返校小测
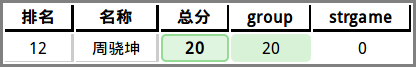
group (Unaccepted)
- 20分暴搜,最后半小时写的
strGame
-
大力puts("Pure"),0分妥妥的
-
先建出tire树来,考虑在树上DP
-
f[x]是放到了x的状态,值为0表示先手想赢不一定能赢,想输不一定能输,1表示先手想赢能赢,想输不一定能输,2表示先手想赢不一定能赢,想输能输,3表示先手想赢能赢,想输能输
-
每放一个字符先后手交换,转移取反就好了,当x为叶子节点的时候先手当然只有输的份
-
如果跟节点值为0,后手相当于操控全场,Dirty胜,如果为1,先手相当于控制全场,Pure胜
-
值为1的话最后一局先手一定会胜,所以倒数第二局都会争取输,那么倒数第三局都会争取胜,所以进行奇数场Pure胜,偶数场Drity胜
-
值为2的话最后一局后手一定会赢,所以倒数第二局都会争取输,那么倒数第三局都会争取输,所以Drity胜
Show Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int read(int x = 0, int f = 1, char c = getchar()) {
for (; c < '0' || c > '9'; c = getchar())
if (c == '-') f = -1;
for (; c >='0' && c <='9'; c = getchar())
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
return x * f;
}
int t[N][26], trc, f[N];
char c[N];
void Insert() {
scanf("%s", c + 1);
int n = strlen(c + 1);
for (int i = 1, p = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int x = c[i] - 'a';
if (!t[p][x]) t[p][x] = ++trc;
p = t[p][x];
}
}
void Dfs(int x) {
bool g = f[x] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
int y = t[x][i];
if (!y) continue;
Dfs(y); g = 1;
f[x] |= f[y] ^ 3;
}
if (!g) f[x] = 2;
}
int main() {
freopen("strgame.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("strgame.out", "w", stdout);
int T = read();
while (T--) {
memset(t, 0, sizeof(t)); trc = 1;
int n = read(), k = read();
while (n--) Insert();
Dfs(1);
puts((f[1] == 3 || (f[1] == 1 && k & 1)) ? "Pure" : "Dirty");
}
return 0;
}
联赛模拟测试32
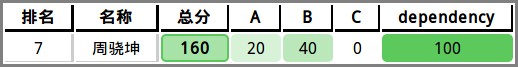
A 循环依赖
- 建图拓扑就完了
Show Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, M = 1e5 + 3;
struct Edge {
int next, t;
}e[N];
int head[N], edc;
void Add(int x, int y) {
e[++edc] = (Edge) {head[x], y};
head[x] = edc;
}
struct Hash {
int next[N], head[N], hac;
ull s[N];
int Find(ull y) {
int x = y % M;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = next[i])
if (y == s[i]) return i;
next[++hac] = head[x];
s[hac] = y;
return head[x] = hac;
}
}h;
int T, m, n, in[N], q[N];
char s[N];
bool v[N], g;
void read() {
char c = getchar(); n = g = 0;
for (; c < 'A' || c > 'Z'; c = getchar());
for (; c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'; c = getchar())
s[++n] = c;
for (; c >= '0' && c <= '9'; c = getchar())
s[++n] = c;
if (c == '
' || c == '
') g = 1;
}
void Print() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
putchar(s[i]);
puts("");
}
void Init() {
h.hac = edc = g = 0;
memset(v, 0, sizeof(v));
memset(in, 0, sizeof(in));
memset(head, 0, sizeof(head));
memset(h.head, 0, sizeof(h.head));
}
int main() {
freopen("dependency.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("dependency.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
Init();
scanf("%d", &m);
while (m--) {
read();
ull ha = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
ha = ha * 131 + s[i];
int x = h.Find(ha);
while (!g) {
read();
ha = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
ha = ha * 131 + s[i];
Add(h.Find(ha), x); in[x]++;
}
}
int l = 1, r = 0, tot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= h.hac; ++i)
if (!in[i]) q[++r] = i;
while (l <= r) {
int x = q[l++]; tot++;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int y = e[i].t;
if (!--in[y]) q[++r] = y;
}
}
puts(tot != h.hac ? "Yes" : "No");
}
return 0;
}
B A (Unaccepted)
-
n*q的暴力一遍20分
-
对于a相同的,推一下式子
- 所以a相同的就总需要看b最大和最小的那个2个,对与a=-1,0,1的情况只有6个函数有用
C B (Unaccepted)
- 1, 3, 4把a数组压成一个数记忆化搜索就行了,全是1的就是(n+1)/2
D C (Unaccepted)
-
本来想到暴力可能可以多那些分,没想到有40,能过1,2,8,9,我考场上直接n2的预处理就把自己卡没了
-
对于(a_i<2)的情况,或起来只会贡献0或1,而且只有在距离为偶数,(a_i)为 1 的情况才会贡献1,
-
所以预处理一个数组表示从当前点每次跳两步,跳到跟节点或其父亲的点中(a_i=1)的点的数量,
-
询问的时候如果从u到lca距离和v到lca距离都为奇数,就是s[u]-s[f[lca]]+s[v]-s[f[lca]]
-
询问的时候如果从u到lca距离和v到lca距离都为偶数,就是s[u]-s[f[f[lca]]]+s[v]-s[lca]
-
询问的时候如果从u到lca距离为奇数,v到lca距离都为偶数,就是s[u]-s[f[lca]]+s[f[v]]-s[f[lca]]
-
询问的时候如果从u到lca距离为偶数,v到lca距离都为奇数,就是s[u]-s[f[f[lca]]]+s[f[v]]-s[lca]
十分满足_
两天的补课
选生物、地理一起上课,为了省老师学校简直了
连续7节地理连排我是没想到的,简直要死
发现困不困与学生、科目其实没啥关系,只要老师讲的够吸引力,叶队都不睡觉了
选地理的是真的惨,地理老师骂学地理的学得菜,生物老师说就是给你们这6个人讲,还不好好听,hhhc
接下来两天期中考试,就不补课,继续集训
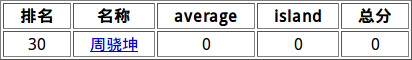
CSP后复活赛
阶段排名30
困死我了,旁边祥哥式子都推出来了,我还在那昏昏沉沉的打.vimrc
我直接反向AK, 复活失败
孤岛症候群
-
正解是 n3 DP,考场上写了个记忆化 DFS,题库里 80,lemon 上 RE 成 0 分,一检查最后返回值的地方写错了,改过来之后题库里就过了
-
吃完饭问了问虎哥和天皇,天皇一看那 405×405×405 的数组就说是内存炸了,我当时算的是 126MB,限制是 128MB,数组改成 402×402×402 就 90 分了。。。
Show Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define re register
const int N = 405;
int n, m, k, ans;
short f[N][N][N];
char a[N][N], c[N];
short Dfs(re int x, re int y, re int l) {
short &s = f[x][y][l];
if (s != -1) return s;
for (re int i = l + 1; i <= k; ++i) {
re int tx = x, ty = y;
if (c[i] == 'L' && --ty < 1) continue;
if (c[i] == 'R' && ++ty > m) continue;
if (c[i] == 'U' && --tx < 1) continue;
if (c[i] == 'D' && ++tx > n) continue;;
if (a[tx][ty] == '0') s = std::max(s, Dfs(tx, ty, i));
}
return ++s;
}
int main() {
freopen("island.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("island.out", "w", stdout);
memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for (re int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%s", a[i] + 1);
scanf("%s", c + 1);
printf("%d
", k - Dfs(1, 1, 0));
return 0;
}
-
随机数据跑的倒是飞快,n4的时间效率当然会被卡,构造一组图全部为0,路径方向都是向右向下,能卡到5秒左右
-
正解是n3的DP,定义f[k][i][j]前k步走到 i,j 最多可以保留多少步,再来个v数组表示这个位置是否可以到达,压个维就好了
Show Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
const int N = 405;
int n, m, s, f[N][N], g[N][N], ans;
bool v[N][N], b[N][N];
char c[N][N], a[N];
int main() {
freopen("island.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("island.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%s", c[i] + 1);
scanf("%s", a + 1);
v[1][1] = 1;
for (int k = 1; k <= s; ++k) {
memcpy(g, f, sizeof(f));
memcpy(b, v, sizeof(v));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
if (c[i][j] == '1') continue;
if (a[k] == 'L' && b[i][j+1])
f[i][j] = std::max(f[i][j], g[i][j+1] + 1), v[i][j] = 1;
if (a[k] == 'R' && b[i][j-1])
f[i][j] = std::max(f[i][j], g[i][j-1] + 1), v[i][j] = 1;
if (a[k] == 'U' && b[i+1][j])
f[i][j] = std::max(f[i][j], g[i+1][j] + 1), v[i][j] = 1;
if (a[k] == 'D' && b[i-1][j])
f[i][j] = std::max(f[i][j], g[i-1][j] + 1), v[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
ans = std::max(ans, f[i][j]);
printf("%d
", s - ans);
return 0;
}
平均值 (Unaccepted)
- 考完才听他们说是原题,一讲就有印象了,但多测没清空,于是50分溜了