上一节,我们定义了组件的基本使用,下面我们看看组件其他的一些特性。
1.组件作用域
同时在Vue对象和组件中定义一个属性,显示结果是怎样的呢?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ msg }}
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'hello world'
},
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>{{ msg }}</div>',
data: function () {
return {
msg: 'hello shijingjing'
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

可见,都在各自的作用域内有效,且组件不影响Vue定义的属性。
如何让组件使用Vue定义的属性呢,上节已经提到过,使用props属性。如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component v-bind:my-msg="msg"></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'hello world'
},
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>{{ myMsg }}</div>',
props: ['myMsg']
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

2.slot占位符
slot的意思是卡槽,也就是一个占位符,内容由组件包含的内容而定。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component>
<div>这是组件里面真正包含的内容</div>
</my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>hello world</div><slot>这只是一个占位符,具体内容由component包含的内容来定</slot>'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:
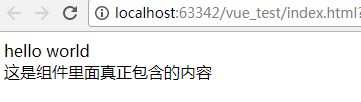
如果组件里面没有包含内容呢?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component>
</my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>hello world</div><slot>这只是一个占位符,具体内容由component包含的内容来定</slot>'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

可以再组件中包含占位符,来定义更为通用的组件。如一个对话框组件,不同时候弹出的标题不同,那么标题可以使用slot定义,真正内容放到组件内部。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component>
<header slot="header">
你好吗
</header>
<div slot="body">
是的
</div>
<footer slot="footer">
再见
</footer>
</my-component>
------------------------------------------------------
<my-component>
<header slot="header">
早上好
</header>
<div slot="body">
中午好
</div>
<footer slot="footer">
晚上好
</footer>
</my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>hello world</div><slot name="header"></slot><slot name="body"></slot><slot name="footer"></slot>'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:
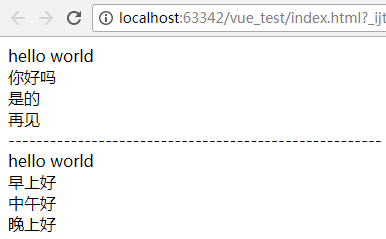
3.组件之间数据访问
1)父组件访问子组件属性 $children
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component':{
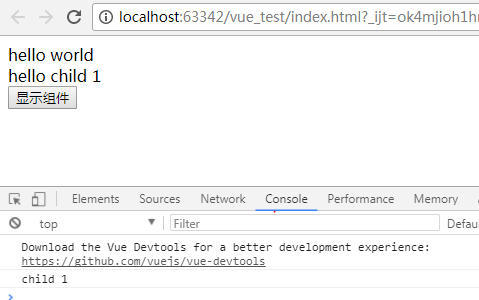
template: '<div>hello world</div><child-component1></child-component1><button v-on:click="showChildData">显示组件</button>',
components:{
'child-component1':{
template: '<div>hello child 1</div>',
data: function () {
return {
msg: 'child 1'
}
}
}
},
methods:{
showChildData: function () {
console.log(this.$children[0].msg);
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

除了$children,还可以使用v-ref:c1来给组件指定一个索引名称c1,查询子组件时,使用$refs.c1找到这个子组件。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>hello world</div><child-component1 v-ref:c1></child-component1><button v-on:click="showChildData">显示子组件</button>',
components:{
'child-component1':{
template: '<div>hello child 1</div>',
data: function () {
return {
msg: 'child 1'
}
}
}
},
methods:{
showChildData: function () {
console.log(this.$refs.c1.msg);
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:
2)子组件访问父组件属性 $parent
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>hello world</div><child-component1></child-component1>',
components:{
'child-component1':{
template: '<div>hello child 1</div><button v-on:click="showParentData">显示父组件</button>',
methods:{
showParentData: function () {
console.log(this.$parent.msg);
}
}
}
},
data: function () {
return {
msg: 'parent'
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

3)子组件访问根组件属性 $root
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'root'
},
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '<div>hello world</div><child-component1></child-component1>',
components:{
'child-component1':{
template: '<div>hello child 1</div><button v-on:click="showRootData">显示根组件</button>',
methods:{
showRootData: function () {
console.log(this.$root.msg);
}
}
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

可见,根元素指的是Vue对象
由$children,$parent,$root可以实现父子组件,以及Vue对象间的数据交互,但是还是尽量使用props属性来传递数据,
可以避免父子组件的过度耦合,以及子组件修改了父组件中的数据。
4.组件之间事件传递
1)派发事件$dispatch,事件沿着父链冒泡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: ''
},
components: {
'my-component':{
template: ' <input v-model="msg" /><button v-on:click="notify">dispatch</button>',
data: function () {
return {
msg: ''
}
},
methods:{
notify: function () {
this.$dispatch('child-msg', this.msg);
}
}
}
},
events:{
'child-msg': function (msg) {
this.message = msg;
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

$.dispatch会将事件派发到父组件的events事件,父组件接收到子组件的派发后,调用child-msg事件。
2)broadcast广播事件,事件向下传导给所有的子组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="message"/>
<button v-on:click="notify">broadcast</button>
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: ''
},
components: {
'my-component':{
template: '{{msg}}',
data: function () {
return {
msg: ''
}
},
events:{
'parent-msg': function (msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
}
},
methods:{
notify: function () {
this.$broadcast('parent-msg', this.message);
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
运行结果:

$.broadcast会将事件广播到子组件的events事件,子组件接收到父组件的广播后,调用parent-msg事件。