One day Kefa found n baloons. For convenience, we denote color of i-th baloon as si — lowercase letter of the Latin alphabet. Also Kefa has k friends. Friend will be upset, If he get two baloons of the same color. Kefa want to give out all baloons to his friends. Help Kefa to find out, can he give out all his baloons, such that no one of his friens will be upset — print «YES», if he can, and «NO», otherwise. Note, that Kefa's friend will not upset, if he doesn't get baloons at all.
The first line contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 100) — the number of baloons and friends.
Next line contains string s — colors of baloons.
Answer to the task — «YES» or «NO» in a single line.
You can choose the case (lower or upper) for each letter arbitrary.
4 2
aabb
YES
6 3
aacaab
NO
In the first sample Kefa can give 1-st and 3-rd baloon to the first friend, and 2-nd and 4-th to the second.
In the second sample Kefa needs to give to all his friends baloons of color a, but one baloon will stay, thats why answer is «NO».
注意题目被标记部分;分不到不会沮丧,分不完会沮丧,所以,某个颜色大于K时就输出NO
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.141592653589793238462 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false) #define INF 1044266558 #define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; int a[30],n,k; char s[110]; int main() { cin>>n>>k; int flag=true; memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); cin>>s; for(int i=0;s[i]!='�';i++) a[s[i]-'a']++; for(int i=0;i<26;i++) { if(a[i]>k) flag=0; } puts(flag?"YES":"NO"); return 0; }
Leha somehow found an array consisting of n integers. Looking at it, he came up with a task. Two players play the game on the array. Players move one by one. The first player can choose for his move a subsegment of non-zero length with an odd sum of numbers and remove it from the array, after that the remaining parts are glued together into one array and the game continues. The second player can choose a subsegment of non-zero length with an even sum and remove it. Loses the one who can not make a move. Who will win if both play optimally?
First line of input data contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106) — length of the array.
Next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Output answer in single line. "First", if first player wins, and "Second" otherwise (without quotes).
4
1 3 2 3
First
2
2 2
Second
In first sample first player remove whole array in one move and win.
In second sample first player can't make a move and lose.
首先,全为偶数时,后手一定赢,偶数加奇数=奇数,偶数加偶数=偶数,所以奇数可以表示为=奇书+n*偶数(即和偶数数目无关),有一个奇数时,先手一次性全拿走,两个时,分两次拿,所以无论哪种情况,有奇数个奇数时,全拿走,偶数个奇数时分两次拿,所以只要存在奇数先手一定赢。
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.141592653589793238462 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false) #define INF 1044266558 #define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; int main() { int pos=0,n,x; scanf("%d",&n); while(n--)(scanf("%d",&x),x%2?pos++:0); puts(pos?"First":"Second"); }
Leha like all kinds of strange things. Recently he liked the function F(n, k). Consider all possible k-element subsets of the set [1, 2, ..., n]. For subset find minimal element in it. F(n, k) — mathematical expectation of the minimal element among all k-element subsets.
But only function does not interest him. He wants to do interesting things with it. Mom brought him two arrays A and B, each consists of m integers. For all i, j such that 1 ≤ i, j ≤ m the condition Ai ≥ Bj holds. Help Leha rearrange the numbers in the array A so that the sum 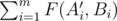 is maximally possible, where A' is already rearranged array.
is maximally possible, where A' is already rearranged array.
First line of input data contains single integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 2·105) — length of arrays A and B.
Next line contains m integers a1, a2, ..., am (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — array A.
Next line contains m integers b1, b2, ..., bm (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — array B.
Output m integers a'1, a'2, ..., a'm — array A' which is permutation of the array A.
5
7 3 5 3 4
2 1 3 2 3
4 7 3 5 3
7
4 6 5 8 8 2 6
2 1 2 2 1 1 2
2 6 4 5 8 8 6
任意子集尽可能大,所以排序后,小得对应大的,大的尽可能排到前面
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.141592653589793238462 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false) #define INF 1044266558 #define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; int a[200006],vis[200006],n; pair<int,int>p[200006]; int main() { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&p[i].first); p[i].second=i; } sort(a,a+n); sort(p,p+n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { vis[p[i].second]=a[n-i-1]; } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(i) printf(" "); printf("%d",vis[i]); } printf(" "); return 0; }