一、实验目的
1.几何变换的原理的掌握;
2.通过几何变换实现任意复杂的几何变换。
二、实验内容
1. 编写程序,实现多边形五种基本几何变换。绕任意一点(Cx,Cy)逆时针旋转theta几何变换,并在屏幕中进行绘制。
要求显示图形的坐标系原点在屏幕中心,画出坐标轴,在屏幕上用鼠标选点绘制多边形,并实现多边形的变换。
三、实验步骤
(一)多边形的五种基本几何变换
1.算法思路:
二维几何变换矩阵T是一个3×3的方阵,简称为二维变换矩阵。

从功能上可以把二维变换矩阵T分为4个子矩阵。其中  是对图形进行比例变换、旋转变换、反射变换和错切变换;
是对图形进行比例变换、旋转变换、反射变换和错切变换;  是对图形进行平移变换;
是对图形进行平移变换;  是对图形进行投影变换;
是对图形进行投影变换;  是对图形进行整体比例变换。
是对图形进行整体比例变换。
(1) 平移变换
平移变换的坐标表示为:
二维平移变换矩阵:
(2) 比例变换
比例变换的坐标表示为:
二维比例变换矩阵:
(3) 旋转变换
旋转变换的坐标表示为:
二维旋转变换矩阵:
(4) 反射变换
- 关于原点反射的坐标表示为:

变换矩阵:
- 关于x轴的二维反射变换矩阵为 :

- 关于y轴的二维反射变换矩阵为 :

(5) 错切变换
a.沿x,y方向的错切变换的坐标表示为:
沿x,y两个方向的二维错切变换矩阵为: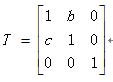
其中b、c为错切参数。
b. 沿x方向的二维错切变换矩阵为:
c. 沿y方向的二维错切变换矩阵为:
(二)代码如下:
在GeometricTransformationView.h 文件中添加:
#include <vector> using std::vector; #include<math.h>
添加一个成员变量: vector<CPoint> points;
添加事件处理函数:
void CGeometricTransformationView::OnPaint() { CPaintDC dc(this); // device context for painting draw(); // TODO: Add your message handler code here // Do not call CView::OnPaint() for painting messages } void CGeometricTransformationView::OnLButtonUp(UINT nFlags, CPoint point) { // TODO: Add your message handler code here and/or call default CRect rect; GetClientRect(rect); points.push_back(CPoint(point.x - rect.Width()/2, point.y - rect.Height()/2)); CView::OnLButtonUp(nFlags, point); } void CGeometricTransformationView::OnRButtonUp(UINT nFlags, CPoint point) { // TODO: Add your message handler code here and/or call default draw(); CView::OnRButtonUp(nFlags, point); } void CGeometricTransformationView::OnMButtonUp(UINT nFlags, CPoint point) { // TODO: Add your message handler code here and/or call default points.clear(); CView::OnMButtonUp(nFlags, point); }
编写一个draw()函数:
void CGeometricTransformationView::draw() { CDC *dc = GetDC(); CRect rect; dc->GetClipBox(rect); dc->SetViewportOrg(rect.Width()/2, rect.Height()/2); // 绘制坐标轴 dc->MoveTo(-rect.Width()/2, 0); dc->LineTo(rect.Width()/2, 0); dc->MoveTo(0, -rect.Height()/2); dc->LineTo(0, rect.Height()/2); if (points.size() < 3) { return; } int i; //绘制多边形 dc->MoveTo(points[0].x, points[0].y); for ( i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) { dc->LineTo(points[i].x, points[i].y); } dc->LineTo(points[0].x, points[0].y); //向下平移300个单位 dc->MoveTo(points[0].x, points[0].y+100); for ( i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) { dc->LineTo(points[i].x, points[i].y+100); } dc->LineTo(points[0].x, points[0].y+100); // 2倍放大后的多边形 dc->MoveTo(2*points[0].x, 2*points[0].y); for ( i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) { dc->LineTo(2*points[i].x, 2*points[i].y); } dc->LineTo(2*points[0].x, 2*points[0].y); // 绕原点旋转60度 double r = sqrt(points[0].x*points[0].x + points[0].y*points[0].y); double pi = acos(-1); double angle = pi*60/180; int x, y; x = points[0].x; y = points[0].y; dc->MoveTo(x*cos(angle)-y*sin(angle), x*sin(angle)+y*cos(angle)); for ( i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) { x = points[i].x; y = points[i].y; dc->LineTo(x*cos(angle)-y*sin(angle), x*sin(angle)+y*cos(angle)); } x = points[0].x; y = points[0].y; dc->LineTo(x*cos(angle)-y*sin(angle), x*sin(angle)+y*cos(angle)); // 关于y轴反射变换 dc->MoveTo(-points[0].x, points[0].y); for ( i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) { dc->LineTo(-points[i].x, points[i].y); } dc->LineTo(-points[0].x, points[0].y); // 错切变换 double k = -2.3; dc->MoveTo(points[0].x + k*points[0].y, points[0].y); for ( i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) { dc->LineTo(points[i].x + k*points[i].y, points[i].y); } dc->LineTo(points[0].x + k*points[0].y, points[0].y); // 绕(-100, 120)旋转30度 int ox = -100; int oy = 120; angle = pi*30/180; x = points[0].x; y = points[0].y; dc->MoveTo((x-ox)*cos(angle)-(y-oy)*sin(angle)+ox, (x-ox)*sin(angle)+(y-oy)*cos(angle)+oy); for ( i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) { x = points[i].x; y = points[i].y; dc->LineTo((x-ox)*cos(angle)-(y-oy)*sin(angle)+ox, (x-ox)*sin(angle)+(y-oy)*cos(angle)+oy); } x = points[0].x; y = points[0].y; dc->LineTo((x-ox)*cos(angle)-(y-oy)*sin(angle)+ox, (x-ox)*sin(angle)+(y-oy)*cos(angle)+oy);
(三)运行结果截图:
 |
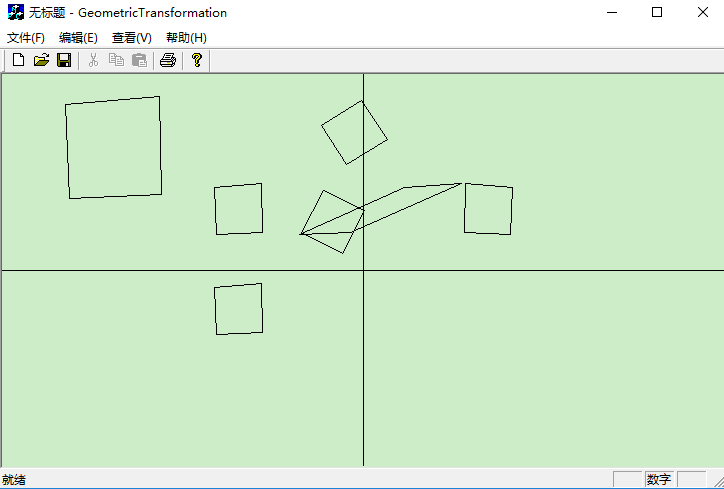 |
 |