前言
Java中的堆和常量池的区别是什么呢?Object.equals与String.equals的区别呢?下面让我们通过一个小示例让你明白它~
1、基础知识
Java的存储空间:寄存器、栈、堆、静态存储区、常量存储区(常量池)、其他存储位置。
此处重点介绍堆和常量存储区:
堆:存储new的对象;
常量池:用来存储final static、String的常量。
2、Object.equals与String.equals的区别
Object.equals(==):比较内存地址;
String.equals: 比较内容即可,不管内存地址。
总结:
Object.equals相等,String.equals一定相等;
String.equals相等,Object.equals不一定相等。
3、实战演练
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
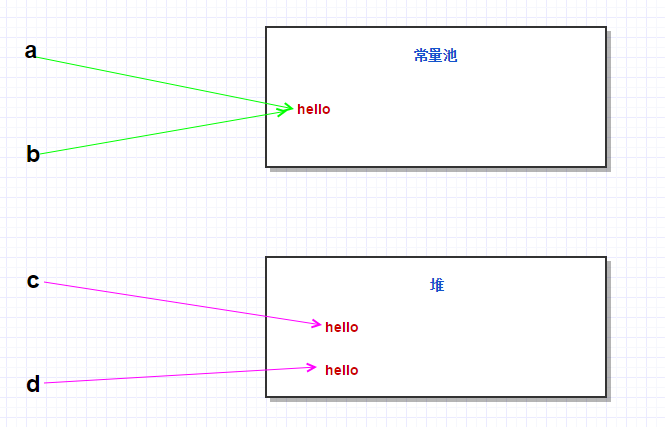
public class TestString { public static void main(String[] args){ // 维护在常量池里面 String a="hello"; String b="hello"; // new出来的所有对象都在堆内存中 // 只要是new出现来的都是新对象 String c=new String("hello"); String d=new String("hello"); // 对比内存地址 //true System.out.println(a==b); //false System.out.println(a==c); //false System.out.println(c==d); //对比内容 //true System.out.println(a.equals(b)); //true System.out.println(a.equals(c)); //true System.out.println(c.equals(d)); }} |
解释:
a,b都是常量,a和b都是指向常量存储区中的常量'hello',所以无论内容还是内存地址都是一样的,因此a==b以及a.equals(b)都是true;
c,d都是变量,他们都是new出来的对象,里面存在两个hello变量,c和d分别指向自己的hello变量,所以c和d内容一样,但是内存地址不一样,因此c==d是false,但是c.equals(d)为true。
to:https://www.cnblogs.com/zx-bob-123/p/8117958.html