本文介绍了三种构建线程解决方案的方式。
一、流水线:每个线程执行同一种操作,并把操作结果传递给下一步骤的线程。

代码示例如下:
终端输入一个int值,每个线程将该值加1,并将结果传给下一个线程。

#include<stdio.h> #include<pthread.h> typedef struct stage_tag { pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t cond; int data; int ready; pthread_t tid; struct stage_tag *next; }stage_t; typedef struct pipe_tag { pthread_mutex_t mutex; stage_t *head; stage_t *tail; int stages; }pipe_t; void pipe_send(stage_t *stage,int data) { stage->data =data; stage->ready = 1; pthread_cond_signal(&stage->cond); } void *thread_route(void *arg) { stage_t *stage = (stage_t *)arg; while(!stage->ready) { pthread_cond_wait(&stage->cond,&stage->mutex); } int data = stage->data+1; stage_t *next = stage->next; if(next!=NULL) { pipe_send(next,data); } return NULL; } void create_pipe(pipe_t *pipe,int stages) { // pipe = (pipe_t *)malloc(sizeof(pipe_t)); pipe->stages = stages; int i; stage_t *stage; stage_t *last; for(i=0;i<=stages;i++) { stage = (stage_t *)malloc(sizeof(stage_t)); stage->data = i; if(i==0) { pipe->head = stage; } if(last!=NULL) { last->next = stage; } last = stage; } last->next=NULL; pipe->tail = last; for(stage=pipe->head;stage->next!=NULL;stage=stage->next) { pthread_create(&stage->tid,NULL,thread_route,(void *)stage); printf("stage %d ",stage->data); } /* free(pipe); for(stage=pipe->head;stage!=NULL;stage=stage->next) { free(stage); } */ } int main(void) { pipe_t my_pipe; long value,result; char line[128]; create_pipe(&my_pipe,10); pipe_send(my_pipe.head,5); sleep(10); printf("result is %d ",my_pipe.tail->data); return 0; }
二、工作组:数据由一组线程分别独立地处理。
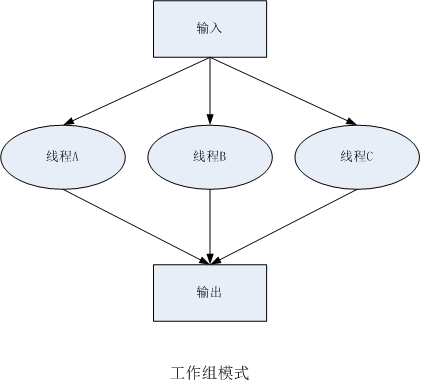
代码示例如下:
程序有两个参数:filepath:文件或目录路径;search:待查找字符串
程序将文件路径排队给工作组,工作组线程判断该路径是文件还是目录,如果是文件,它将在文件中搜索字符串;如果是目录,它将使用readdir_r查找该目录中的所有子目录和文件,并将每一项添加到工作队列。

#include<stdio.h> #include<pthread.h> #include<dirent.h> #include<sys/stat.h> typedef struct work_tag { struct work_tag *next; char *path; char *search; }work_t,*work_p; typedef struct worker_tag { int index; pthread_t tid; struct crew_tag *crew; }worker_t,*worker_p; typedef struct crew_tag { pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t cond; pthread_cond_t done; long work_count; work_t *first,*last; worker_t workers[4]; }crew_t,*crew_p; void *thread_route(void *arg) { worker_p worker = (worker_t *)arg; crew_p crew = worker->crew; struct dirent *entry; entry = (struct dirent*)malloc(sizeof(struct dirent)+sizeof(size_t)); pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex); while(crew->work_count ==0) { pthread_cond_wait(&crew->cond,&crew->mutex); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex); printf("worker is running: %d ",worker->index); while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex); while(crew->first==NULL) { pthread_cond_wait(&crew->cond,&crew->mutex); } printf("worker %d woke %#lx %d ",worker->index,crew->first,crew->work_count); work_p work = crew->first; crew->first = work->next; if(crew->first==NULL) crew->last = NULL; printf("worker %d took %#lx,leave first %#lx,last %#lx ",worker->index,work,crew->first,crew->last); pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex); struct stat filestat; lstat(work->path,&filestat); if(S_ISLNK(filestat.st_mode)) printf("worker %d:%s is a link,skipping. ",worker->index,work->path); else if(S_ISDIR(filestat.st_mode)){ DIR *dir; struct dirent *result; dir = opendir(work->path); while(1){ readdir_r(dir,entry,&result); if(result==NULL) break; if(strcmp(entry->d_name,".")==0) continue; if(strcmp(entry->d_name,"..")==0) continue; work_p new_work = (work_p)malloc(sizeof(work_t)); printf("test "); path_max = pathconf (work->path, _PC_PATH_MAX); new_work->path = (char*)malloc (path_max); strcpy (new_work->path, work->path); strcat (new_work->path, "/"); strcat (new_work->path, entry->d_name); // char *new_dir = strcat(work->path,entry->d_name); //new_work->path = new_dir; new_work->search = work->search; new_work->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex); if(crew->first==NULL) { crew->first = new_work; crew->last = new_work; } else{ crew->last->next = new_work; crew->last = new_work; } crew->work_count++; printf("worker %d add work %#lx,first %#lx,last %#lx,%d ",worker->index,new_work,crew->first,crew->last,crew->work_count); pthread_cond_signal(&crew->cond); pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex); } closedir(dir); } else if(S_ISREG(filestat.st_mode)){ FILE *file; char buffer[256]; file = fopen(work->path,"r"); fgets(buffer,sizeof(buffer),file); char *search_ptr; search_ptr = strstr(buffer,work->search); if(search_ptr!=NULL){ printf("worker %d found "%s" in %s ",worker->index,work->search,work->path); } fclose(file); } else{ printf("worker %d:%s format is error. ",worker->index,work->path); } free(work->path); free(work); pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex); crew->work_count--; printf("worker %d decremented work to %d ",worker->index,crew->work_count); if(crew->work_count<=0){ pthread_cond_broadcast(&crew->done); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex); } free(entry); return NULL; } void crew_create(crew_t *crew) { int worker_index; crew->work_count = 0; crew->first = NULL; crew->last = NULL; pthread_mutex_init(&crew->mutex,NULL); pthread_cond_init(&crew->cond,NULL); pthread_cond_init(&crew->done,NULL); for(worker_index=0;worker_index<4;worker_index++){ crew->workers[worker_index].index = worker_index; crew->workers[worker_index].crew = crew; pthread_create(&crew->workers[worker_index].tid, NULL,thread_route,(void *)&crew->workers[worker_index]); } } void crew_start(crew_t *crew,char *filepath,char *search) { pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex); work_p work = (work_p)malloc(sizeof(work_t)); work->path = filepath; work->search = search; work->next = NULL; crew->first = work; crew->last = work; crew->work_count++; pthread_cond_signal(&crew->cond); while(crew->work_count>0) { pthread_cond_wait(&crew->done,&crew->mutex); } printf("crew is done! "); pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex); } int main(void) { crew_t crew; crew_create(&crew); char *filepath = "/home/ubuntu/programs"; char *search = "errno"; crew_start(&crew,filepath,search); return 0; }
三、客户端/服务器:客户端线程将工作排队,交给一个服务器线程去处理。客户端或者以同步方式等待服务器执行,或异步执行并在后面需要时查找结果。
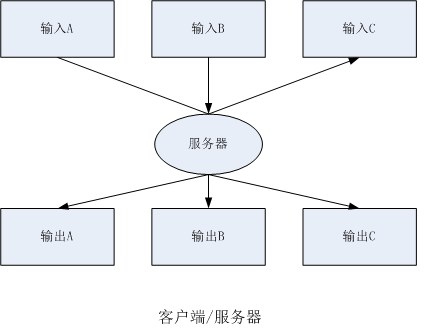
代码示例如下:
一组线程都需要从stdin中读取输入,这将导致提示-读(prompt-and-read)操作可能有些混乱。一个方法是使用flockfile和funlockfile函数来锁住stdin和stdout。,另一个方式是,使用服务器线程,将客户端读写操作排队,由服务器线程依次处理读写操作队列。

#include<stdio.h> #include<pthread.h> #define REQ_READ 1 #define REQ_WRITE 2 #define REQ_QUIT 3 typedef struct client_tag { struct client_tag *next; int oper; int sync; int done_flag; char prompt[32]; char text[128]; pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t mutex; }client_t; typedef struct server_tag { client_t *first,*last; pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t cond; }server_t; server_t server={NULL,NULL,PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER,PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER}; pthread_mutex_t main_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_cond_t main_cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; int thread_count = 4; void client_request(int oper,int sync,const char *prompt,char *string) { pthread_mutex_lock(&server.mutex); client_t *client; client = (client_t *)malloc(sizeof(client_t)); client->next = NULL; client->oper = oper; client->sync = sync; if(prompt!=NULL) strncpy(client->prompt,prompt,32); if(oper==REQ_WRITE&&string!=NULL) strncpy(client->text,string,128); if(server.first==NULL) { server.first = client; server.last = client; }else{ server.last->next = client; server.last = client; } pthread_cond_signal(&server.cond); if(sync) { while(!client->done_flag) { pthread_cond_wait(&client->cond,&server.mutex); } if(oper==REQ_READ) { if(strlen(client->text)>0) strcpy(string,client->text); } } pthread_cond_destroy(&client->cond); free(request); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&server.mutex); } void *client_route(void *arg) { int index = (int)arg; int loops; char prompt[32]; char string[128],formatted[128]; sprintf(prompt,"Client %d>",index); while(1) { client_request(REQ_READ,1,prompt,string); if(strlen(string)==0) break; for(loops=0;loops<4;loops++) { sprintf(formatted,"(%d#%d) %s",index,loops,string); client_request(REQ_WRITE,0,NULL,formatted); sleep(1); } } } void *server_route(void *arg) { client_t *client; int oper; while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&server.mutex); while(server.first==NULL) { pthread_cond_wait(&server.cond,&server.mutex); } client = server.first; server.first = client.next; if(server.first==NULL) server.last = NULL; pthread_mutex_unlock(&server.mutex); oper = client->oper; switch(oper){ case REQ_QUIT: break; case REQ_READ: if(strlen(client->prompt)>0) printf(client->prompt); fgets(client->text,128,stdin); break; case REQ_WRITE: puts(client->text); break; default: break; } free(client); if(oper==REQ_QUIT) break; } return NULL; } int main(void) { pthread_t sid; pthread_create(&sid,NULL,server_route,NULL); pthread_t cid; int i; for(i=0;i<thread_count;i++) { pthread_create(&cid,NULL,client_route,(void *)count); } pthread_mutex_lock(&main_mutex); while(thread_count>0) { pthread_cond_wait(&main_cond,&main_mutex); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&main_mutex); printf("Done! "); client_request(REQ_QUIT,1,NULL,NULL); return 0; }
参考资料:《POSIX多线程程序设计》 pp.81-110
