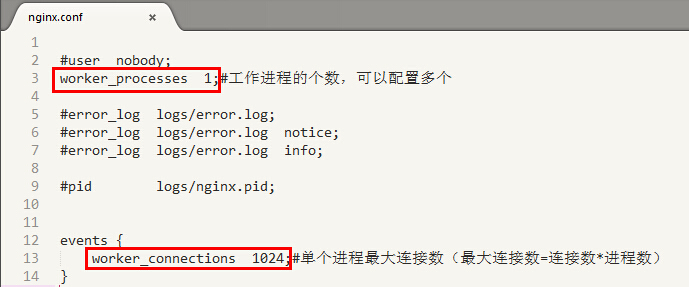
(1) 进程数与每个进程的最大连接数:
- nginx进程数,建议设置为等于CPU总核心数
- 单个进程最大连接数,那么该服务器的最大连接数=连接数*进程数
(2) Ngnix的基本配置
- 监听端口一般都为http端口:80;
- 域名可以有多个,用空格隔开:例如 server_name www.ha97.com ha97.com;

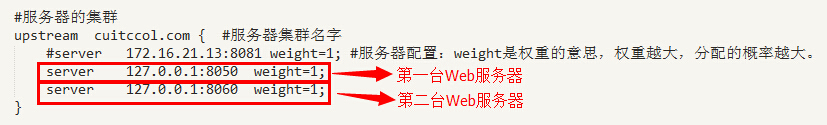
(3) 负载均衡列表基本配置:
- location / {}:对aspx后缀的进行负载均衡请求,假如我们要对所有的aspx后缀的文件进行负载均衡时,可以这样写:location ~ .*.aspx$ {}
- proxy_pass:请求转向自定义的服务器列表,这里我们将请求都转向标识为http://cuitccol.com的负载均衡服务器列表;

- 在负载均衡服务器列表的配置中,weight是权重,可以根据机器配置定义权重(如果某台服务器的硬件配置十分好,可以处理更多的请求,那么可以 为其设置一个比较高的weight;而有一台的服务器的硬件配置比较差,那么可以将前一台的weight配置为weight=2,后一台差的配置为 weight=1)。weigth参数表示权值,权值越高被分配到的几率越大;
(4) 总结:最基本的Nginx配置差不多就是上面这些内容,当然仅仅是最基础的配置。(详细的配置内容请下载底部的nginx-1.4.7详细查看)
(5) 添加Ngnix对静态文件的缓存配置
为了提高响应速度,减轻真实服务器的负载,对于静态资源我们可以在反向代理服务器中进行缓存,这也是反向代理服务器的一个重要的作用。
1> 缓存静态资源之图片文件
root /nginx-1.4.7/staticresources/image:对于配置中提到的jpg/png等文件均定为到/nginx-1.4.7/staticresources/image文件夹中进行寻找匹配并将文件返回;
expires 7d:过期时效为7天,静态文件不怎么更新,过期时效可以设大一点,如果频繁更新,则可以设置得小一点;
TIPS:下面的样式、脚本缓存配置同这里一样,只是定位的文件夹不一样而已,不再赘述。



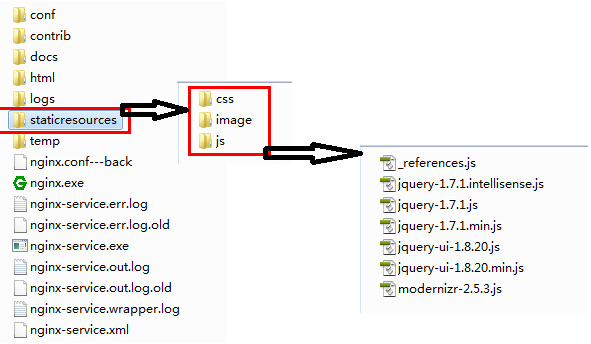
2> 在nginx服务文件夹中创建静态资源文件夹,并要缓存的静态文件拷贝进去:这里我主要将Web程序中用到的image、css以及js文件拷贝了进去;
总结:通过配置静态文件的缓存设置,对于这些静态文件的请求可以直接从反向代理服务器中直接返回,而无需再将这些静态资源请求转发到具体的Web服务器进行处理了,可以提高响应速度,减轻真实Web服务器的负载压力。
另附配置文件一份:
#user nobody; worker_processes 1;#工作进程的个数,可以配置多个 #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024;#单个进程最大连接数(最大连接数=连接数*进程数) } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; #服务器的集群 upstream cultccol.com{ #服务器集群名字 #server 172.16.21.13.8081 weight=1; #服务器配置:weight是权重的意思,权重越大,非配的概率越大 server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=1;#第一台web服务器 #server 127.0.0.1:8060 weight=2;#第二台web服务器 } server { listen 80;# http 监听80端口,可以改成其它端口 server_name localhost;#这里是本地测试,所以localhost #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { proxy_pass http://cultccol.com; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } #缓存静态资源-图片文件 location ~ .(jpg|png|jpeg|bmp|gif|swf)$ { root /nginx-1.13.7/staticresources/image; if (-f $request_filename) { expires 7d; break; } } #缓存静态资源之样式文件 location ~ .(css)$ { root /nginx-1.13.7/staticresources/css; if (-f $request_filename) { expires 7d; break; } } #缓存静态资源之脚本文件 location ~ .(js)$ { root /nginx-1.13.7/staticresources/js; if (-f $request_filename) { expires 7d; break; } } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ .php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ .php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }