出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308513.html
我们知道Collection是和Map架构平级的,我们看一下这个架构是怎样的。
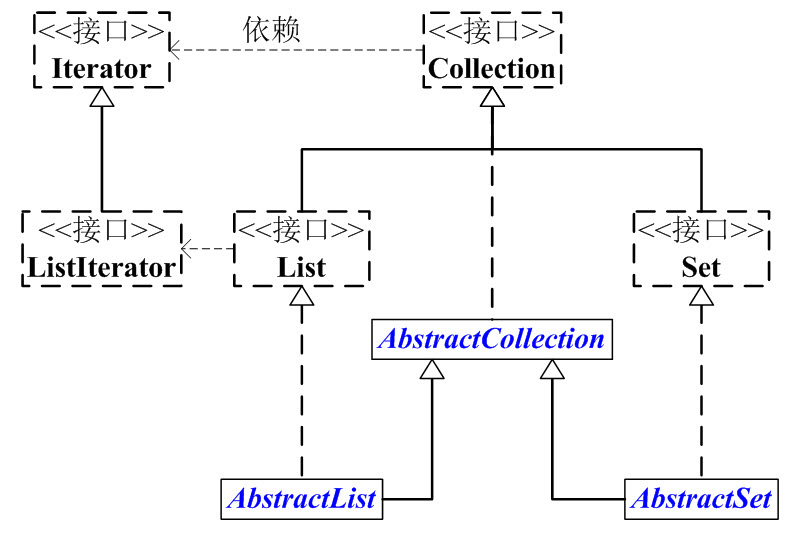
他主要的两个分支是List和Set。
List和Set都是接口,它们继承于Collection。List是有序的队列,List中可以有重复的元素;而Set是数学概念中的集合,Set中没有重复元素!
List和Set都有它们各自的实现类。
为了方便,我们抽象出了AbstractCollection抽象类,它实现了Collection中的绝大部分函数;这样,在Collection的实现类中,我们就可以通过继承AbstractCollection省去重复编码。AbstractList和AbstractSet都继承于AbstractCollection,具体的List实现类继承于AbstractList,而Set的实现类则继承于AbstractSet。
另外,Collection中有一个iterator()函数,它的作用是返回一个Iterator接口。通常,我们通过Iterator迭代器来遍历集合。ListIterator是List接口所特有的,在List接口中,通过ListIterator()返回一个ListIterator对象。
接下来,我们看看各个接口和抽象类的介绍;然后,再对实现类进行详细的了解。
1:Collection的定义如下:
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {}
它是一个接口。是高度抽象出来的集合。它包含了集合的基本操作:添加、删除、清空、遍历(读取)、是否为空、获取大小、是否保护某元素等等。
Collection接口的所有子类(直接子类和间接子类)都必须实现2种构造函数:不带参数的构造函数 和 参数为Collection的构造函数。带参数的构造函数,可以用来转换Collection的类型。
// Collection的API abstract boolean add(E object) abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract void clear() abstract boolean contains(Object object) abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract int hashCode() abstract boolean isEmpty() abstract Iterator<E> iterator() abstract boolean remove(Object object) abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract int size() abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) abstract Object[] toArray()
2:List接口:
List的定义如下:
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {}
List是一个继承于Collection的接口,即List是集合中的一种。List是有序的队列,List中的每一个元素都有一个索引;第一个元素的索引值是0,往后的元素的索引值依次+1。和Set不同,List中允许有重复的元素。
关于API方面。既然List是继承于Collection接口,它自然就包含了Collection中的全部函数接口;由于List是有序队列,它也额外的有自己的API接口。主要有“添加、删除、获取、修改指定位置的元素”、“获取List中的子队列”等。
// Collection的API abstract boolean add(E object) abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract void clear() abstract boolean contains(Object object) abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract int hashCode() abstract boolean isEmpty() abstract Iterator<E> iterator() abstract boolean remove(Object object) abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract int size() abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) abstract Object[] toArray() // 相比与Collection,List新增的API: abstract void add(int location, E object) abstract boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract E get(int location) abstract int indexOf(Object object) abstract int lastIndexOf(Object object) abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location) abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator() abstract E remove(int location) abstract E set(int location, E object) abstract List<E> subList(int start, int end)
3:Set的简介:
Set的定义如下:
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> {}
Set是一个继承于Collection的接口,即Set也是集合中的一种。Set是没有重复元素的集合。
关于API方面。Set的API和Collection完全一样。
// Set的API abstract boolean add(E object) abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract void clear() abstract boolean contains(Object object) abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract int hashCode() abstract boolean isEmpty() abstract Iterator<E> iterator() abstract boolean remove(Object object) abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract int size() abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) abstract Object[] toArray()
4:AbstractCollection:
AbstractCollection的定义如下:
*/ package java.util; public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> { /** * Sole constructor. (For invocation by subclass constructors, typically * implicit.) */ protected AbstractCollection() { } // Query Operations /** * Returns an iterator over the elements contained in this collection. * * @return an iterator over the elements contained in this collection */ public abstract Iterator<E> iterator(); public abstract int size(); /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation returns <tt>size() == 0</tt>. */ public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation iterates over the elements in the collection, * checking each element in turn for equality with the specified element. * * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} */ public boolean contains(Object o) { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); if (o==null) { while (it.hasNext()) if (it.next()==null) return true; } else { while (it.hasNext()) if (o.equals(it.next())) return true; } return false; } public Object[] toArray() { // Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements Object[] r = new Object[size()]; Iterator<E> it = iterator(); for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) { if (! it.hasNext()) // fewer elements than expected return Arrays.copyOf(r, i); r[i] = it.next(); } return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r; } public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { // Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements int size = size(); T[] r = a.length >= size ? a : (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array .newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); Iterator<E> it = iterator(); for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) { if (! it.hasNext()) { // fewer elements than expected if (a != r) return Arrays.copyOf(r, i); r[i] = null; // null-terminate return r; } r[i] = (T)it.next(); } return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r; } /** * The maximum size of array to allocate. * Some VMs reserve some header words in an array. * Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in * OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * Reallocates the array being used within toArray when the iterator * returned more elements than expected, and finishes filling it from * the iterator. * * @param r the array, replete with previously stored elements * @param it the in-progress iterator over this collection * @return array containing the elements in the given array, plus any * further elements returned by the iterator, trimmed to size */ private static <T> T[] finishToArray(T[] r, Iterator<?> it) { int i = r.length; while (it.hasNext()) { int cap = r.length; if (i == cap) { int newCap = cap + (cap >> 1) + 1; // overflow-conscious code if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCap = hugeCapacity(cap + 1); r = Arrays.copyOf(r, newCap); } r[i++] = (T)it.next(); } // trim if overallocated return (i == r.length) ? r : Arrays.copyOf(r, i); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError ("Required array size too large"); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } // Modification Operations /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation always throws an * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalStateException {@inheritDoc} */ public boolean add(E e) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation iterates over the collection looking for the * specified element. If it finds the element, it removes the element * from the collection using the iterator's remove method. * * <p>Note that this implementation throws an * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the iterator returned by this * collection's iterator method does not implement the <tt>remove</tt> * method and this collection contains the specified object. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} */ public boolean remove(Object o) { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); if (o==null) { while (it.hasNext()) { if (it.next()==null) { it.remove(); return true; } } } else { while (it.hasNext()) { if (o.equals(it.next())) { it.remove(); return true; } } } return false; } // Bulk Operations /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation iterates over the specified collection, * checking each element returned by the iterator in turn to see * if it's contained in this collection. If all elements are so * contained <tt>true</tt> is returned, otherwise <tt>false</tt>. * * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @see #contains(Object) */ public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) { for (Object e : c) if (!contains(e)) return false; return true; } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation iterates over the specified collection, and adds * each object returned by the iterator to this collection, in turn. * * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> unless <tt>add</tt> is * overridden (assuming the specified collection is non-empty). * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalStateException {@inheritDoc} * * @see #add(Object) */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { boolean modified = false; for (E e : c) if (add(e)) modified = true; return modified; } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation iterates over this collection, checking each * element returned by the iterator in turn to see if it's contained * in the specified collection. If it's so contained, it's removed from * this collection with the iterator's <tt>remove</tt> method. * * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the iterator returned by the * <tt>iterator</tt> method does not implement the <tt>remove</tt> method * and this collection contains one or more elements in common with the * specified collection. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * * @see #remove(Object) * @see #contains(Object) */ public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { boolean modified = false; Iterator<?> it = iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { if (c.contains(it.next())) { it.remove(); modified = true; } } return modified; } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation iterates over this collection, checking each * element returned by the iterator in turn to see if it's contained * in the specified collection. If it's not so contained, it's removed * from this collection with the iterator's <tt>remove</tt> method. * * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the iterator returned by the * <tt>iterator</tt> method does not implement the <tt>remove</tt> method * and this collection contains one or more elements not present in the * specified collection. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * * @see #remove(Object) * @see #contains(Object) */ public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { boolean modified = false; Iterator<E> it = iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { if (!c.contains(it.next())) { it.remove(); modified = true; } } return modified; } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation iterates over this collection, removing each * element using the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt> operation. Most * implementations will probably choose to override this method for * efficiency. * * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the iterator returned by this * collection's <tt>iterator</tt> method does not implement the * <tt>remove</tt> method and this collection is non-empty. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} */ public void clear() { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { it.next(); it.remove(); } } // String conversion /** * Returns a string representation of this collection. The string * representation consists of a list of the collection's elements in the * order they are returned by its iterator, enclosed in square brackets * (<tt>"[]"</tt>). Adjacent elements are separated by the characters * <tt>", "</tt> (comma and space). Elements are converted to strings as * by {@link String#valueOf(Object)}. * * @return a string representation of this collection */ public String toString() { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); if (! it.hasNext()) return "[]"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append('['); for (;;) { E e = it.next(); sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e); if (! it.hasNext()) return sb.append(']').toString(); sb.append(',').append(' '); } } }
AbstractCollection是一个抽象类,它实现了Collection中除iterator()和size()之外的函数。
AbstractCollection的主要作用:它实现了Collection接口中的大部分函数。从而方便其它类实现Collection,比如ArrayList、LinkedList等,它们这些类想要实现Collection接口,通过继承AbstractCollection就已经实现了大部分的接口了。
5:AbstractList
AbstractList的定义如下:
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {}
AbstractList是一个继承于AbstractCollection,并且实现List接口的抽象类。它实现了List中除size()、get(int location)之外的函数。
AbstractList的主要作用:它实现了List接口中的大部分函数。从而方便其它类继承List。
另外,和AbstractCollection相比,AbstractList抽象类中,实现了iterator()接口。
6:AbstractSet:
AbstractSet的定义如下:
public abstract class AbstractSet<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Set<E> {}
AbstractSet是一个继承于AbstractCollection,并且实现Set接口的抽象类。由于Set接口和Collection接口中的API完全一样,Set也就没有自己单独的API。和AbstractCollection一样,它实现了List中除iterator()和size()之外的函数。
AbstractSet的主要作用:它实现了Set接口中的大部分函数。从而方便其它类实现Set接口。
7;Iterator:
Iterator的定义如下:
public interface Iterator<E> { /** * Returns {@code true} if the iteration has more elements. * (In other words, returns {@code true} if {@link #next} would * return an element rather than throwing an exception.) * * @return {@code true} if the iteration has more elements */ boolean hasNext(); /** * Returns the next element in the iteration. * * @return the next element in the iteration * @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no more elements */ E next(); /** * Removes from the underlying collection the last element returned * by this iterator (optional operation). This method can be called * only once per call to {@link #next}. The behavior of an iterator * is unspecified if the underlying collection is modified while the * iteration is in progress in any way other than by calling this * method. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove} * operation is not supported by this iterator * * @throws IllegalStateException if the {@code next} method has not * yet been called, or the {@code remove} method has already * been called after the last call to the {@code next} * method */ void remove(); }
Iterator是一个接口,它是集合的迭代器。集合可以通过Iterator去遍历集合中的元素。Iterator提供的API接口,包括:是否存在下一个元素、获取下一个元素、删除当前元素。
注意:Iterator遍历Collection时,是fail-fast机制的。即,当某一个线程A通过iterator去遍历某集合的过程中,若该集合的内容被其他线程所改变了;那么线程A访问集合时,就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常,产生fail-fast事件。关于fail-fast的详细内容,我们会在后面专门进行说明。TODO
8:ListIterator:
ListIterator的定义如下:
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {}
ListIterator是一个继承于Iterator的接口,它是队列迭代器。专门用于便利List,能提供向前/向后遍历。相比于Iterator,它新增了添加、是否存在上一个元素、获取上一个元素等等API接口。
// ListIterator的API // 继承于Iterator的接口 abstract boolean hasNext() abstract E next() abstract void remove() // 新增API接口 abstract void add(E object) abstract boolean hasPrevious() abstract int nextIndex() abstract E previous() abstract int previousIndex() abstract void set(E object)