1. 内聚和耦合举例
内聚和耦合是衡量模块独立性的两种标准。
内聚——衡量一个模块内部各元素之间的关系;耦合——衡量模块间的关系。
1.1 内聚类型
1) 功能内聚:一个模块只完成一个单一功能。例:用户权限模块,该模块只负责与权限相关的实现。
2) 分层内聚:分层实现,上层能访问底层,底层不可访问上层。例:业务逻辑层能访问数据库实现层,反之不可。
3) 通信内聚:访问相同数据的操作集中放到一个类或模块中实现。例:对数据库中某个表的增删改查定义在一个类中实现。
4) 顺序内聚:模块内的处理按照顺序执行,且前者的输出做为后者的输入。例:将一个集合内的元素按指定规则排序,然后将排序后的集合输出。
5) 过程内聚:模块内部的处理按照顺序执行,前者与后者之间没有数据传递。例:先校验参数的合法性,校验通过后将参数在控制台输出。
6) 暂时内聚:模块内的操作是为了完成某一特定要求或状态。
7) 实用内聚:模块各部分之间没有联系或联系松散。例:一个处理字符串的工具类。
内聚举例: 参见EmployeeManager类中的各个方法
通信内聚: getEmployeeAge(Date birthDate)与isEmployeeRetired(Date birthDate)间存在通信内聚。
public class EmployeeManager {
// 功能内聚
private int getEmployeeAge(Date birthDate) {
int employeeAge = 0;
// TODO: 用当前日期计算与出生日期计算员工年龄
return employeeAge;
}
// 功能内聚
private boolean isEmployeeRetired(Date birthDate) {
int employeeAge = getEmployeeAge(birthDate);
if (employeeAge > 60) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 顺序内聚
private boolean isEmployeeRetired(Date birthDate) {
int employeeAge = 0;
// TODO: 用当前日期计算与出生日期计算员工年龄
if (employeeAge > 60) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 逻辑内聚
private void printEmployeeSalary(int flag, int daySalary) {
int monthSalary = daySalary * 30;
int yearSalary = monthSalary * 12;
switch (flag) {
case 0:
// 打印日工资;
System.out.println(daySalary);
case 1:
// 打印月工资;
System.out.println(monthSalary);
case 2:
// 打印年工资;
System.out.println(yearSalary);
default:
// 打印月工资;
System.out.println(monthSalary);
}
}
// 过程内聚, 暂时内聚
private void printEmployeeInfo(Employee employee){
String name = employee.getName();
String sex = employee.getSex();
String address = employee.getAddress();
StringBulider printInfo = new StringBuilder();
printInfo.append("雇员的个人信息————");
printInfo.append("姓名:");
printInfo.append(name);
printInfo.append(" | 性别:");
printInfo.append(sex);
printInfo.append(" | 地址:");
printInfo.append(address);
System.out.println(printInfo.toString());
}
}
1.2 耦合类型
1) 内容耦合:类Employee与TestB间存在内容耦合
public class Employee {
// 雇员当前年龄
public int curAge ;
// 雇员还有多少年退休
public int retireYear;
}
public class TestB {
private void printEmployeeInfo(){
Employee employeeA = new Employee();
employeeA.curAge = 20;
employeeA.retireYear = 65 - employeeA.curAge;
System.out.println("employeeA curAge is ", employeeA.curAge);
System.out.println("employeeA retireYear is ", employeeA.retireYear);
}
}
2) 共用耦合:类ScoreUtil与TestA间存在共用耦合
public class ScoreUtil {
public static int MinScore = 60;
public static int getAvgScore(int score1, int score2){
int sumScore = score1 + score2;
return sumScore/2;
}
}
public class TestA {
private void printScoreLevel(){
int score1 = 50;
int score2 = 100;
int avgScore = ScoreUtil.getAvgScore(score1, score2);
if(avgScore>ScoreUtil.MinScore){
System.out.println("Score is higher than min score.");
}else{
System.out.println("Score is lower than min score.");
}
}
}
3) 控制耦合:类ScoreUtil与TestA间存在控制耦合
public class ScoreUtil {
public static int getScore(boolean isGetAvg){
int score = 0;
if(isGetAvg){
//TODO get avg score
}else{
//TODO get max score }
return score;
}
}
public class TestA {
private int getAvgScore(){
return ScoreUtil.getScore(true);
}
}
4) 数据耦合:类ScoreUtil与TestA间存在数据耦合
public class ScoreUtil {
public static int getAvgScore(int score1, int score2){
int sumScore = score1 + score2;
return sumScore/2;
}
}
public class TestA {
private void printAvgScore(){
int score1 = 50;
int score2 = 100;
System.out.println(ScoreUtil.getAvgScore(score1, score2));
}
}
5) 印记耦合:printStudentNames和printStudentAvgAge之间存在印记耦合
import java.util.List;
public class TestB { private void printStudentNames(List<Student> students){ for(Student student: students){ System.out.println(student.getName()); } } private void printStudentAvgAge(List<Student> students){ int totalAge = 0; for(Student student: students){ totalAge = totalAge + student.getAge(); } System.out.println(totalAge/students.size()); } }
6) 类型使用耦合: 印记耦合的例子中的TestB类与Student类存在类型调用耦合
7) 例程调用耦合: 印记耦合的例子中的TestB类中的printStudentNames()调用了Student类中的getName(),存在例程调用耦合。
8) 包含/导入耦合:印记耦合的例子中的TestB类中引入了java.util.List。
9) 外部耦合:main方法与getStudentAvgScore方法,printAvgScore方法存在外部耦合
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int avgScore = getStudentAvgScore();
printAvgScore(avgScore);
}
private static int getStudentAvgScore(){
int avgScore = 0;
//TODO
return avgScore;
}
private static void printAvgScore(int avgScore){
}
}
2. 进度条列示
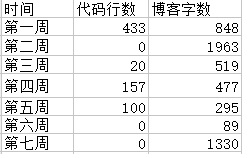
2.1 代码行数累积线段图

2.2 博客字数累积线段图

3. PSP
| job | type | date | start | end | total(min) |
| 写随笔 | 随笔 | 2016.4.20 | 12:30 | 13:15 | 45 |
| 添加耦合例子 | 随笔 | 2016.4.21 | 21:30 | 22:51 | 81 |
| 添加聚合例子,进度条,博客字数累积线段图 | 随笔 | 2016.4.22 | 12:00 | 13:02 | 62 |
4. 工作量表
| 代码行数 | 博客字数 | 知识点 | |
| 第七周 | 0 | 1380 |
β发布 |