集合中的pojo对象的属性" /> </collection> </resultMap>
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wuskzuo/article/details/79186144
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="long" resultType="map"> select user_id ,name form user where user_id=#{userId} </select>